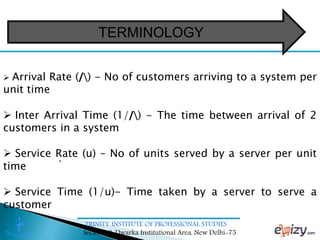
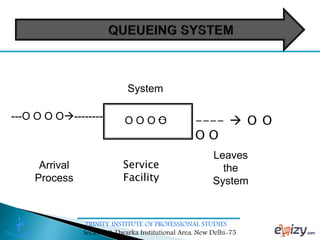
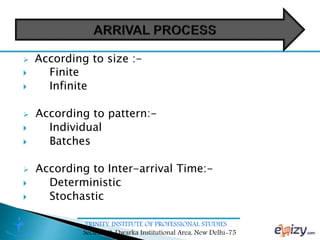
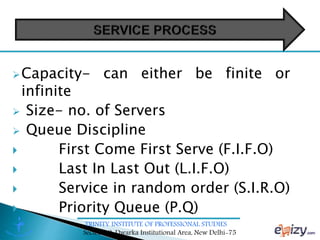
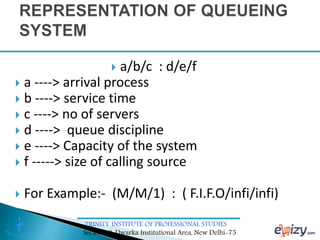
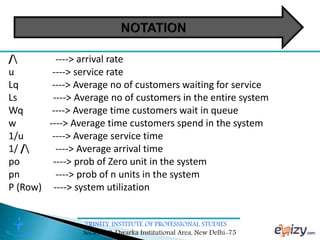
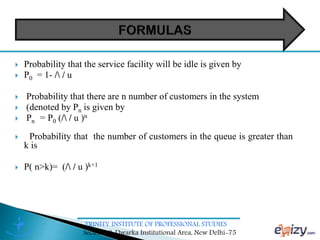
The document discusses queueing theory, focusing on the formation of queues due to limited service facilities and infinite customer arrivals. It outlines key concepts such as arrival rate, service rate, queue discipline, and various metrics like average wait time and system utilization. Additionally, it provides an example scenario involving a retail outlet to illustrate the application of the single-channel queuing model.