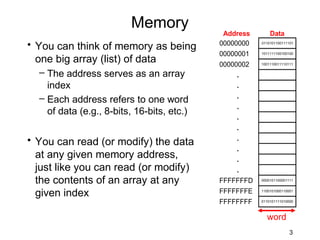
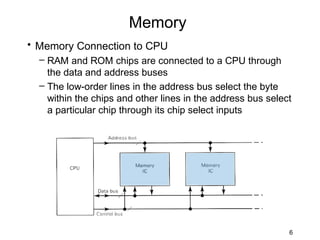
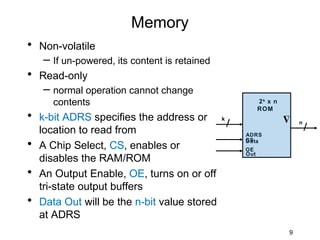
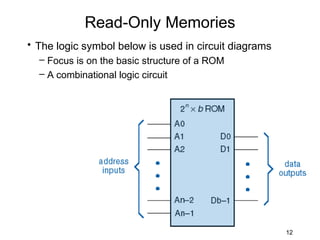
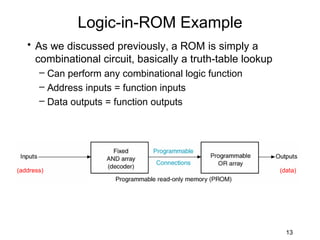
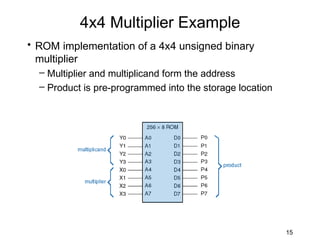
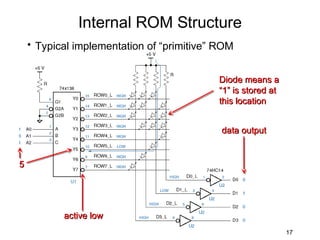
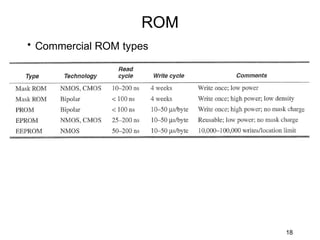
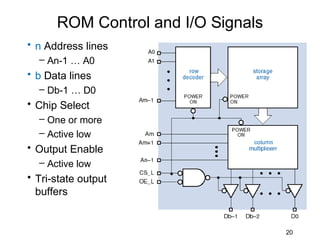
The document discusses various types of memory used in digital systems, including Read-Only Memory (ROM), Programmable ROM (PROM), Erasable Programmable ROM (EPROM), and Random Access Memory (RAM). It explains how memory is structured, addressed, and connected to the CPU, along with timing characteristics and advantages/disadvantages of ROM. The content also covers methods of programming and the function of ROM in storing data permanently without the ability to modify it during typical operation.