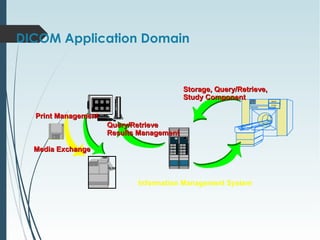
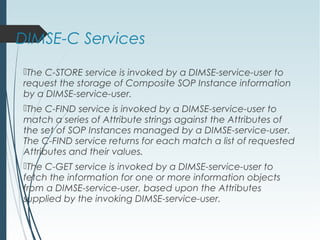
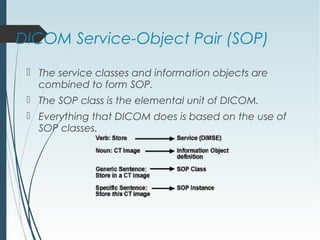
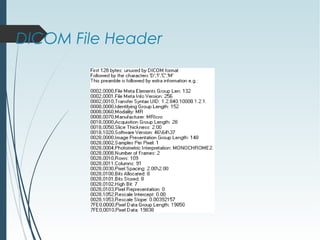
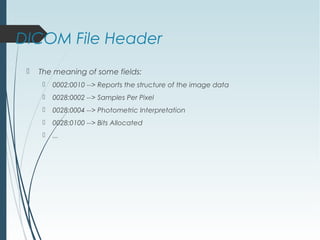
DICOM is a standard for digital imaging and communications in medicine. It was developed by NEMA and ACR to enable sharing of medical images and associated data between devices. DICOM defines formats for images, communication protocols, and a data model for medical imaging applications. It allows for storage, printing, distribution, and analysis of medical images through different systems.