Embed presentation
Downloaded 359 times
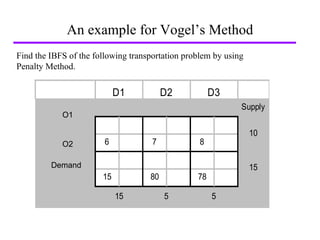
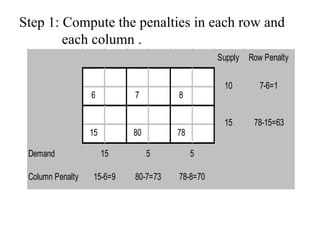
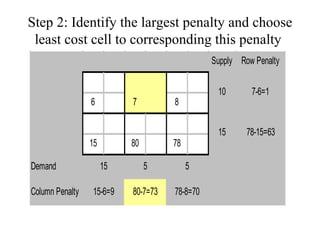
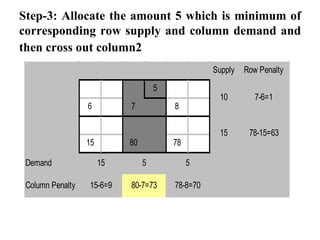
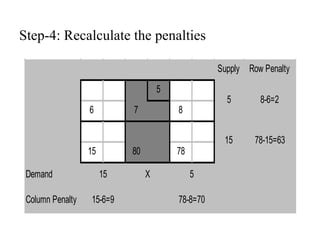


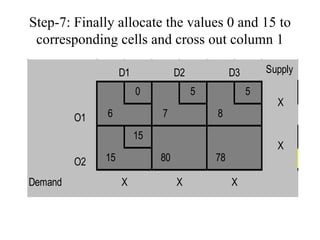

Vogel's Approximation Method (VAM) is a 3 step process for solving transportation problems: 1) Compute penalties for each row and column based on smallest costs. 2) Identify largest penalty and assign lowest cost variable the highest possible value, crossing out exhausted row or column. 3) Recalculate penalties and repeat until all requirements are satisfied.









