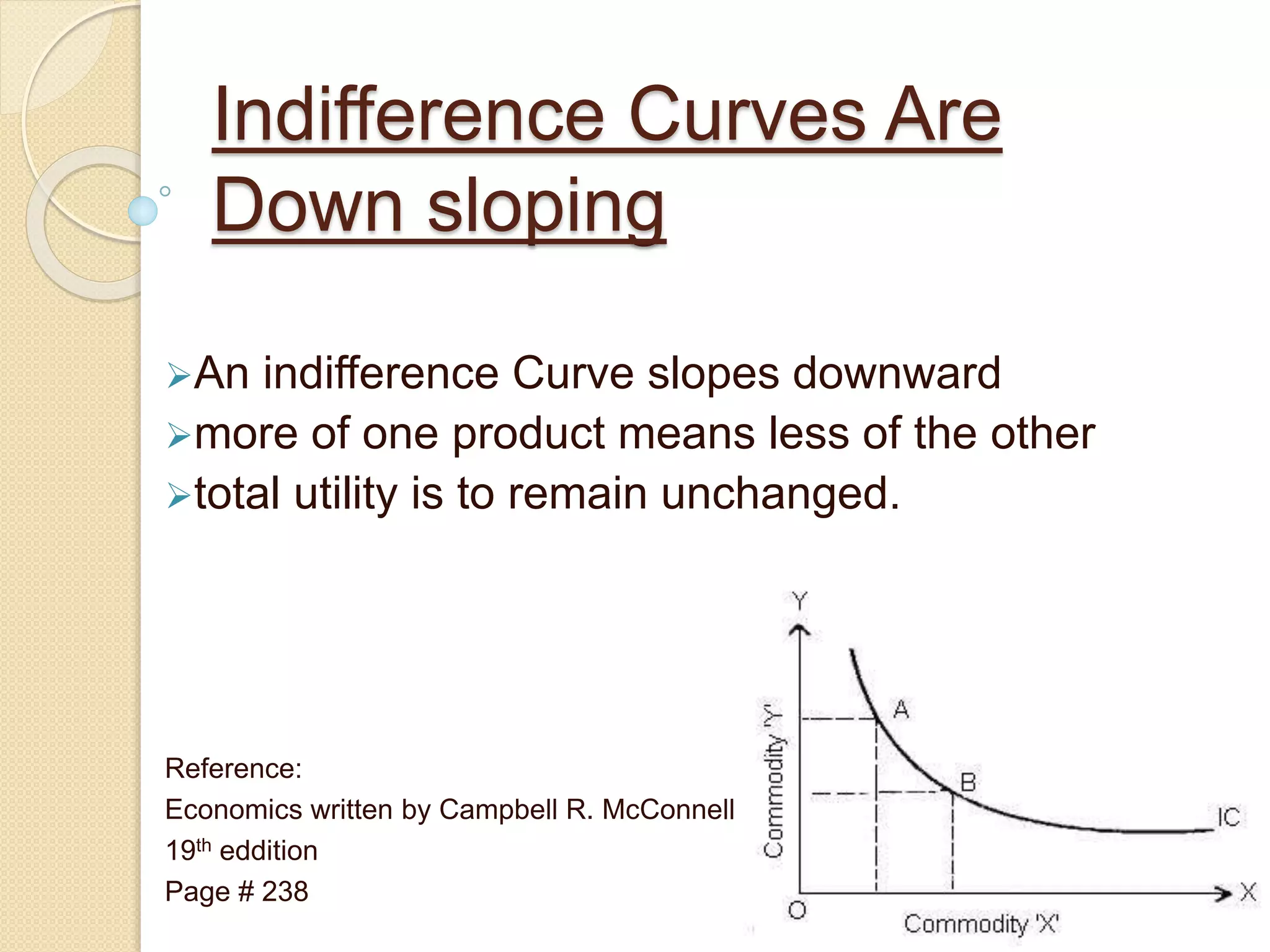
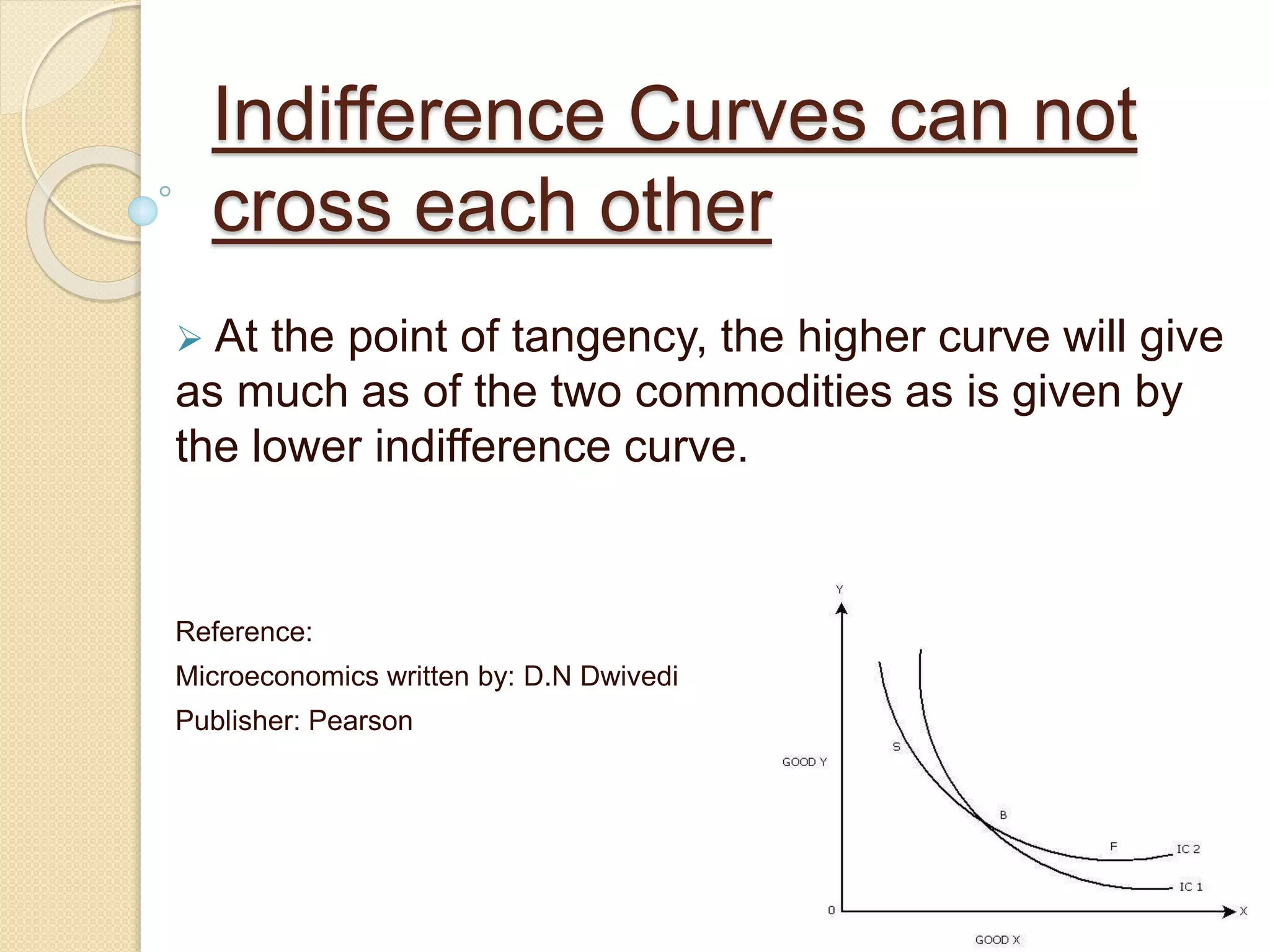
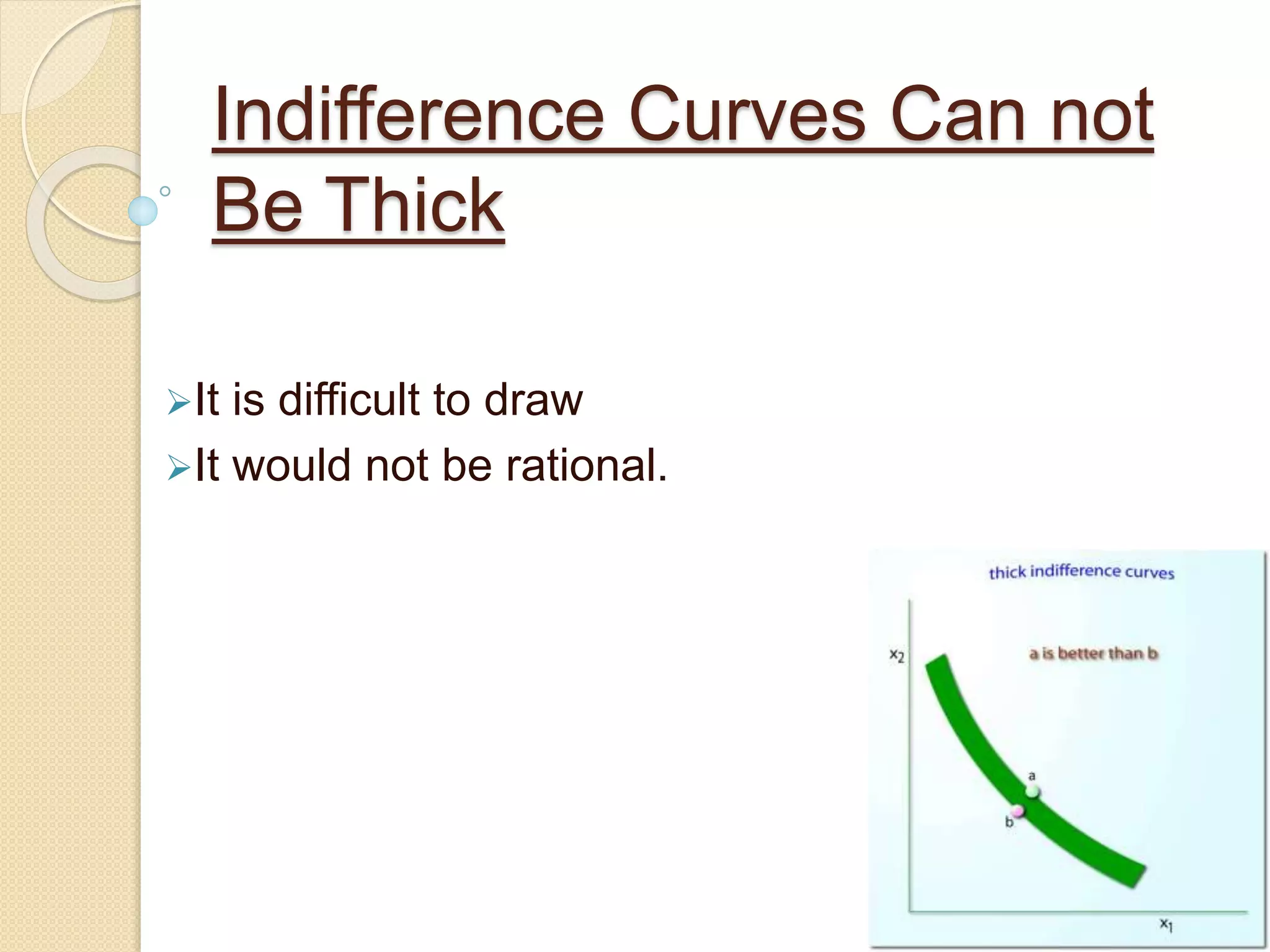
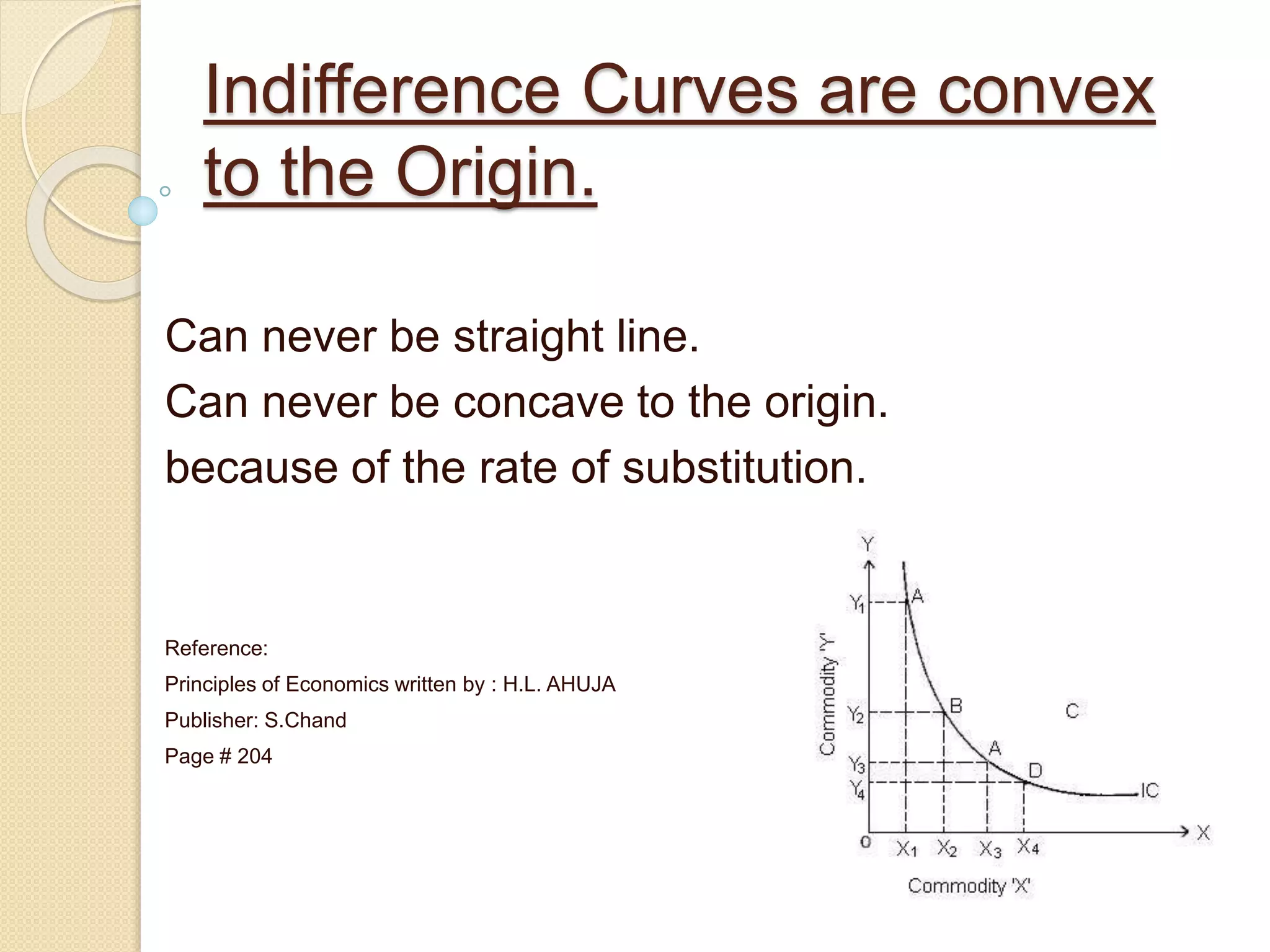
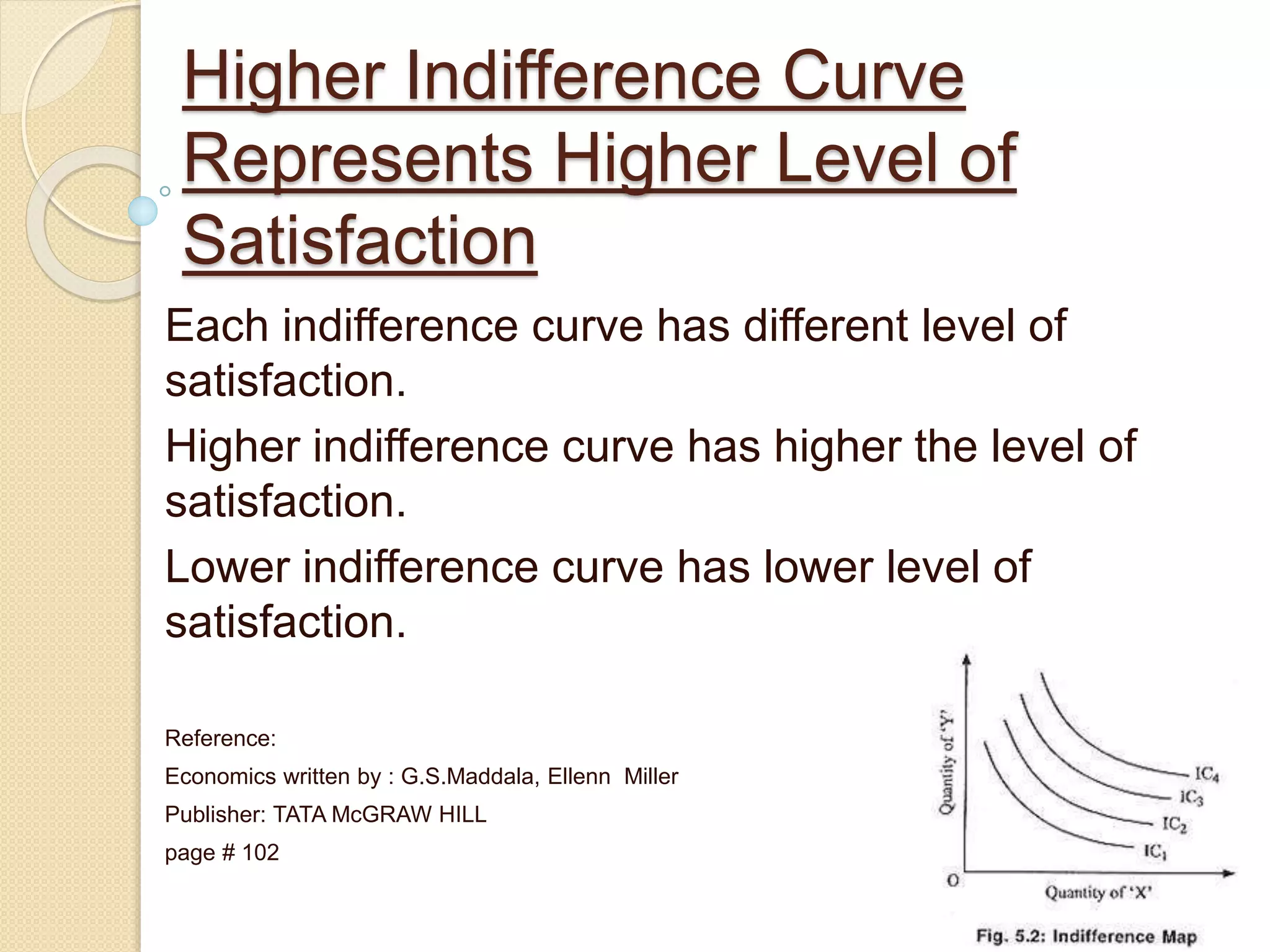
An indifference curve represents combinations of two goods that provide the same level of satisfaction to a consumer. Indifference curves have several key properties:
1) They slope downward, meaning more of one good requires less of the other to maintain the same satisfaction level.
2) They cannot cross, as a higher curve always provides at least as much satisfaction as a lower curve.
3) They are convex to the origin, never being a straight line or concave shape, due to the rate of substitution between goods.
4) Higher curves represent greater satisfaction levels than lower curves.