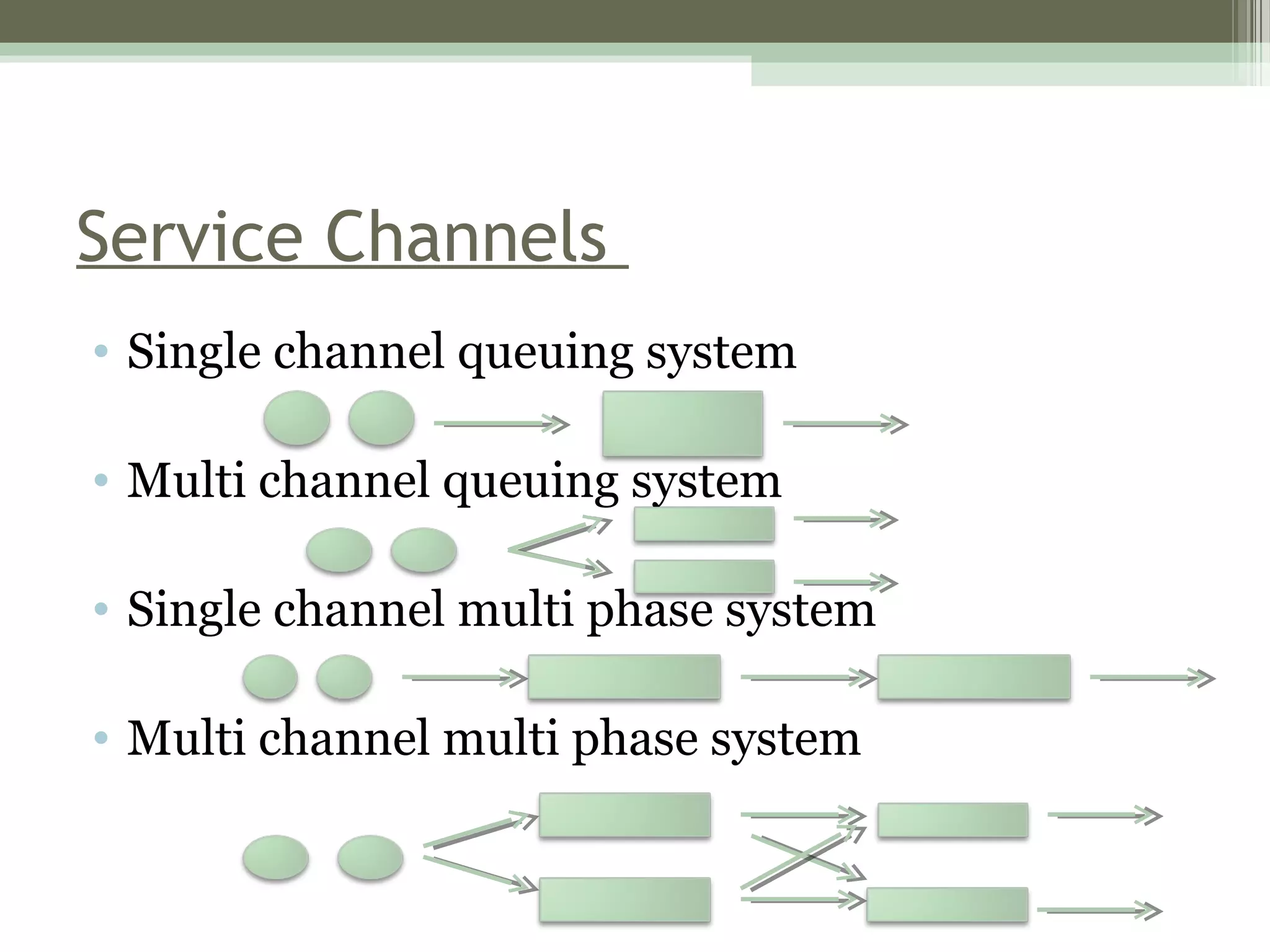
Queuing theory is used to model waiting lines in systems where demand fluctuates. It can be used to optimize resource allocation to minimize costs associated with customer wait times and unused service capacity. The key elements of a queuing system include arrivals, a queue or waiting line, service channels, and a service discipline for determining order of service. Customers arrive according to a Poisson distribution and service times follow an exponential distribution. The goal of queuing analysis is to determine the number of service channels needed to balance wait time costs and idle resource costs.













![Totalexpectedcostof
operatingfacility
Increased service
Total expected cost
Cost of providing
service
Waiting time costs
Total expected cost = waiting time cost + cost
of providing service
Let Cw = expected waiting
cost/unit time
Ls= expected no. of units
Cf = cost of servicing one unit
Expected waiting cost= Cw. Ls
=Cw.[λ /(μ-λ )]
Expected service cost/unit time=
Cf.μ
Total cost , C = Cw. [λ/(μ-λ)] +μCf
This will be minimum if d/dμ(C)=0
Or if
-Cw.[λ/(μ-λ)²]+Cf=0 ,
Which gives ..
μ=λ±sqrt(Cw .λ/Cf)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/queuingtheory-141114115954-conversion-gate02/75/Queuing-theory-15-2048.jpg)



