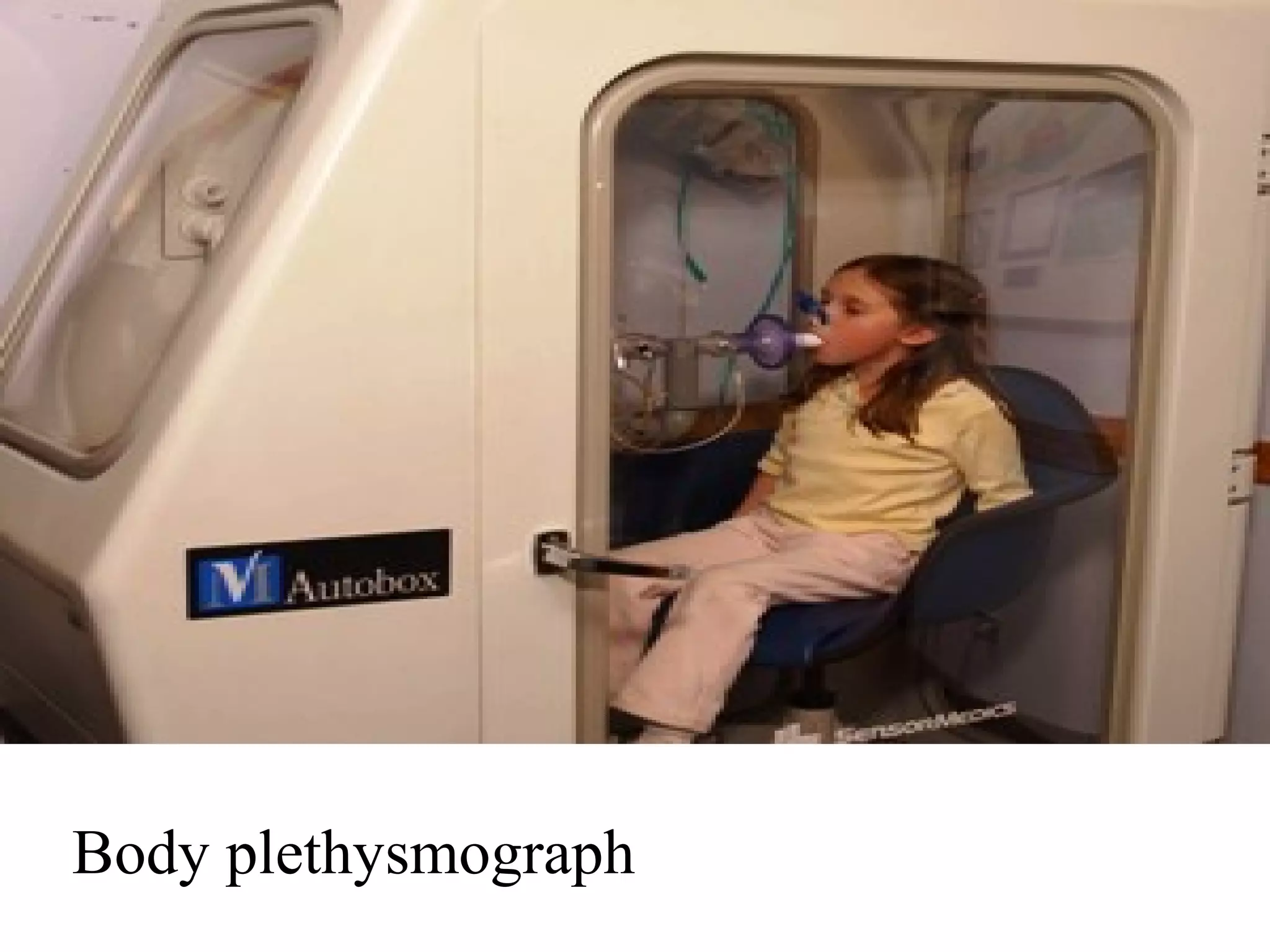
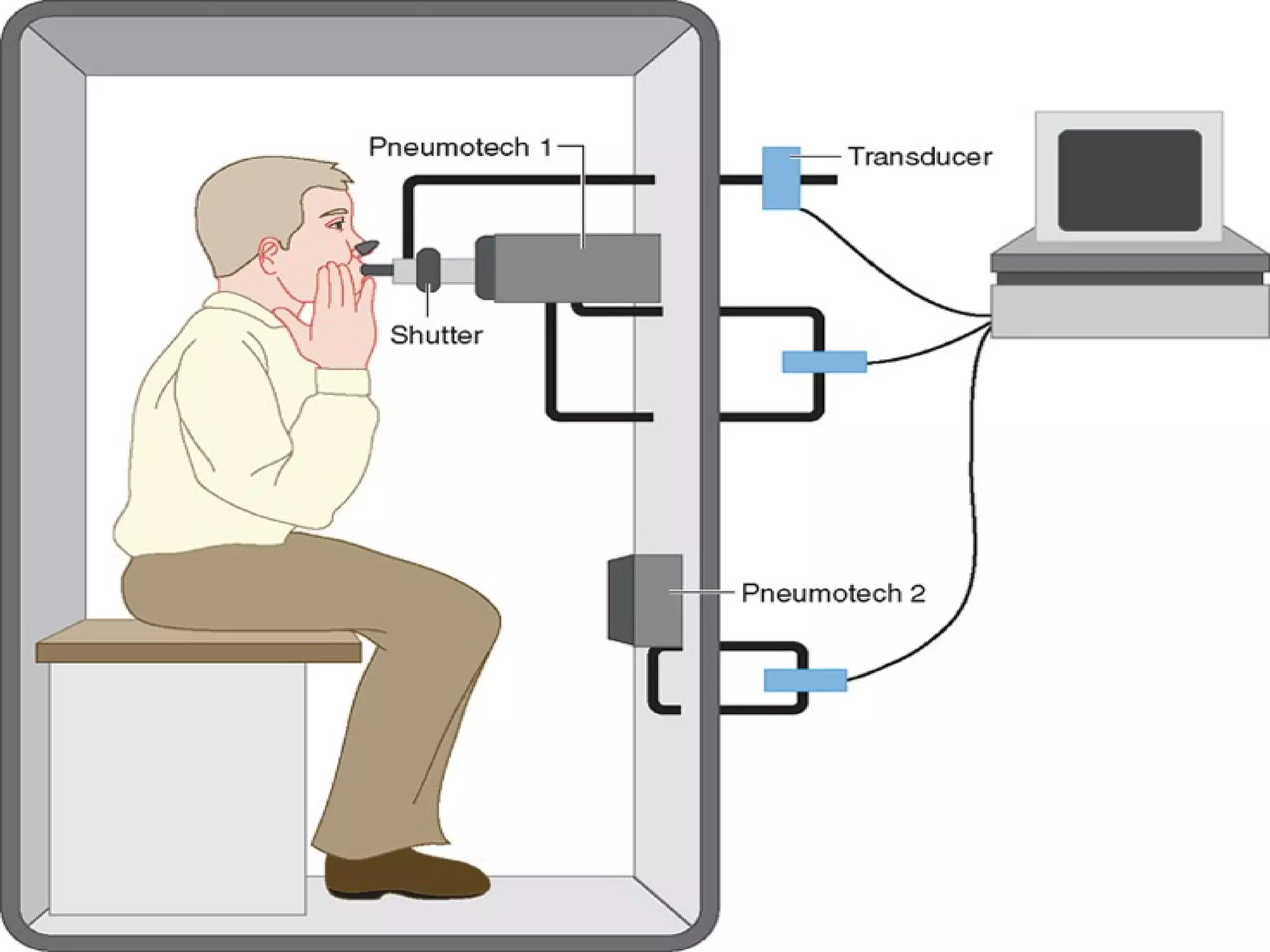
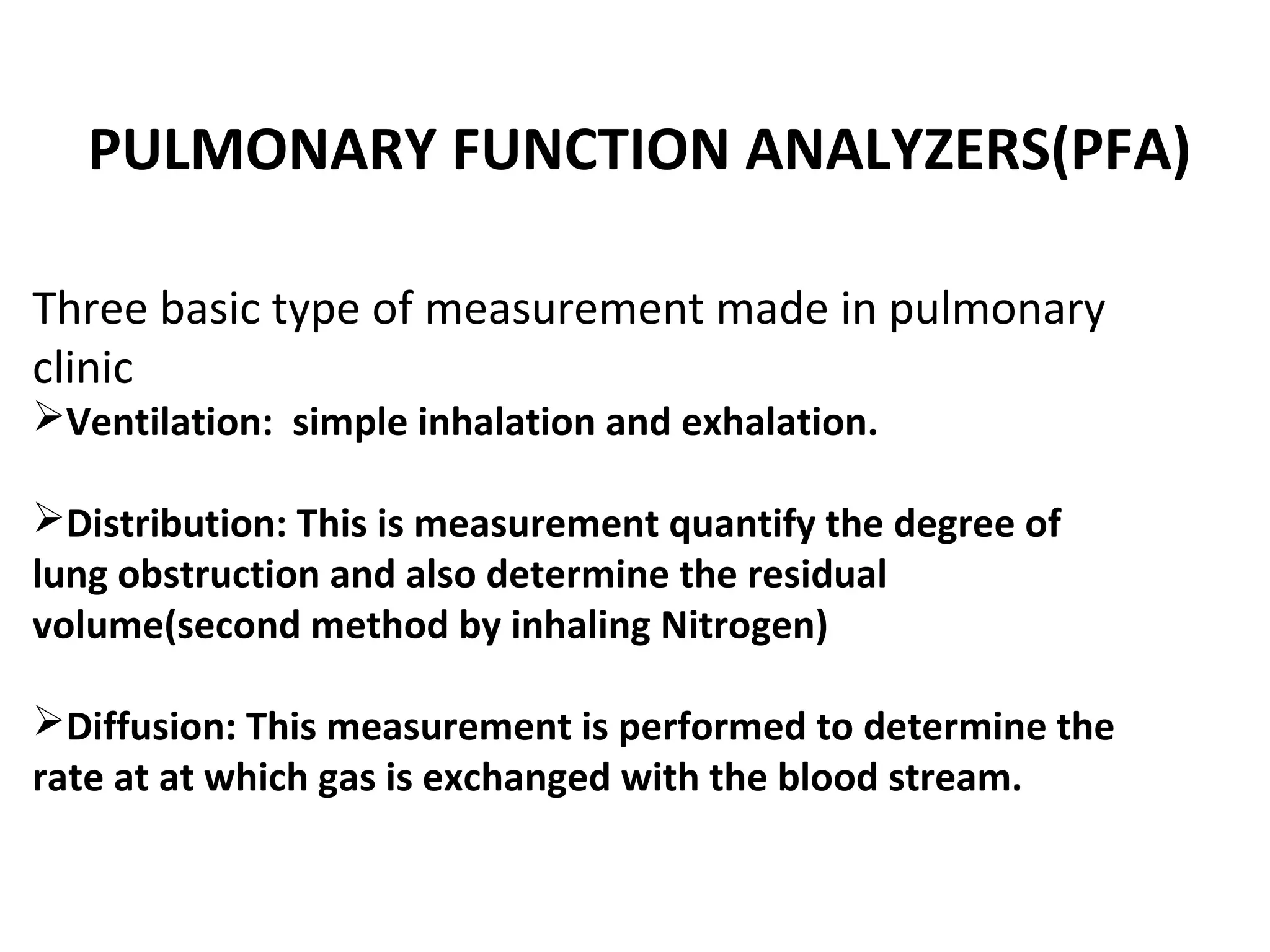
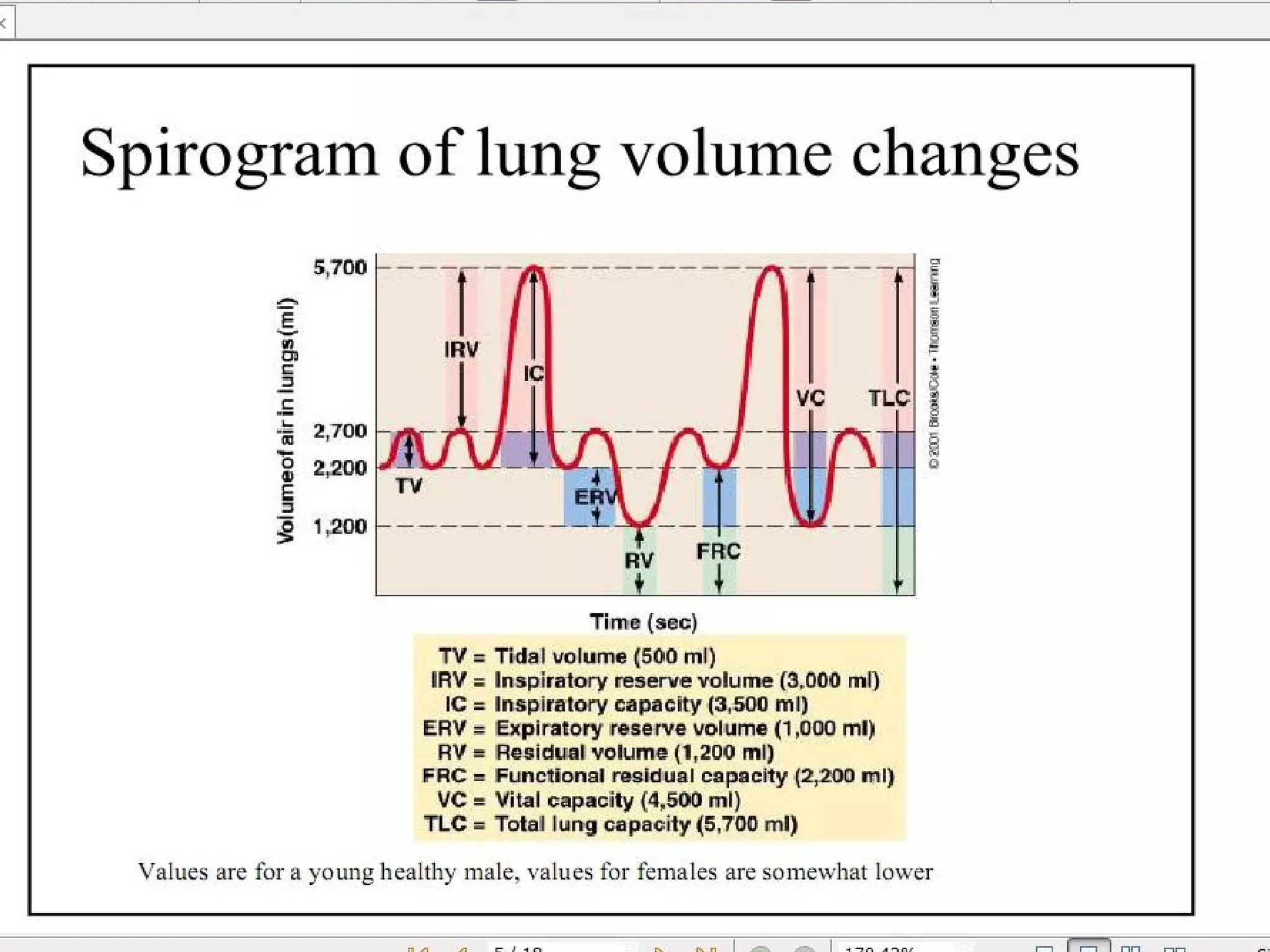
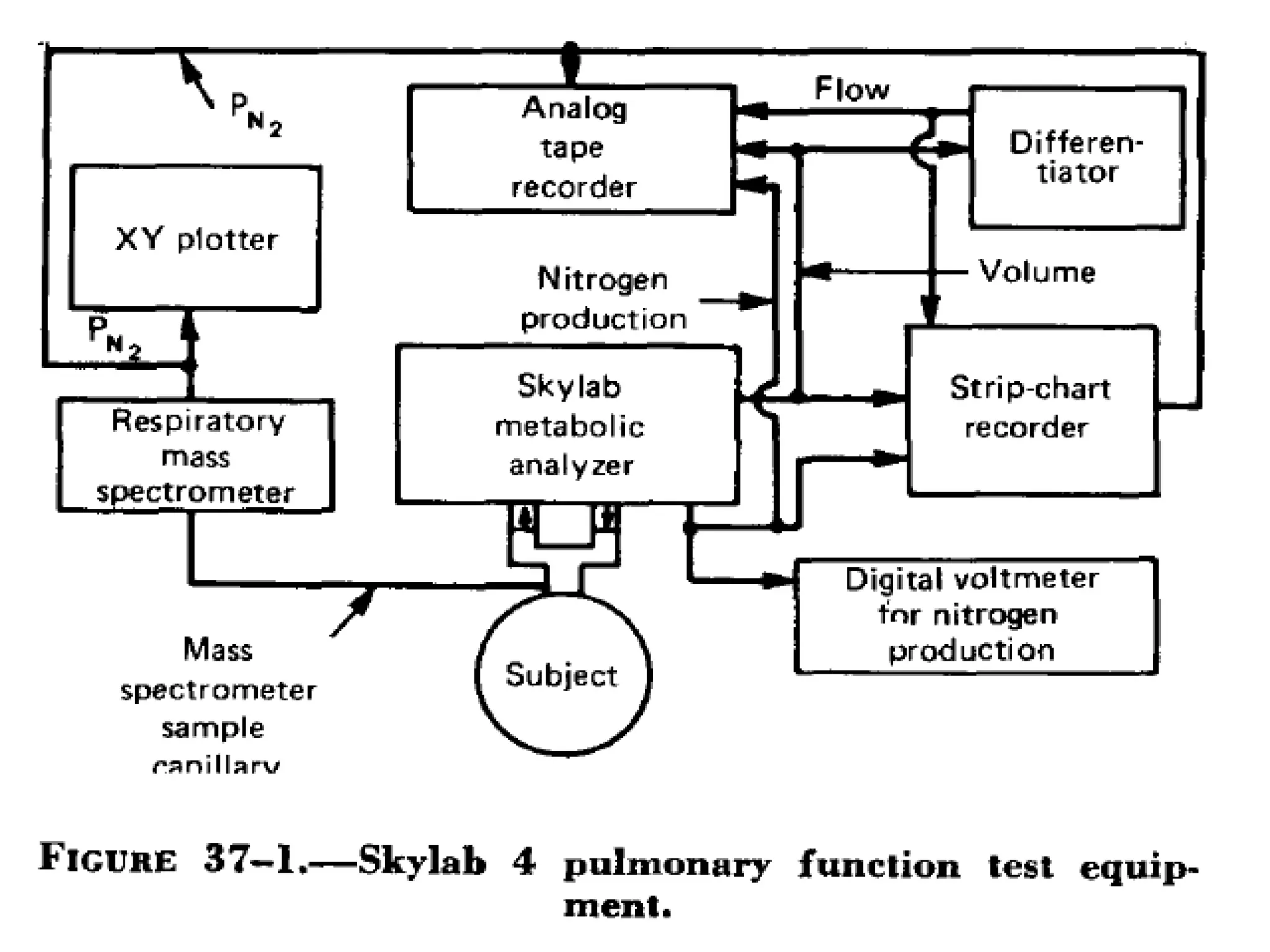
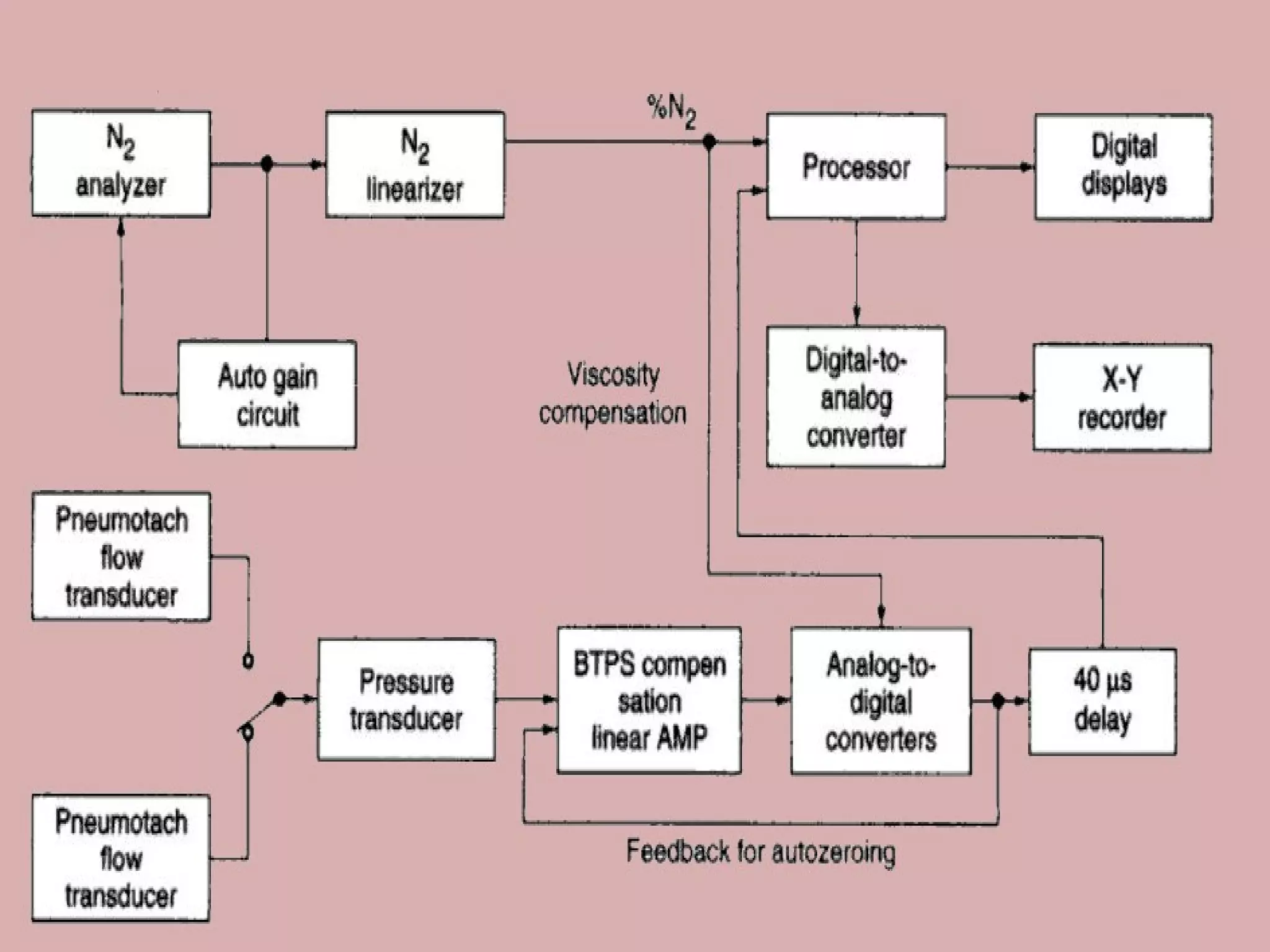
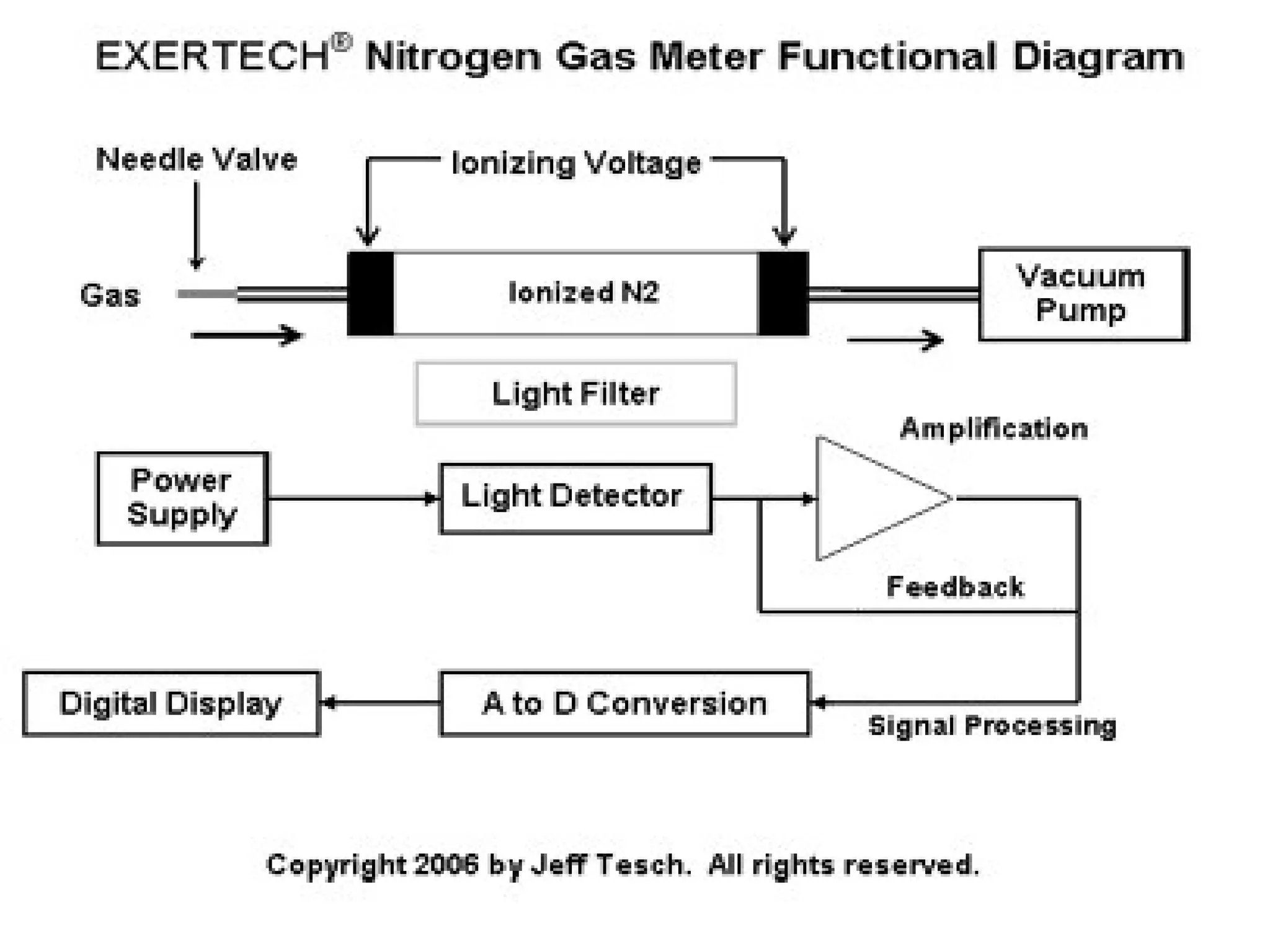
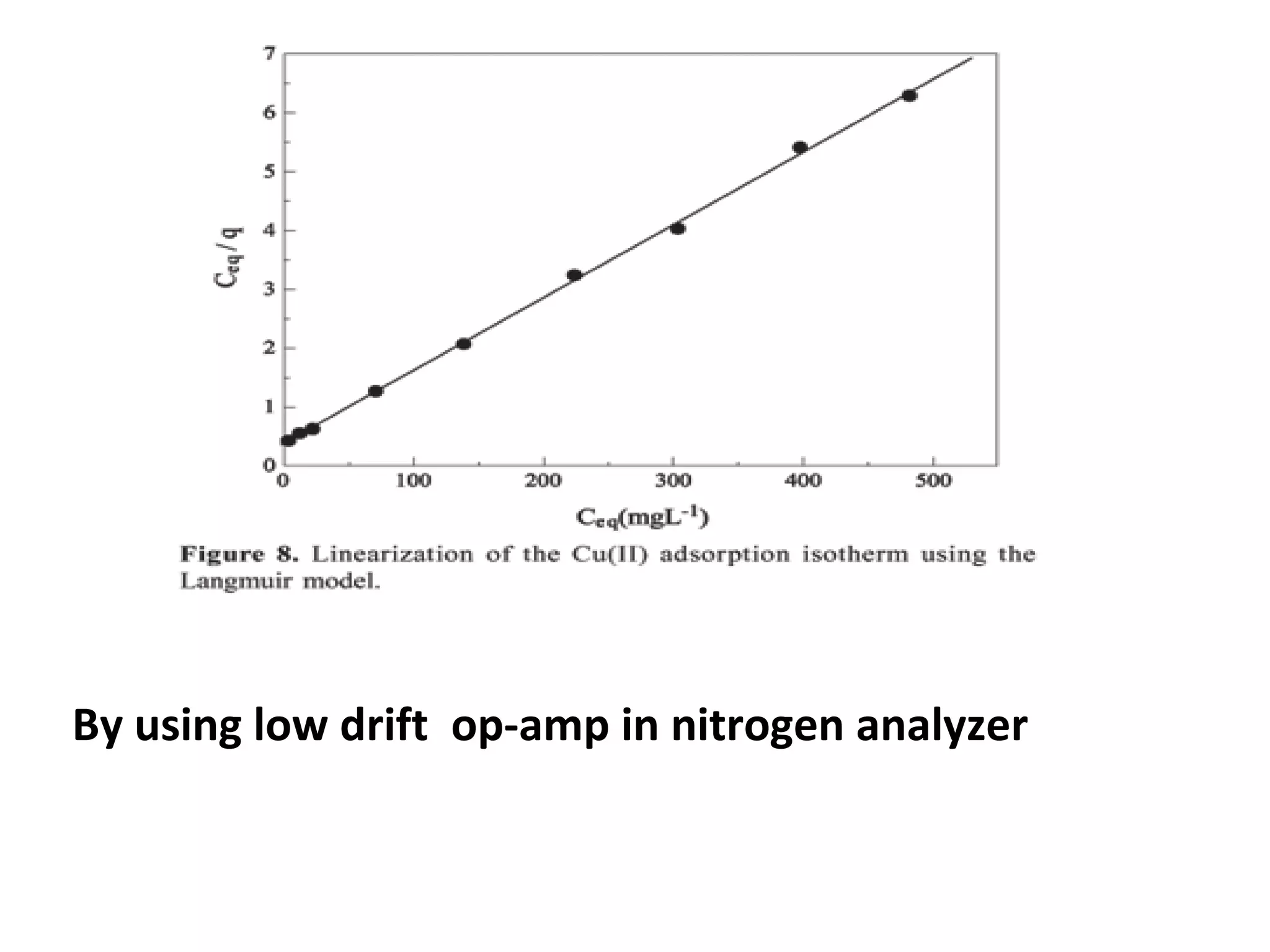
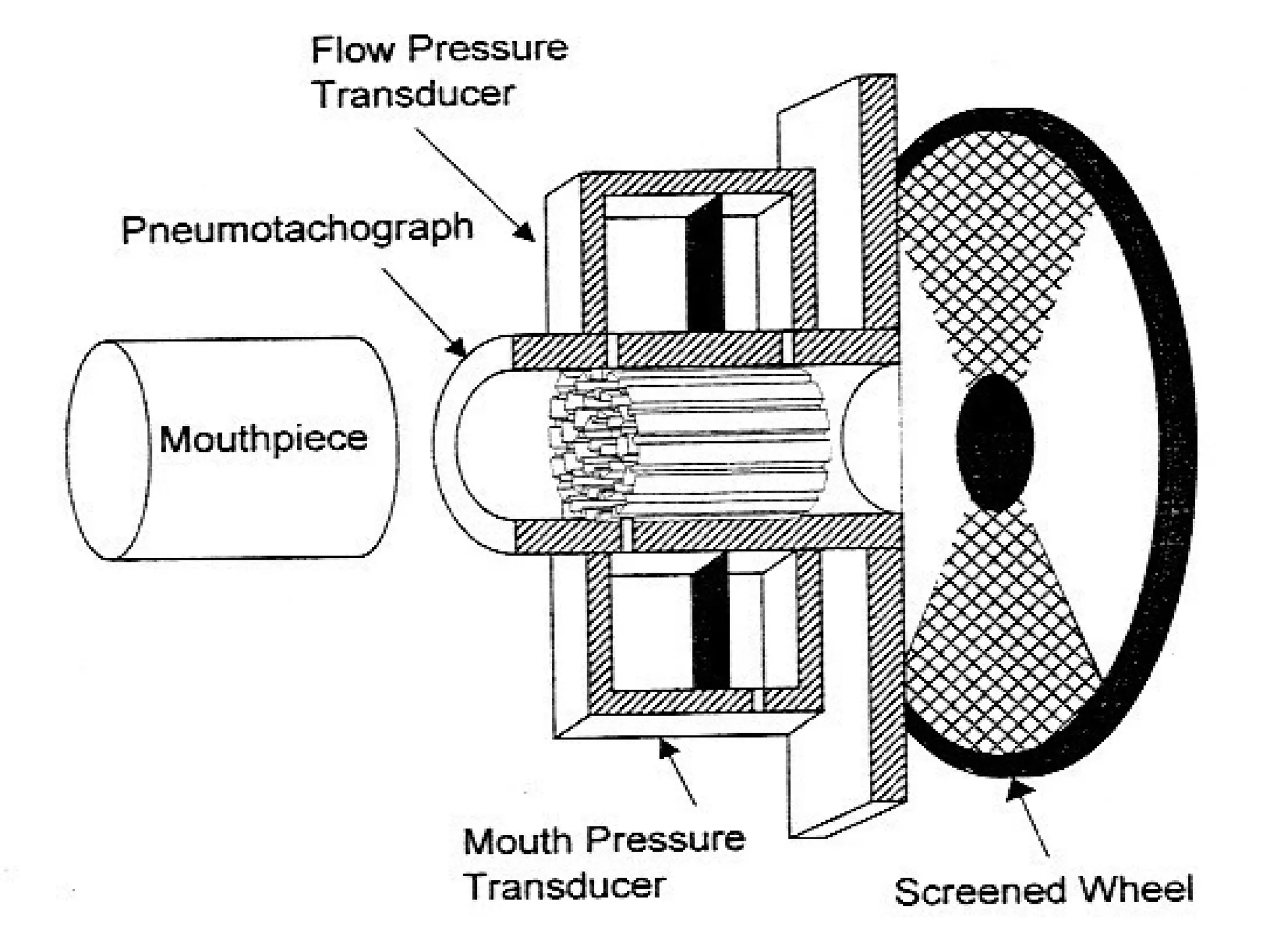
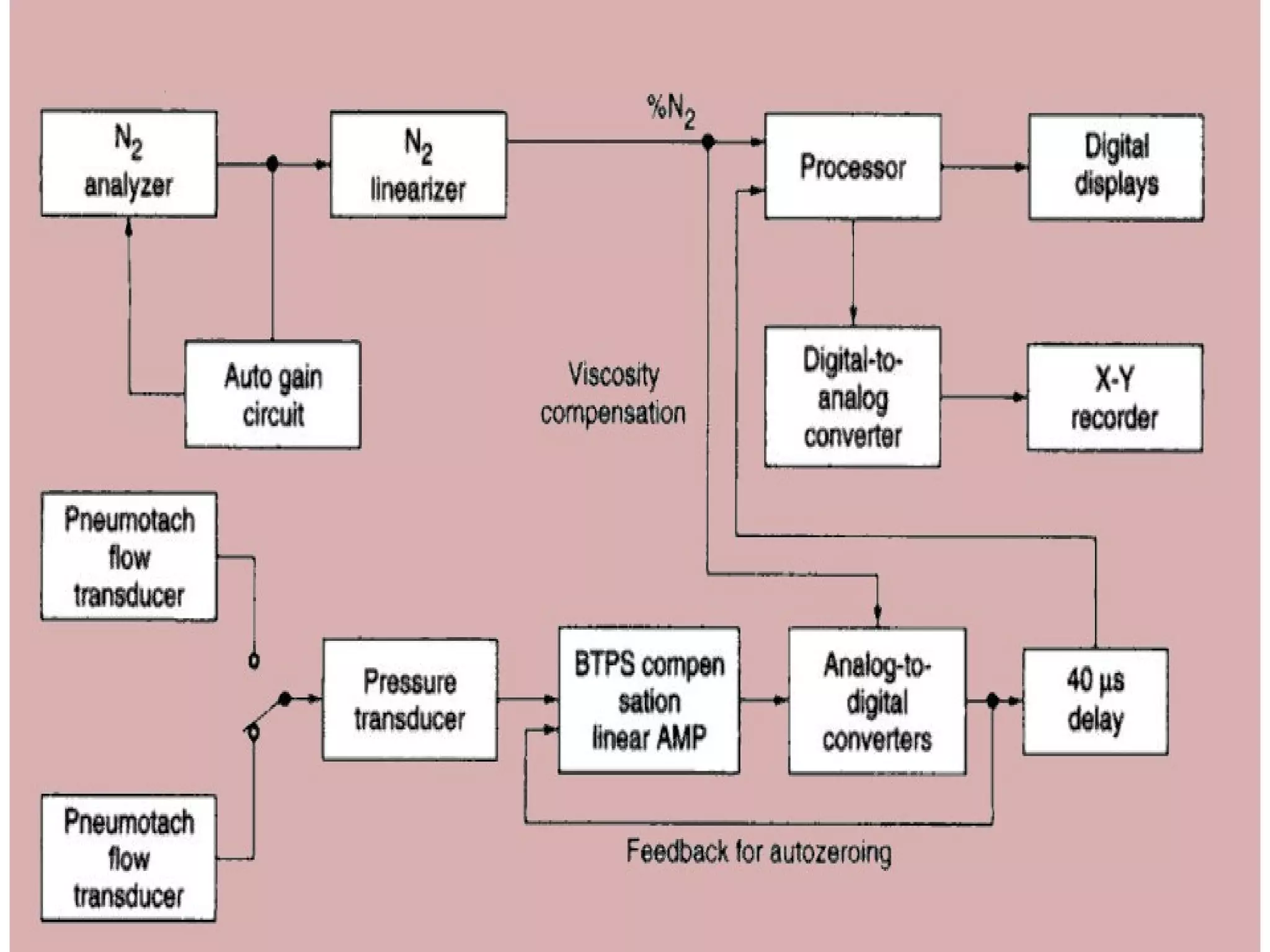
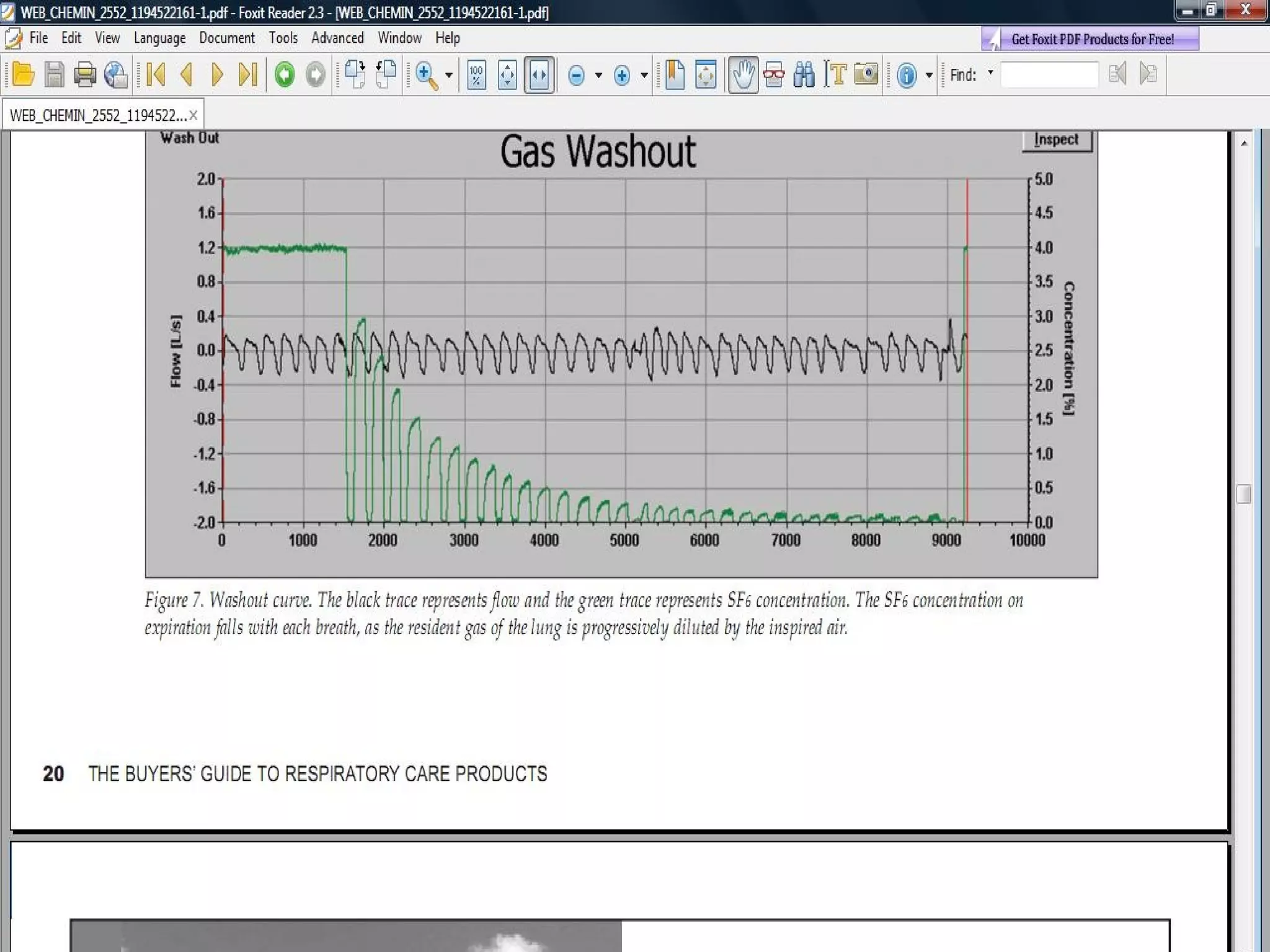
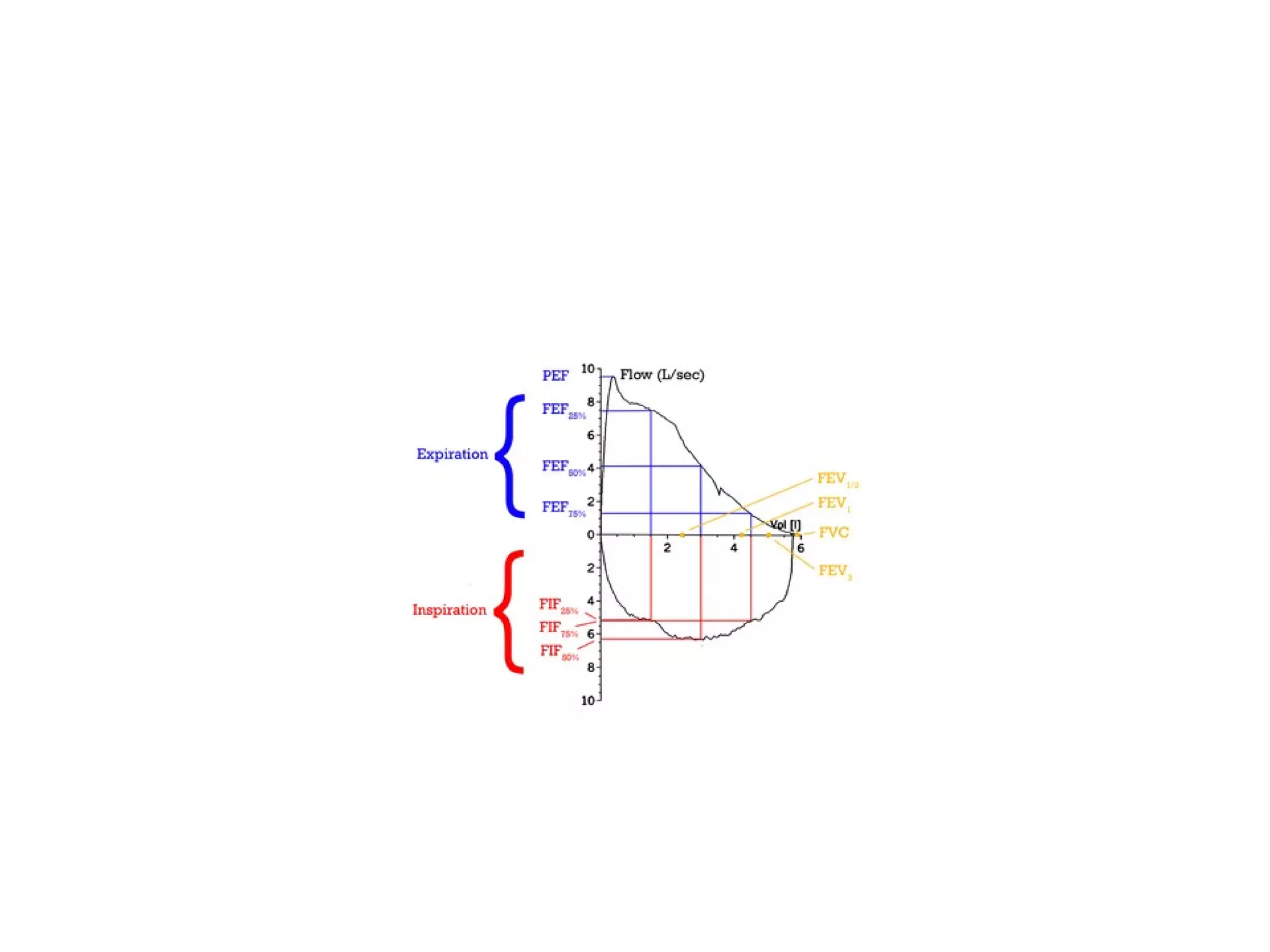
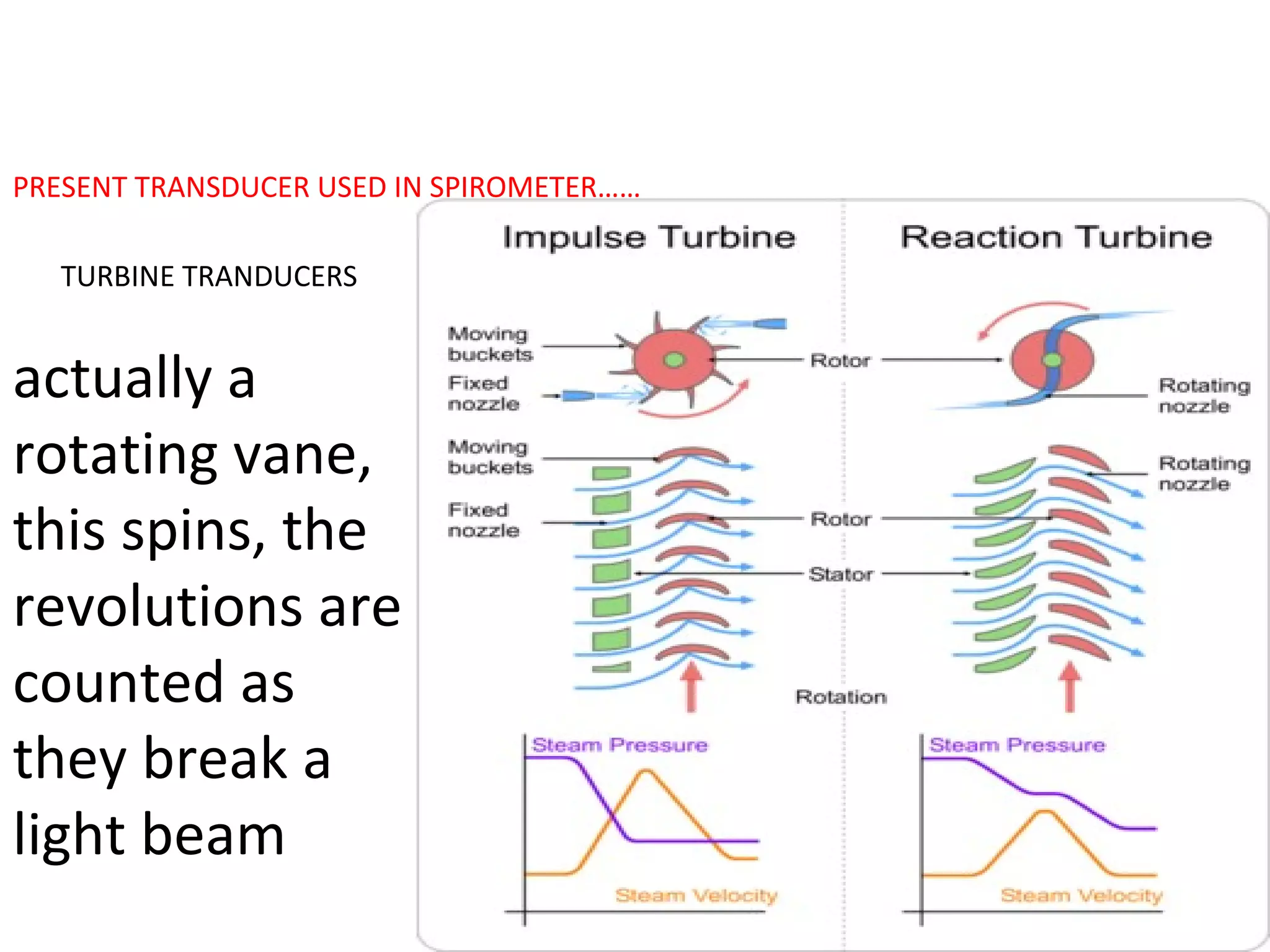
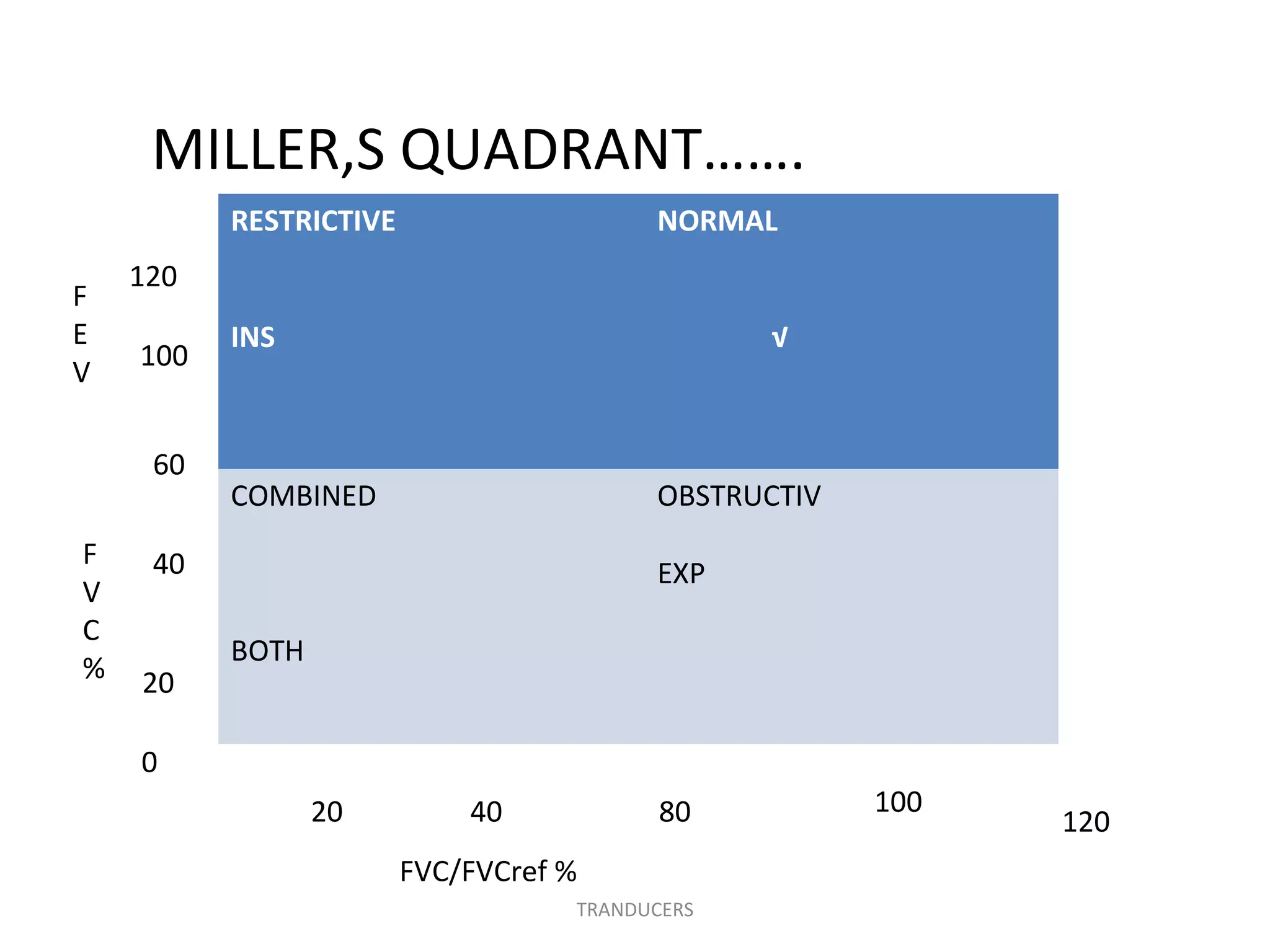
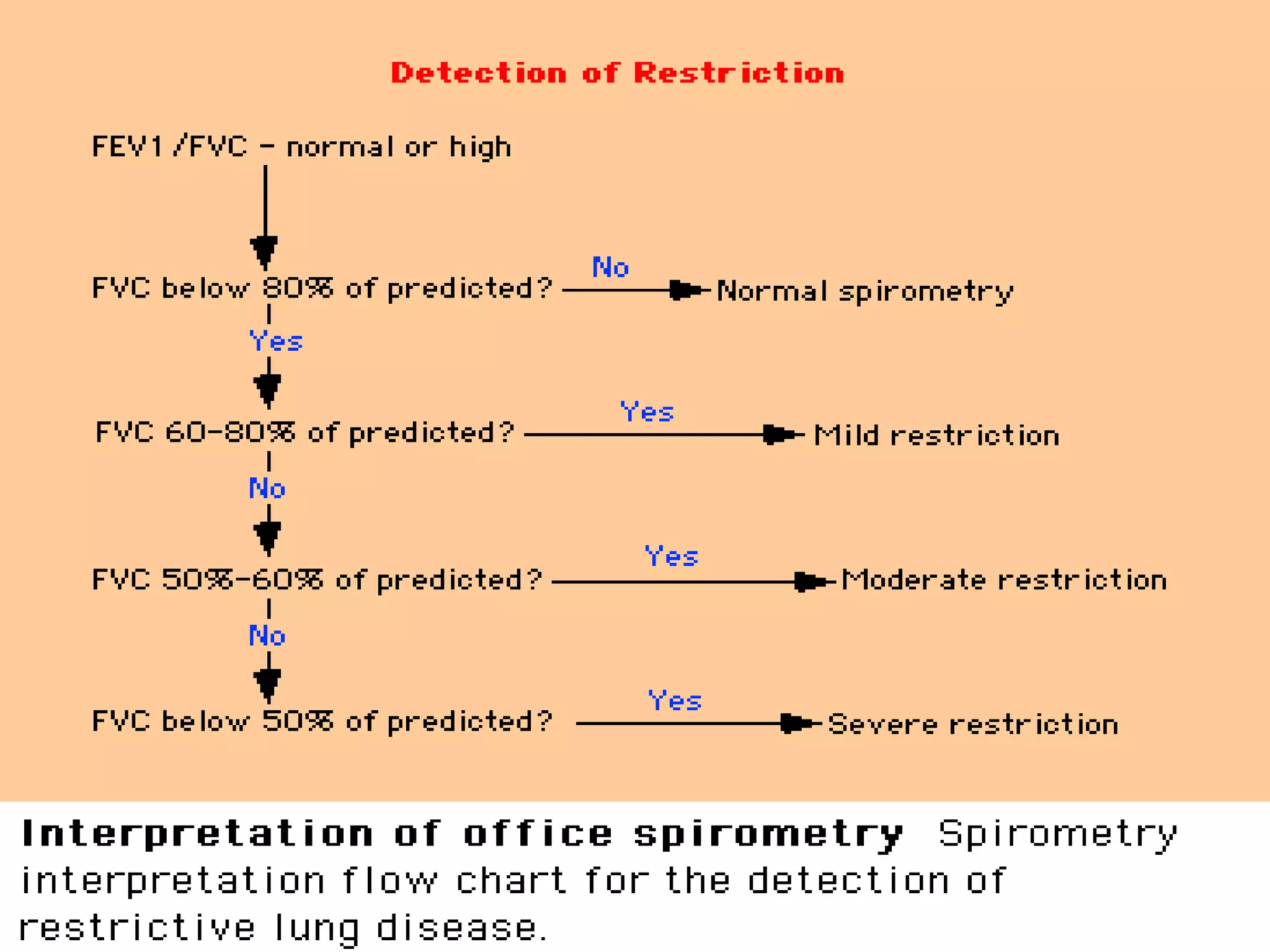
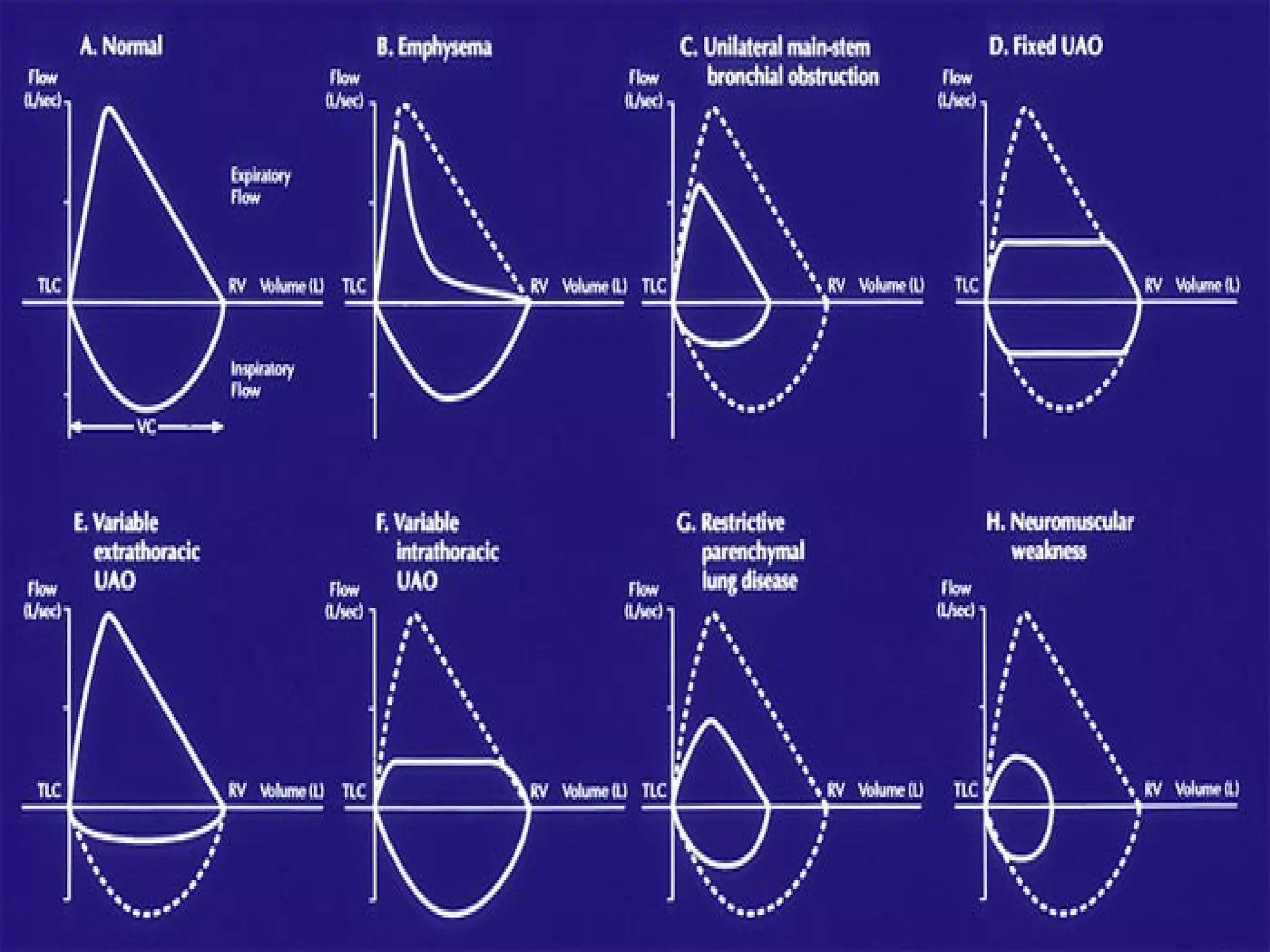
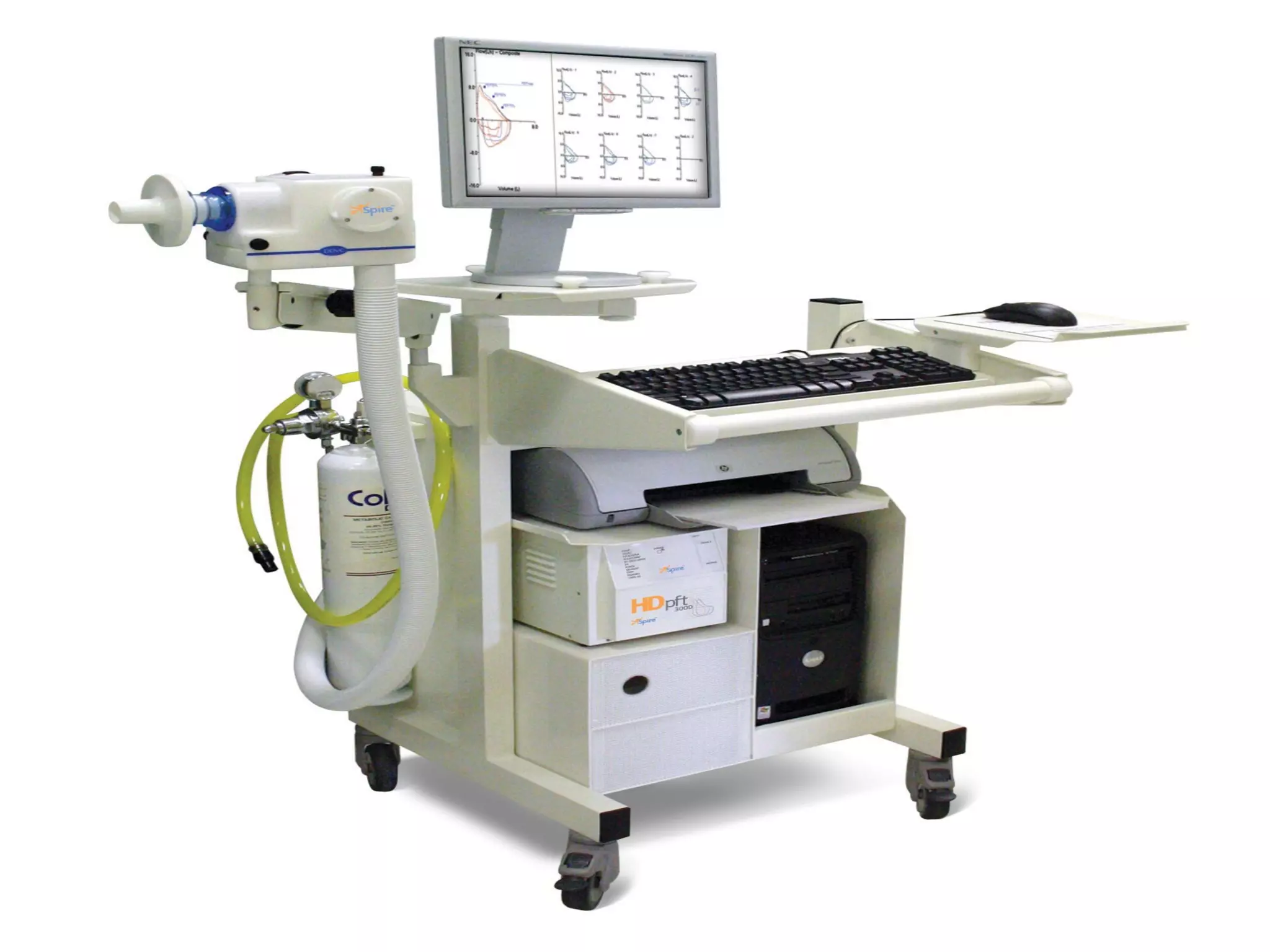
Pulmonary function tests (PFTs) measure how well the lungs work. There are several types of PFTs: spirometry measures airflow; lung volume measures how much air is in the lungs; and diffusion testing measures how well oxygen moves from the lungs into the bloodstream. PFTs can diagnose lung diseases like asthma, identify causes of shortness of breath, and assess treatment effectiveness. Abnormal PFT results usually mean the subject may have a lung disease if values are less than 80% of predicted normal levels based on factors like age, height and sex. PFT devices precisely measure things like airflow, gas volumes and pressures to evaluate lung function.