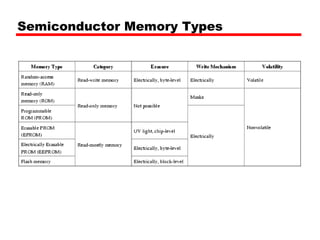
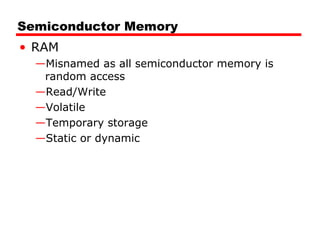
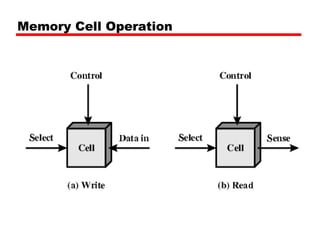
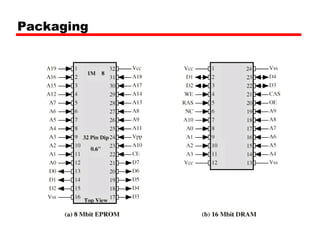
1. Dynamic RAM (DRAM) and Static RAM (SRAM) are the main types of semiconductor memory. DRAM is simpler and cheaper but requires refreshing, while SRAM is faster but more expensive.
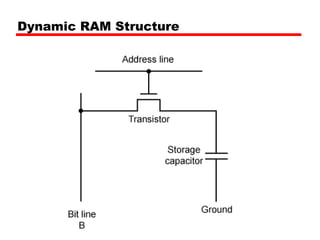
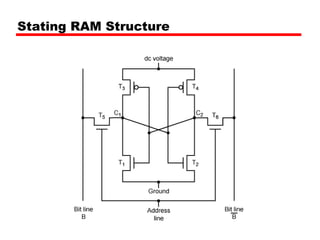
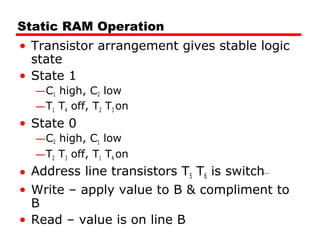
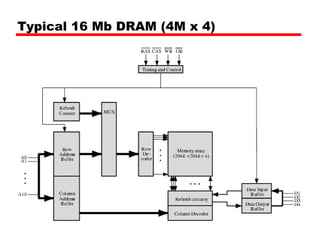
2. DRAM stores bits as electric charges in capacitors, requiring refreshing even when powered. SRAM uses flip-flops to store bits without refreshing.
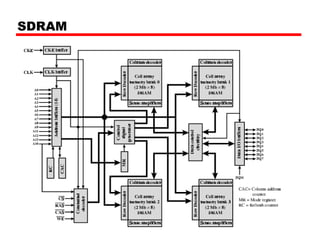
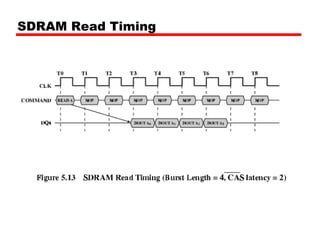
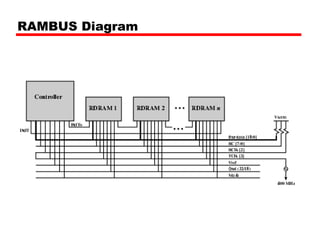
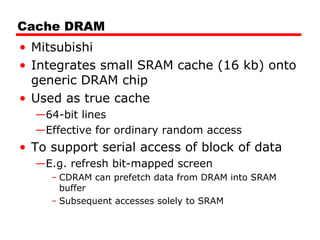
3. Memory technologies continue to evolve, with synchronous DRAM (SDRAM) and double data rate SDRAM (DDR SDRAM) allowing faster data transfer rates by synchronizing with a clock or transferring data on both edges of the clock cycle.