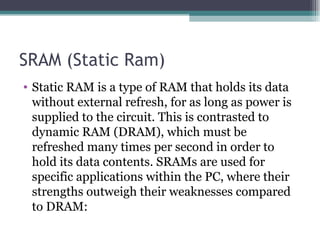
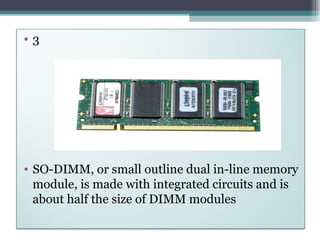
RAM, or Random Access Memory, is a type of volatile memory that can be accessed randomly. There are two main types of RAM: SRAM (Static RAM) and DRAM (Dynamic RAM). SRAM does not need to be refreshed, while DRAM must be refreshed regularly to maintain its data. DRAM is faster than SRAM but also more expensive. DRAM is the most common type used in computers today and comes in memory module forms like DIMMs, SO-DIMMs, and memory sticks.