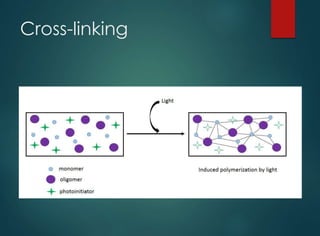
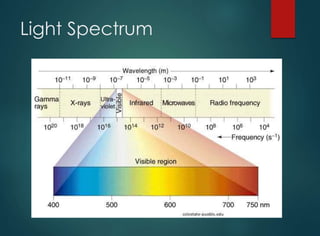
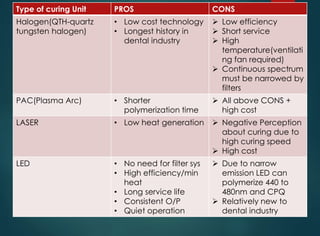
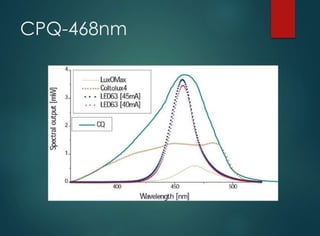
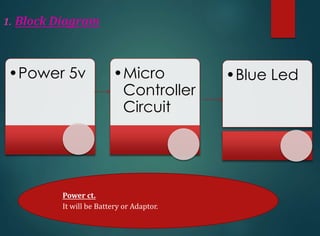
The document discusses dental curing lights, focusing on their application, working principles, and various technologies such as halogen and LED. It highlights the importance of matching the light wavelength to the photo initiator for effective polymerization of dental materials and addresses common misconceptions about curing lights. Additionally, it explores market challenges and the benefits of using blue LED technology in terms of efficiency, size, and comfort.