This document summarizes electronic spectroscopy of diatomic molecules. It discusses:
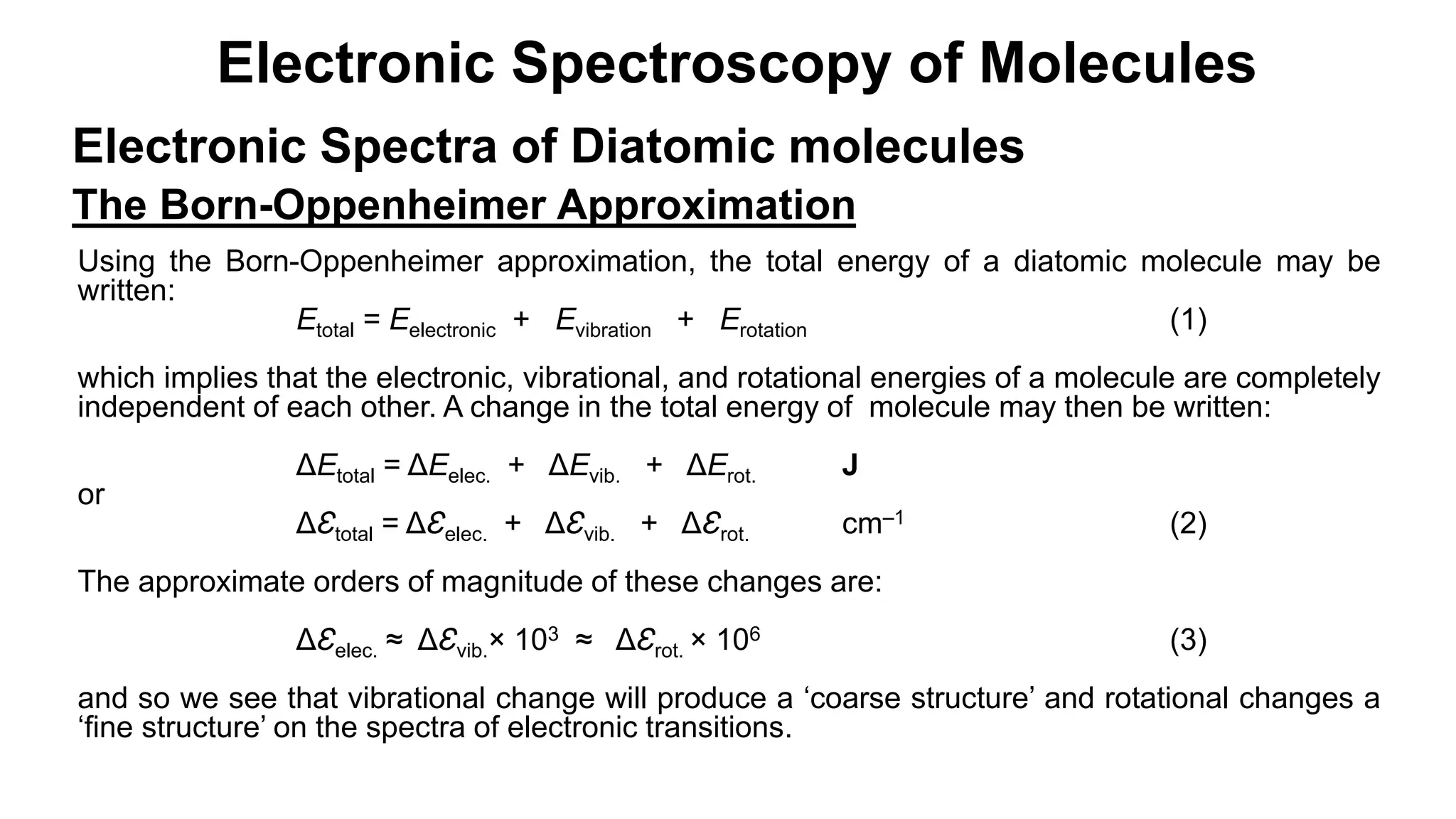
1) The Born-Oppenheimer approximation which treats electronic, vibrational, and rotational energies as independent.
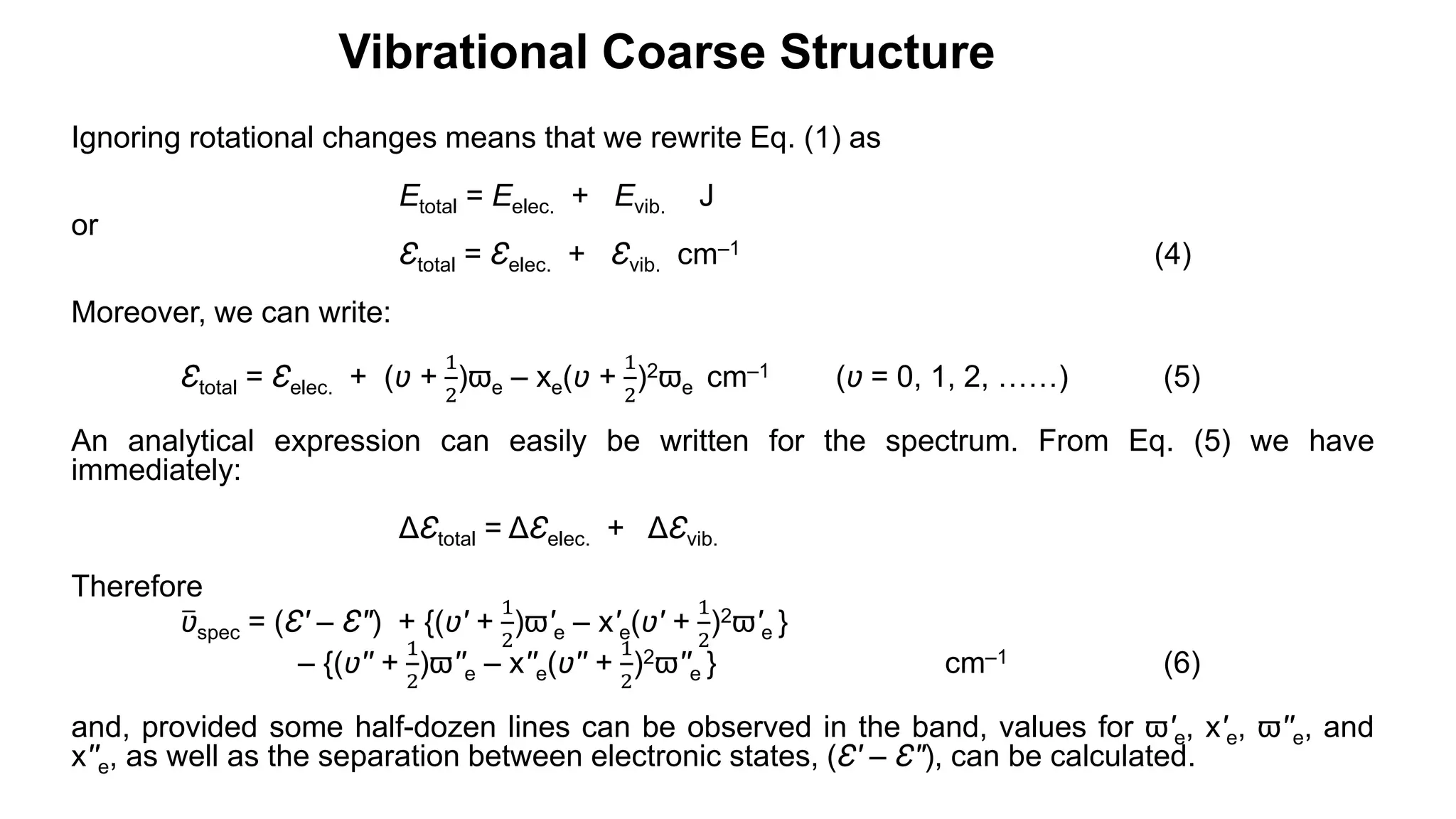
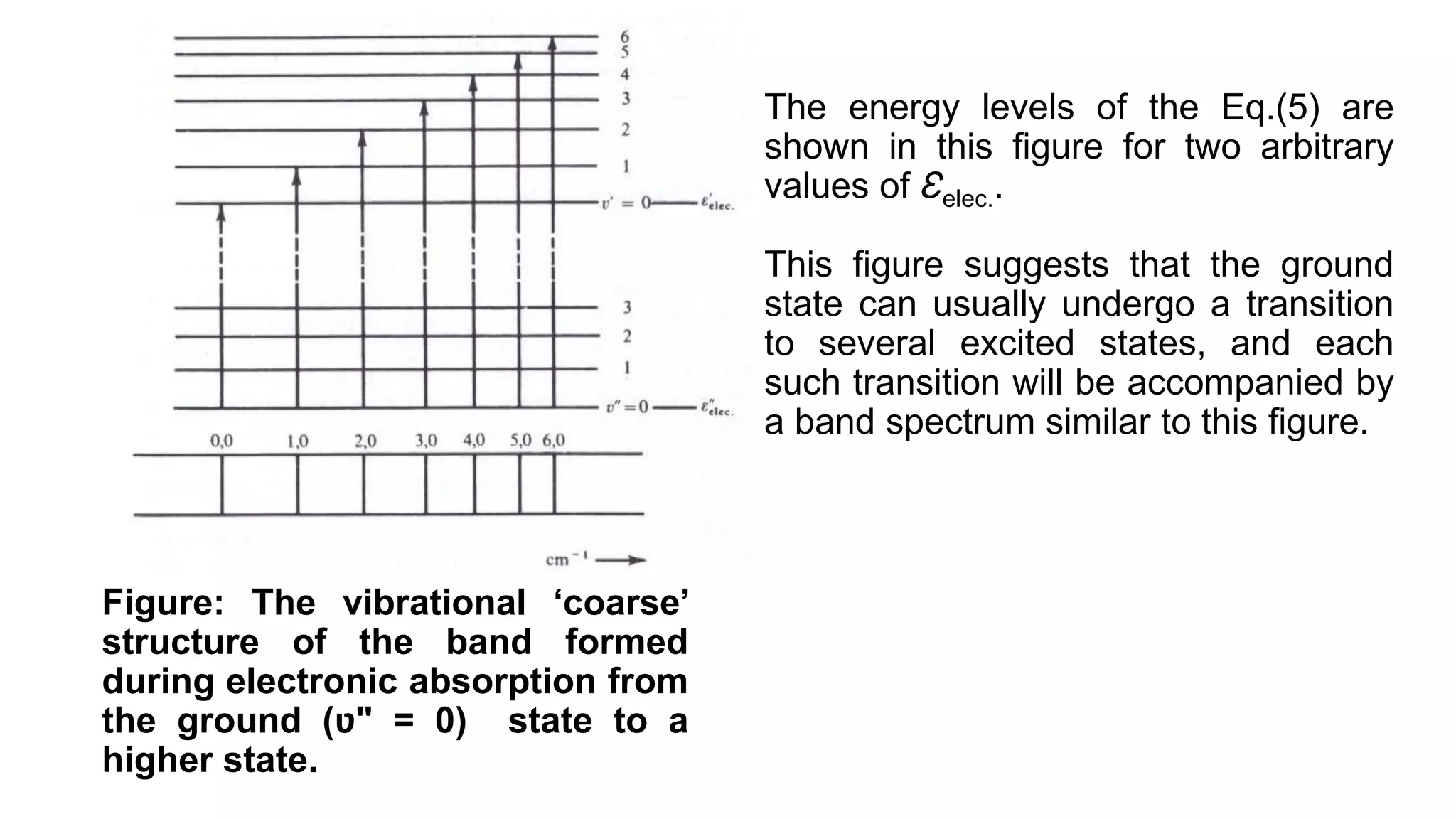
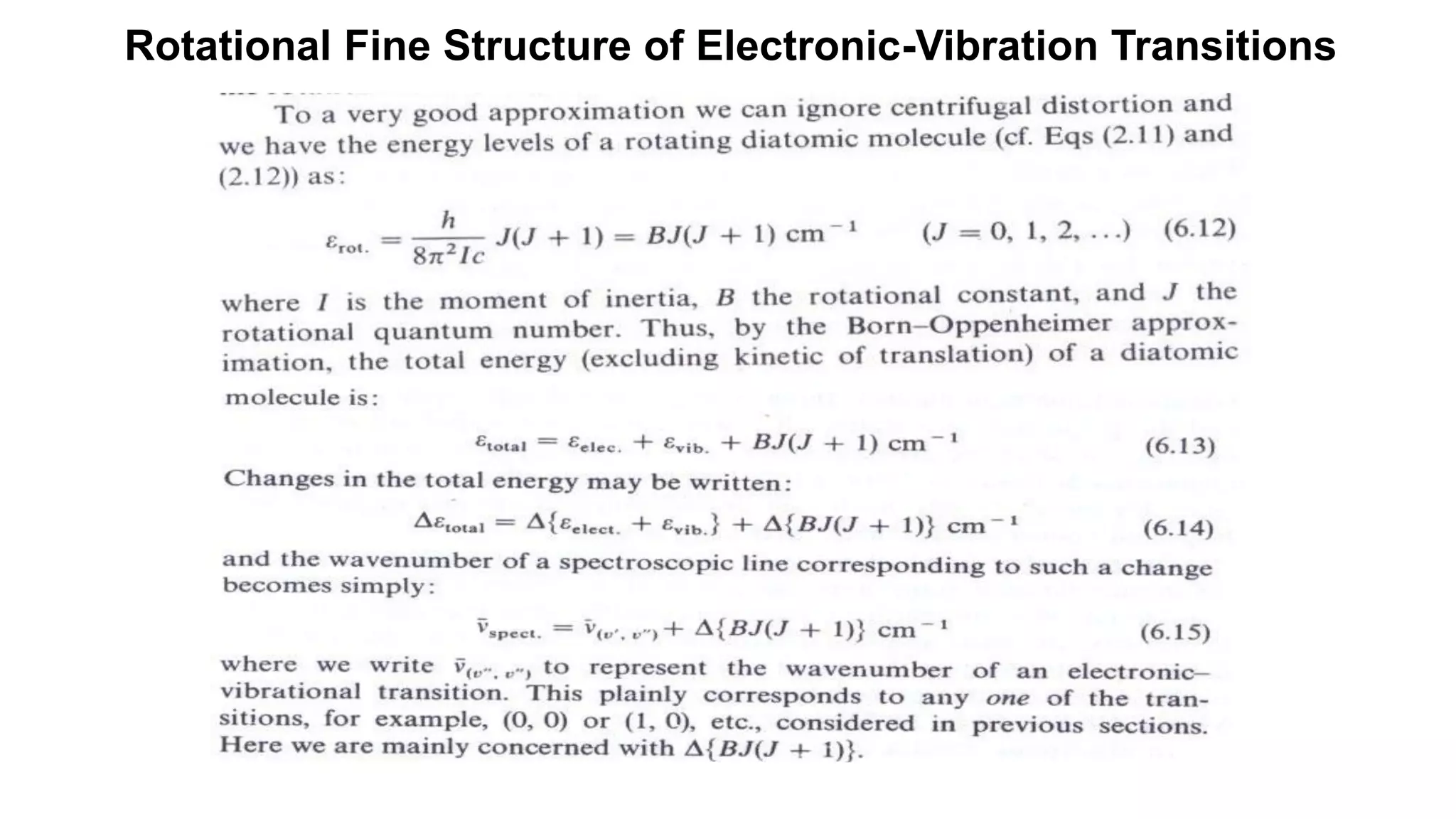
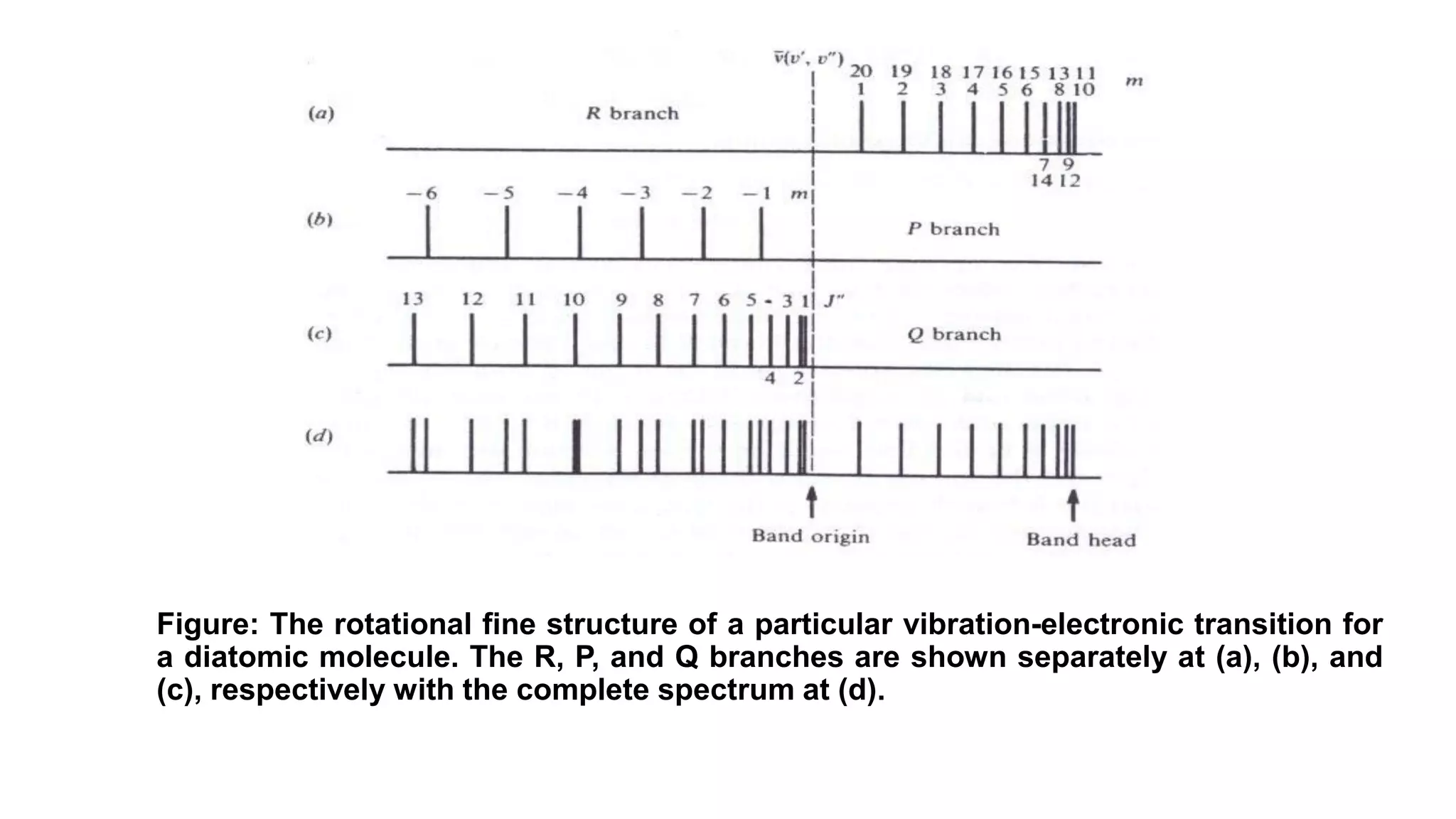
2) Vibrational transitions produce a "coarse structure" spectrum and rotational transitions a "fine structure".
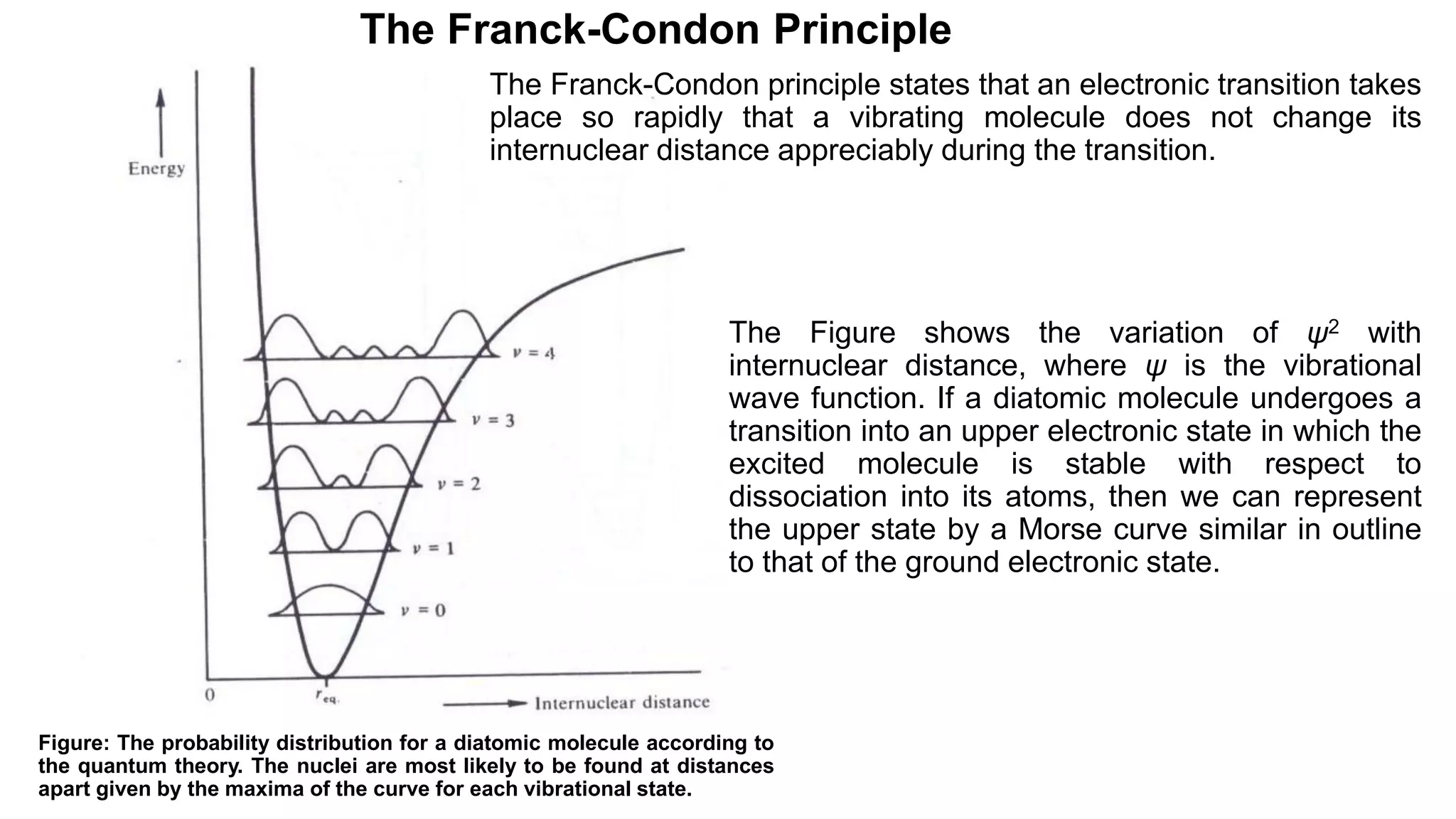
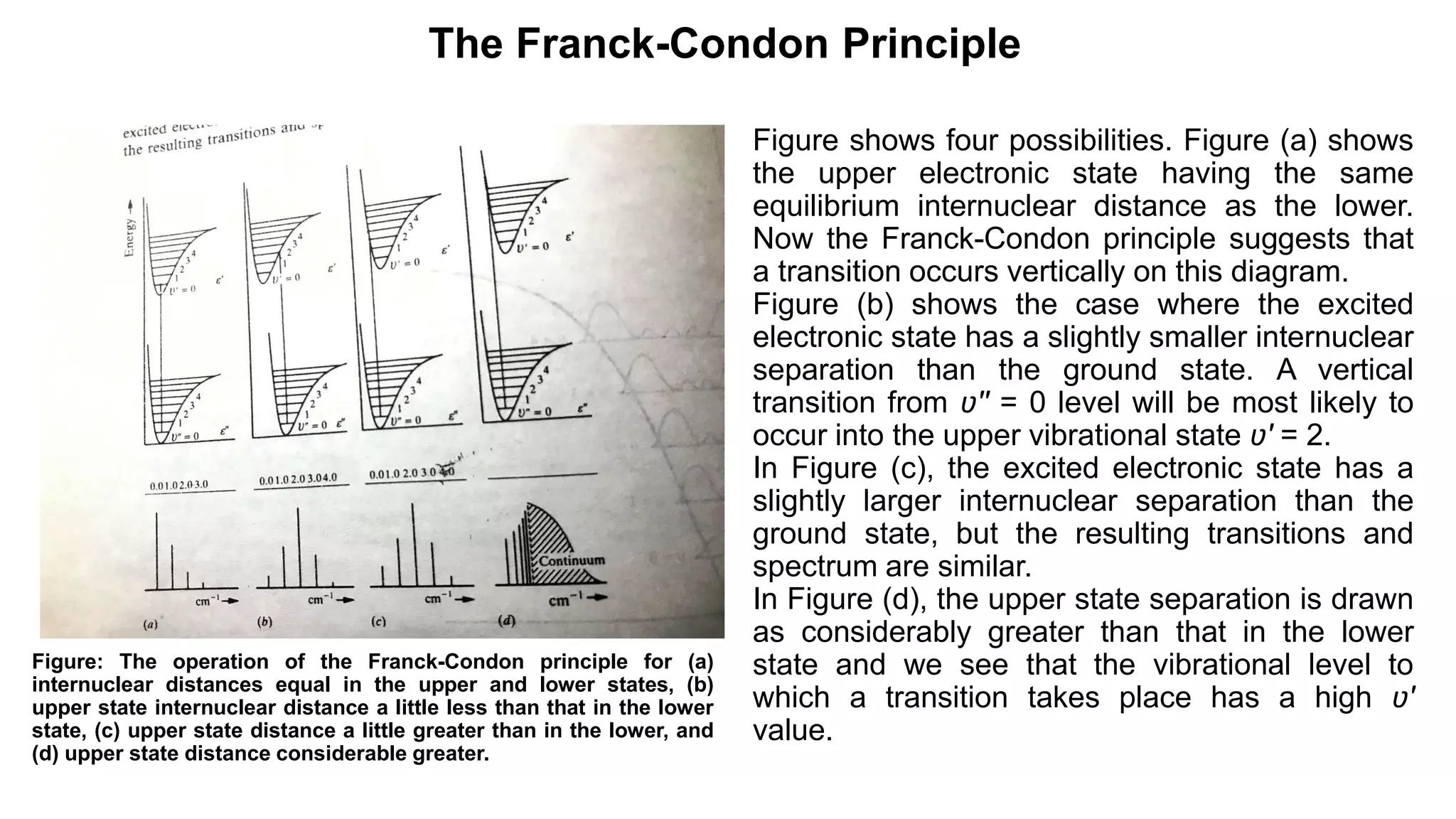
3) The Franck-Condon principle which states that electronic transitions occur rapidly without changes in internuclear distance, leading to vertical transitions between vibrational levels.
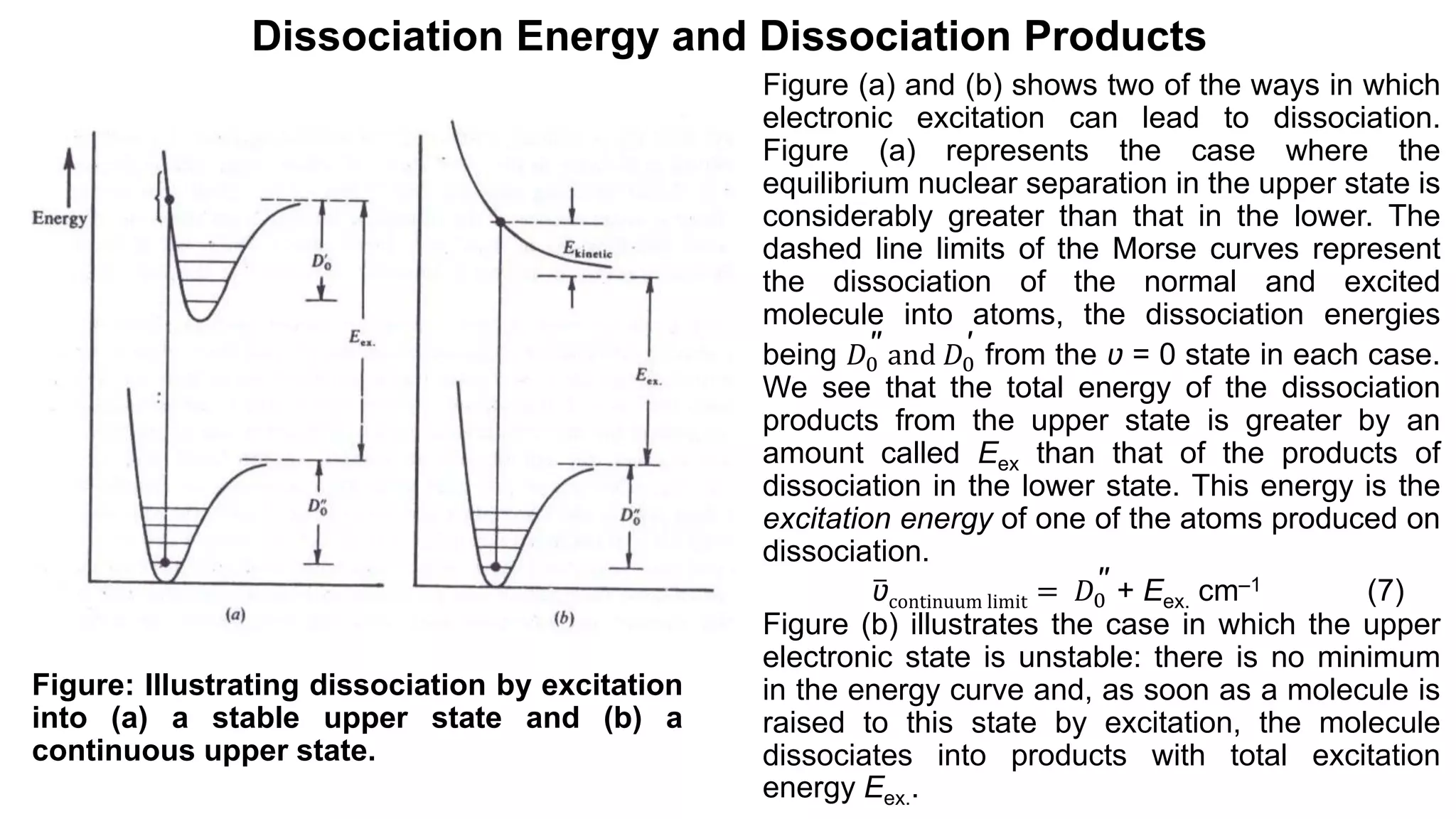
4) Dissociation of electronically excited molecules and the relationship between dissociation energies and excitation energies.







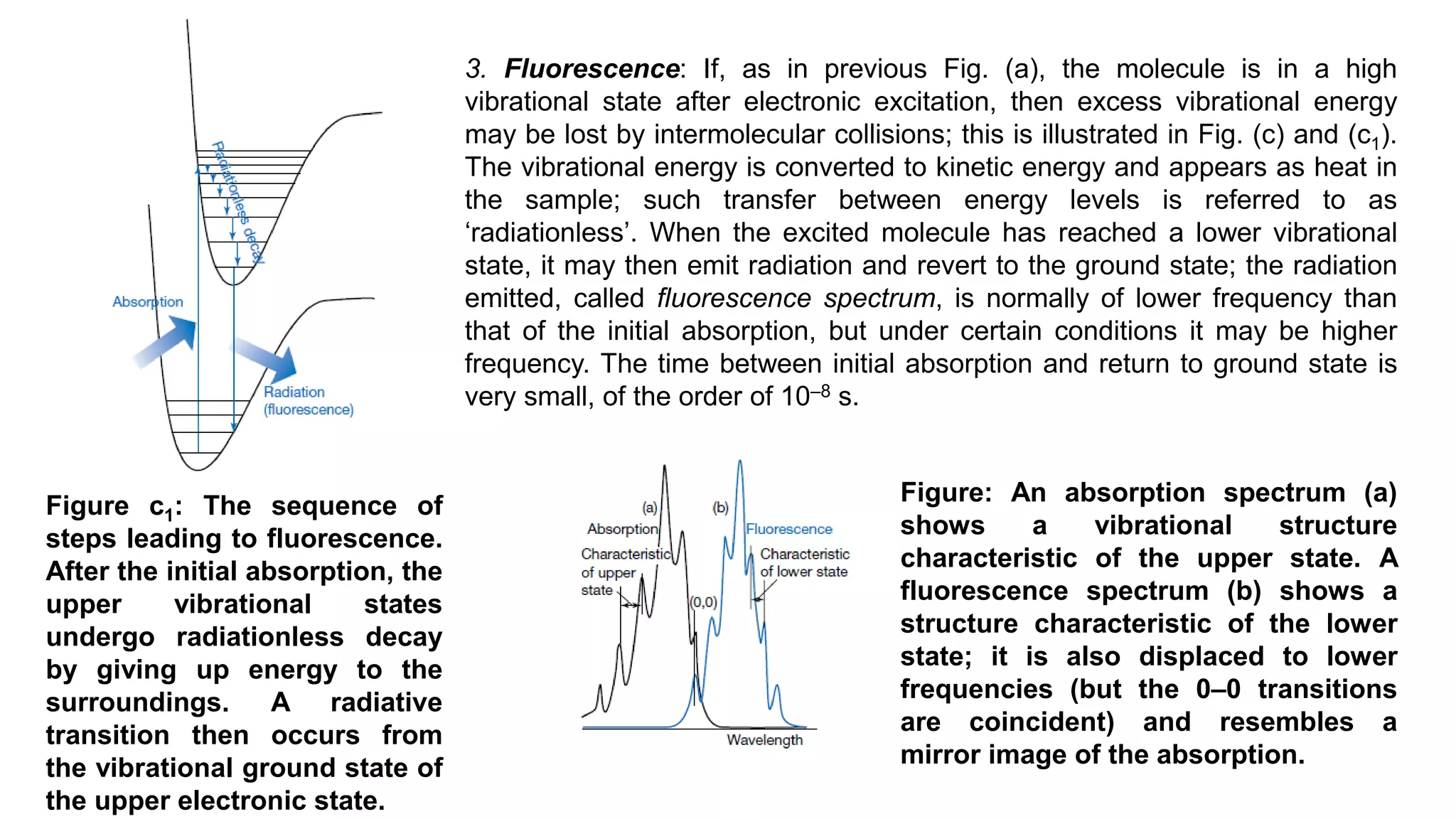
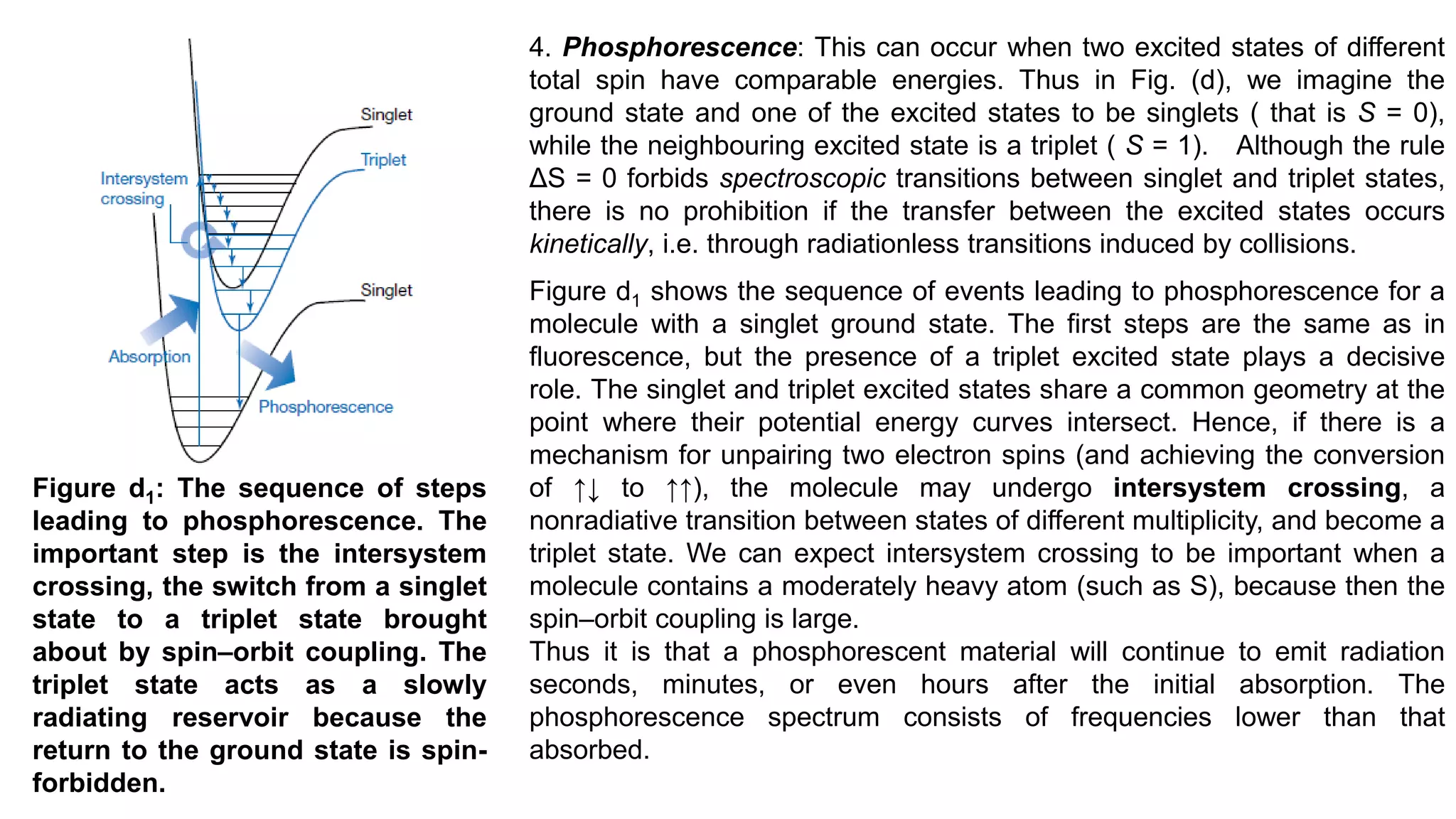
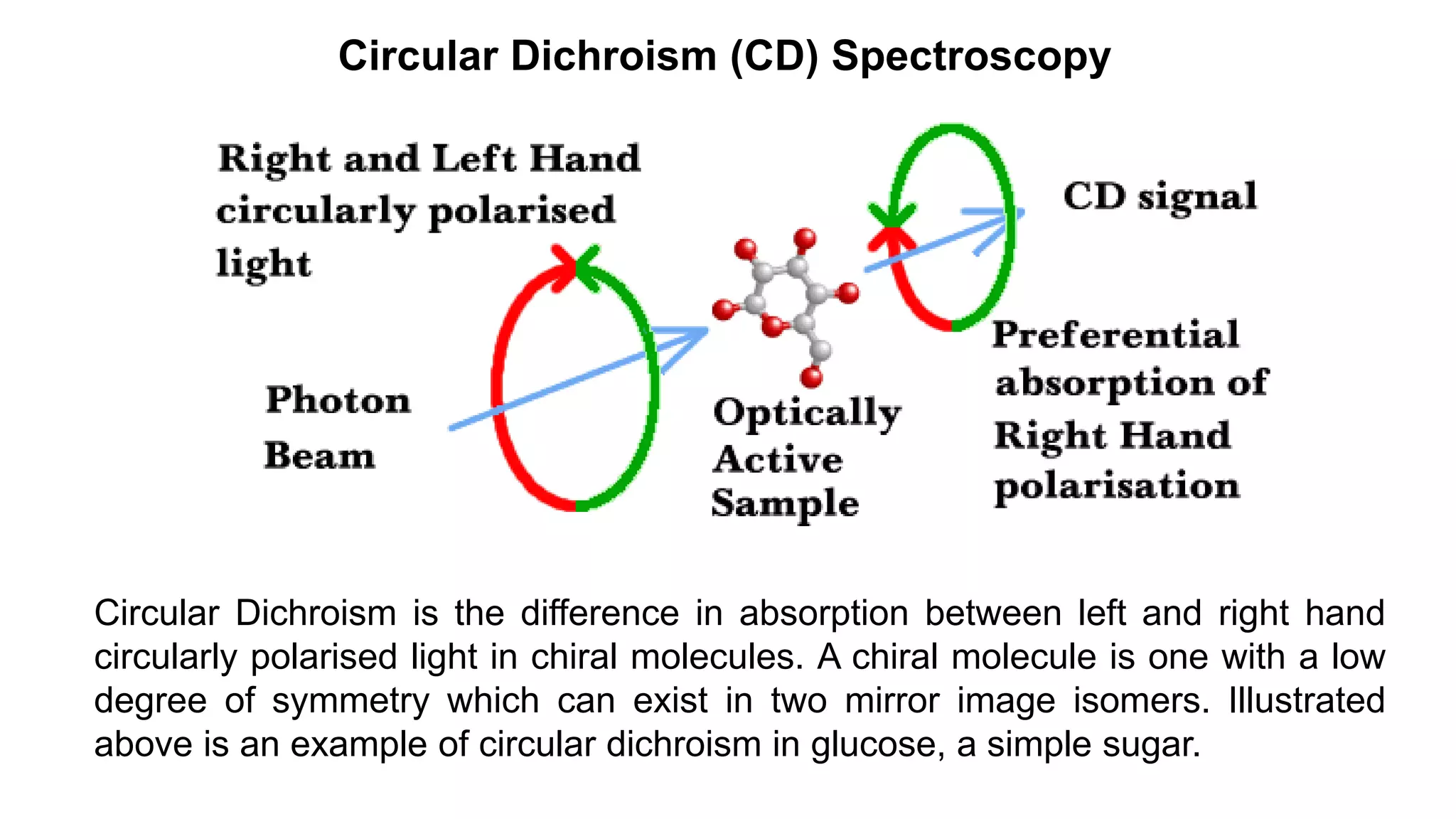

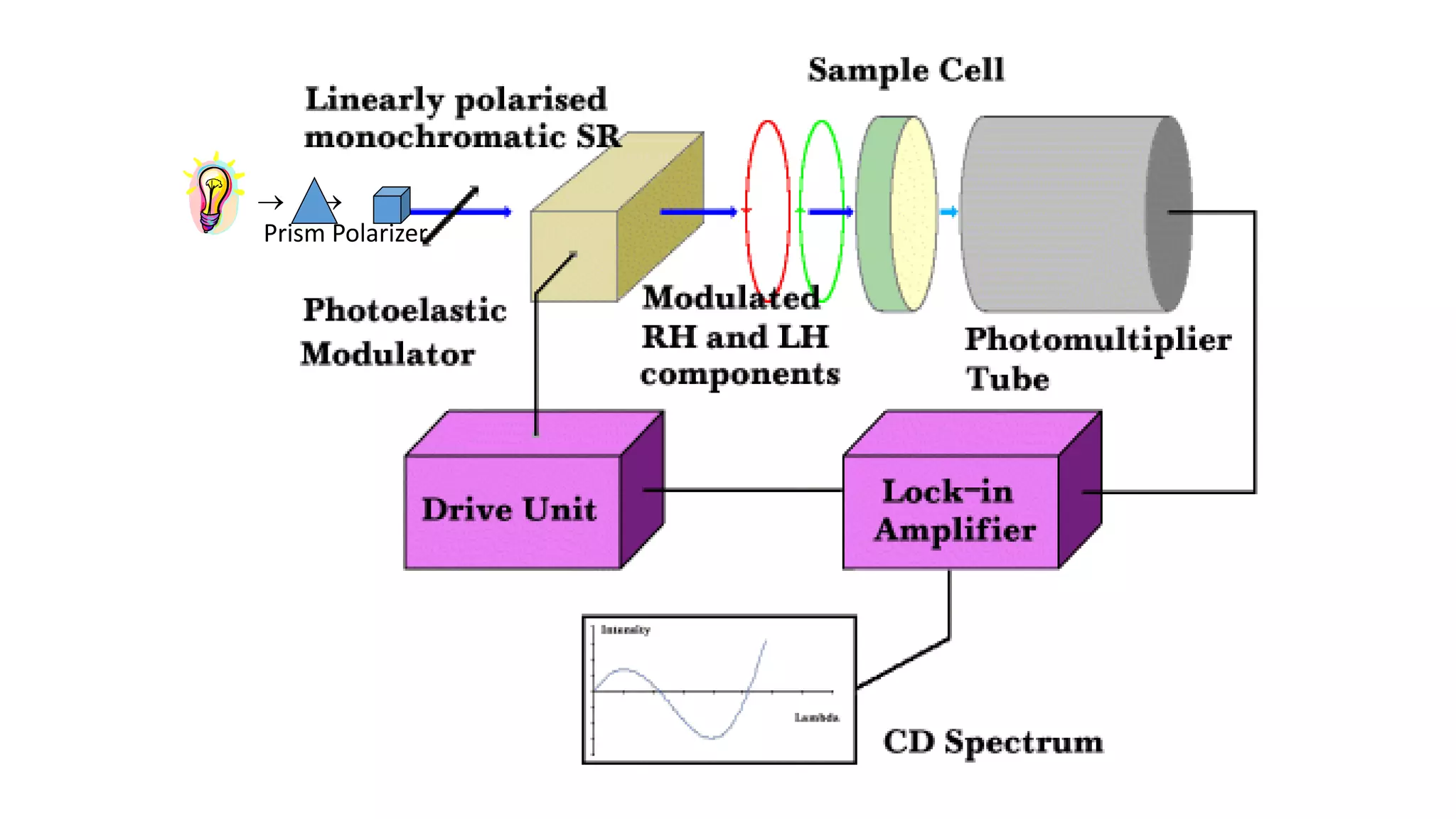
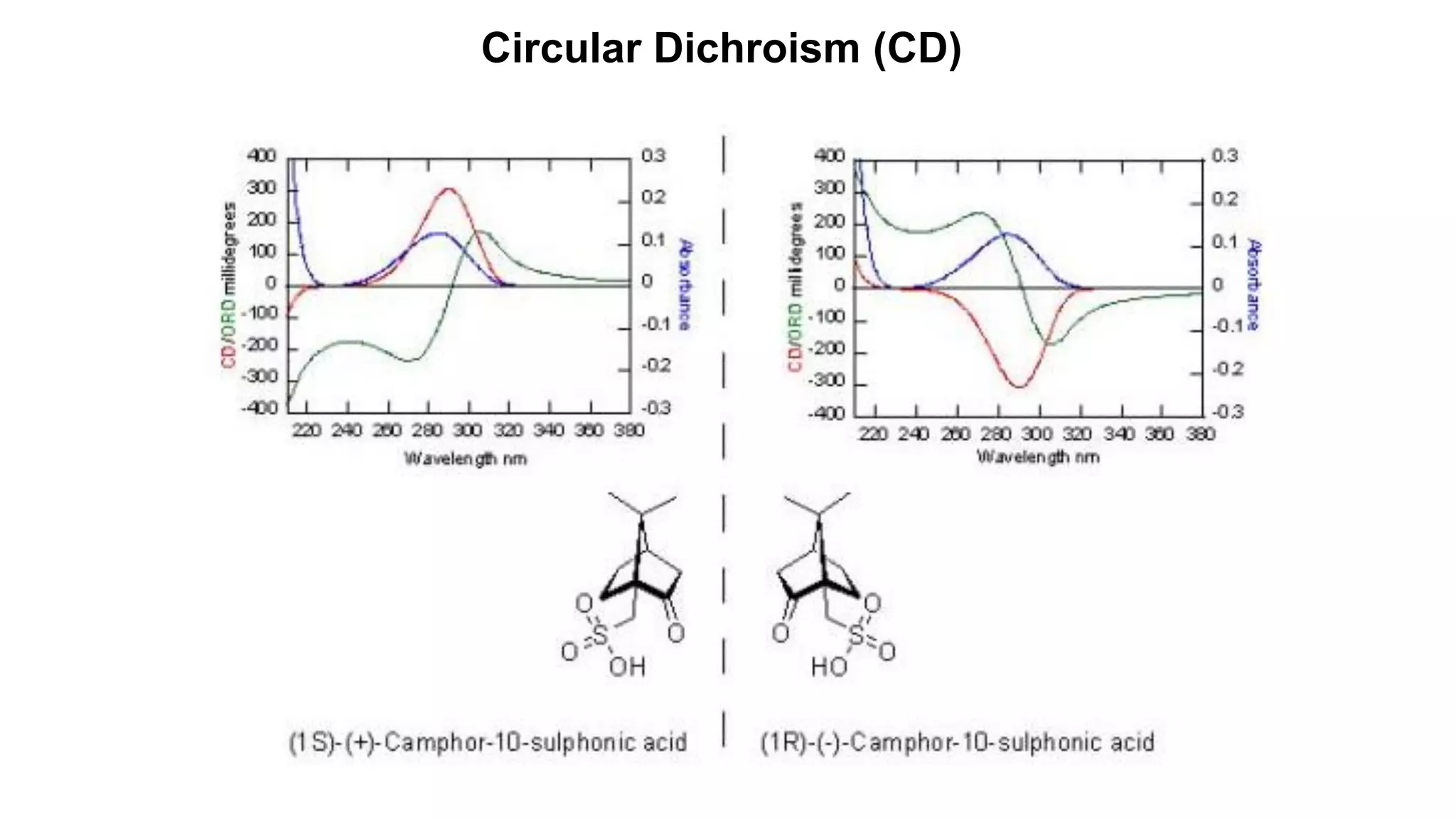
![The secondary structure conformation and the CD spectra of protein structural elements.
Right : a peptide in an α-helix; Left: a peptide in a β-sheet. Centre: CD spectra for these
different conformations.
The most commonly used units are mean residue ellipticity, (degree·cm2/dmol), and the
difference in molar extinction coefficients called the molar circular dichroism, εL-εR = Δε
(liter/mol·cm).
The molar ellipticity [] is related to the difference in extinction coefficients by [] = 3298 Δε.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter6-electronicspectroscopyofmolecules-230412212002-9b5c093d/75/Chapter-6-Electronic-Spectroscopy-of-Molecules-pdf-27-2048.jpg)