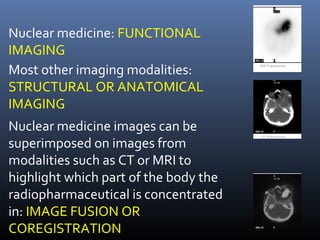
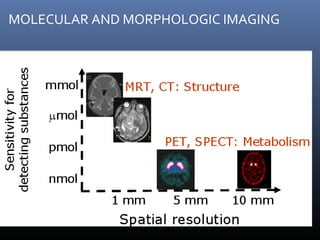
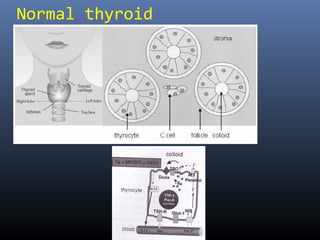
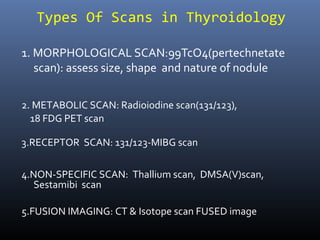
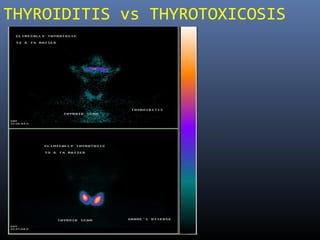
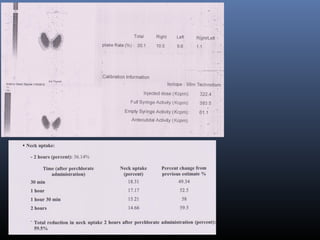
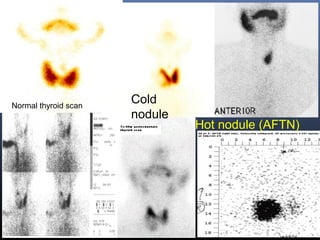
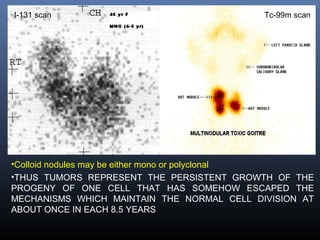
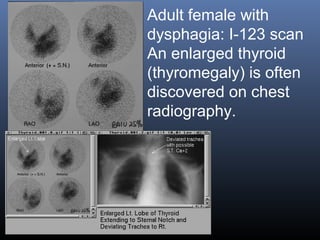
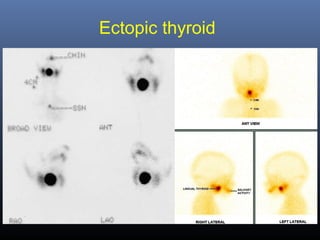
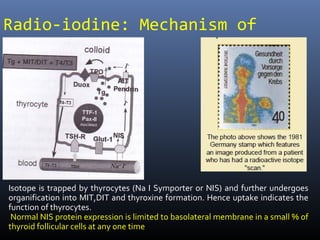
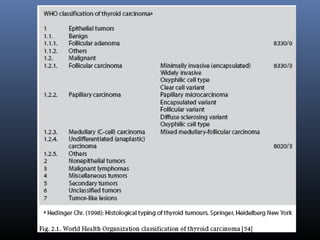
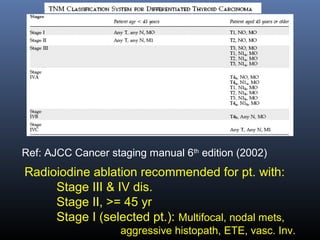
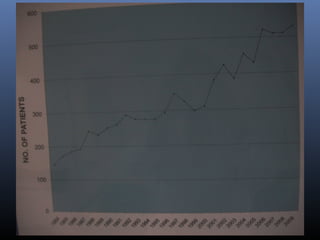
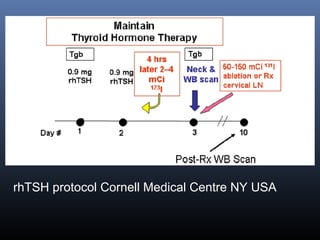
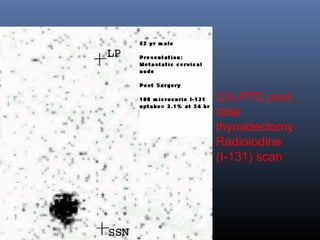
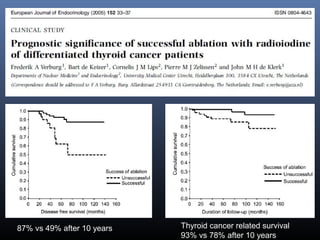
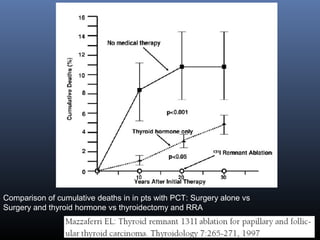
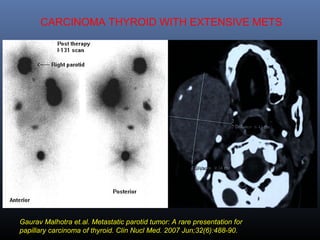
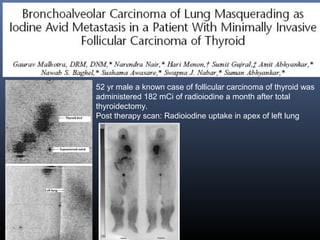
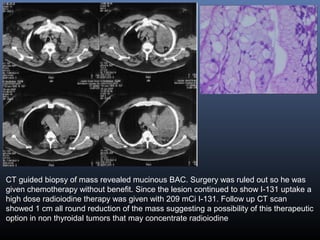
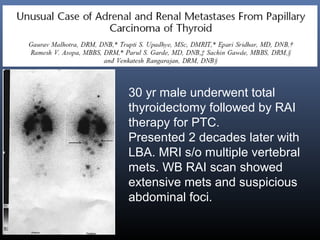
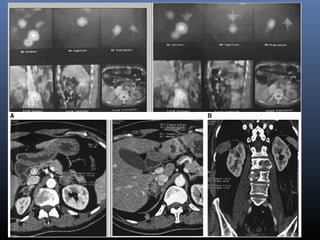
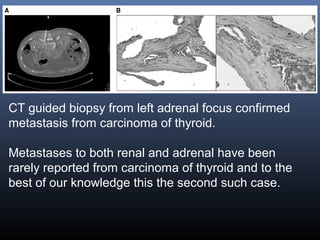
Nuclear medicine techniques such as radioactive iodine scans and therapy are important in evaluating and treating thyroid diseases. Radioactive iodine is selectively taken up and concentrated in the thyroid gland, allowing functional imaging and selective internal radiotherapy for hyperthyroidism and thyroid cancer. Radioactive iodine therapy is the primary treatment for Graves' disease and toxic multinodular goiter. It is also used to ablate residual thyroid tissue after surgery and treat thyroid cancer metastases. Precautions must be taken after radioactive iodine therapy to limit radiation exposure to others.