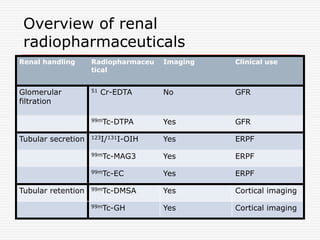
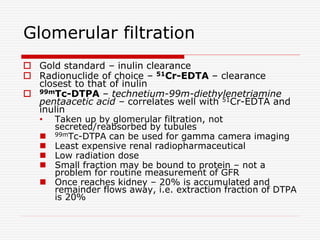
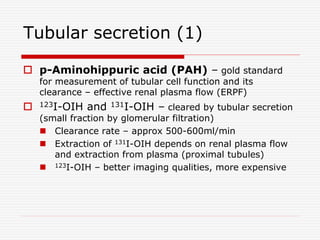
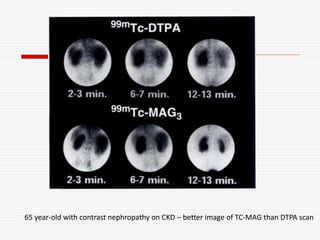
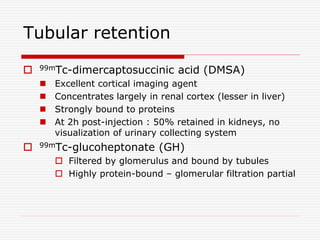
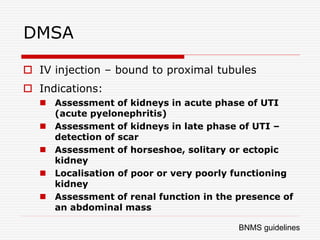
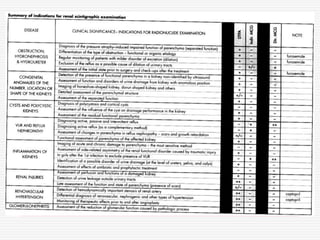
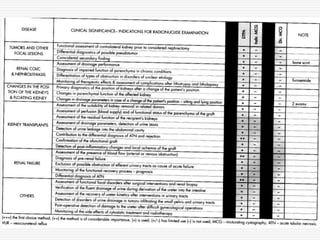
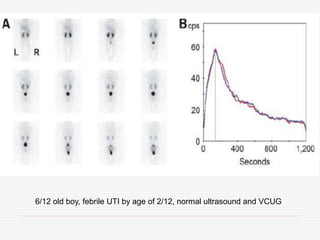
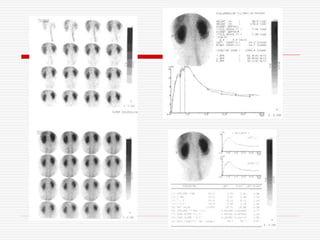
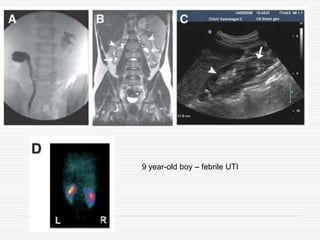
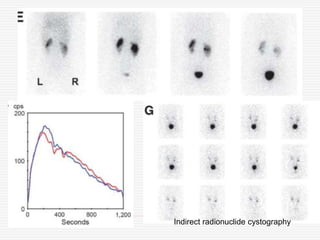
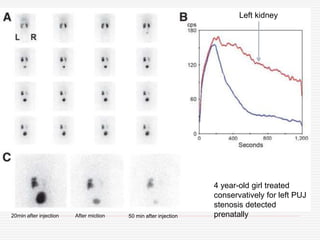
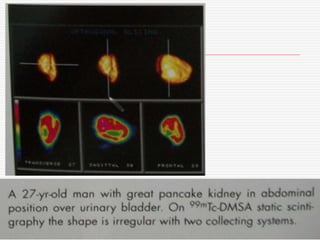
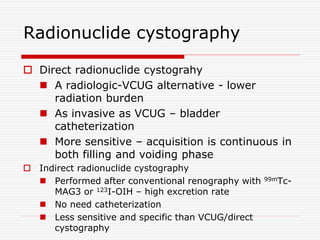
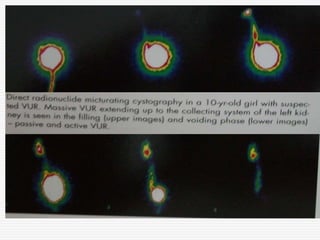
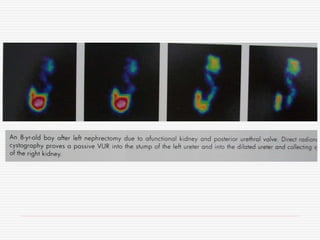
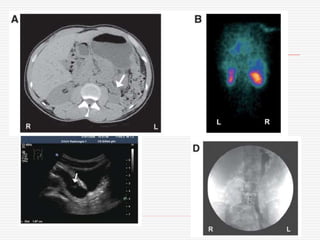
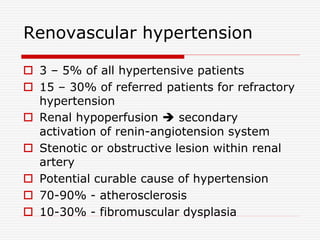
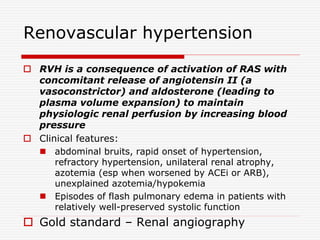
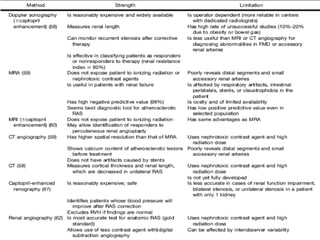
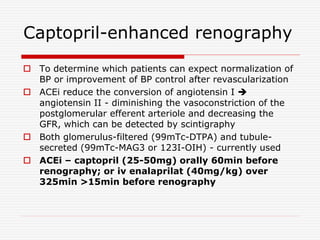
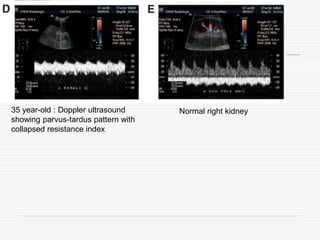
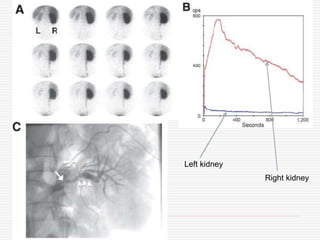
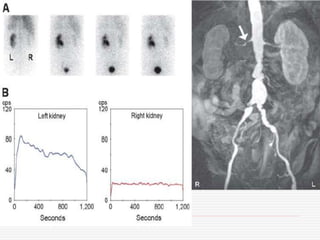
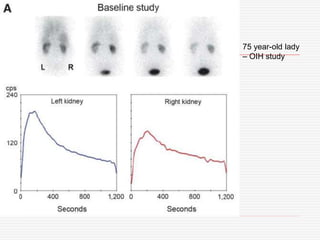
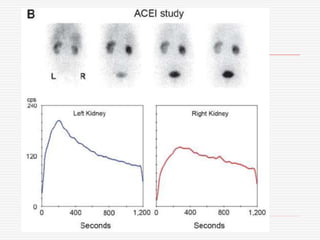
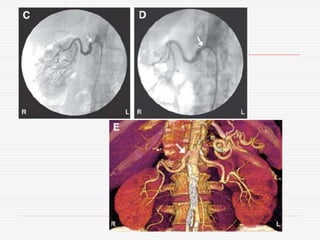
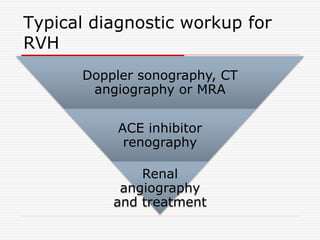
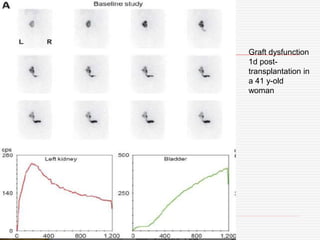
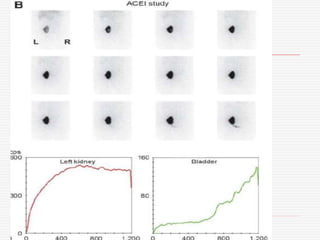
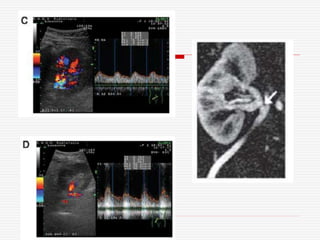
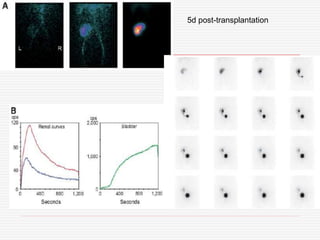
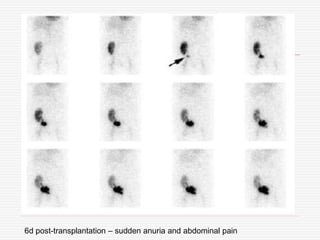
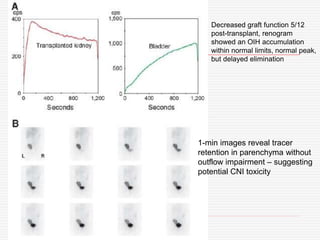
Nuclear imaging techniques can evaluate renal function and detect abnormalities. Radiotracers that are filtered, secreted, or retained by the kidneys provide information. Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and effective renal plasma flow (ERPF) are measured to assess kidney function. Obstructions are identified by delayed tracer excretion. Diuretic renography distinguishes dilated but unobstructed systems from true stenoses. Techniques require specialized cameras but provide functional details and separate evaluation of each kidney without invasive procedures.