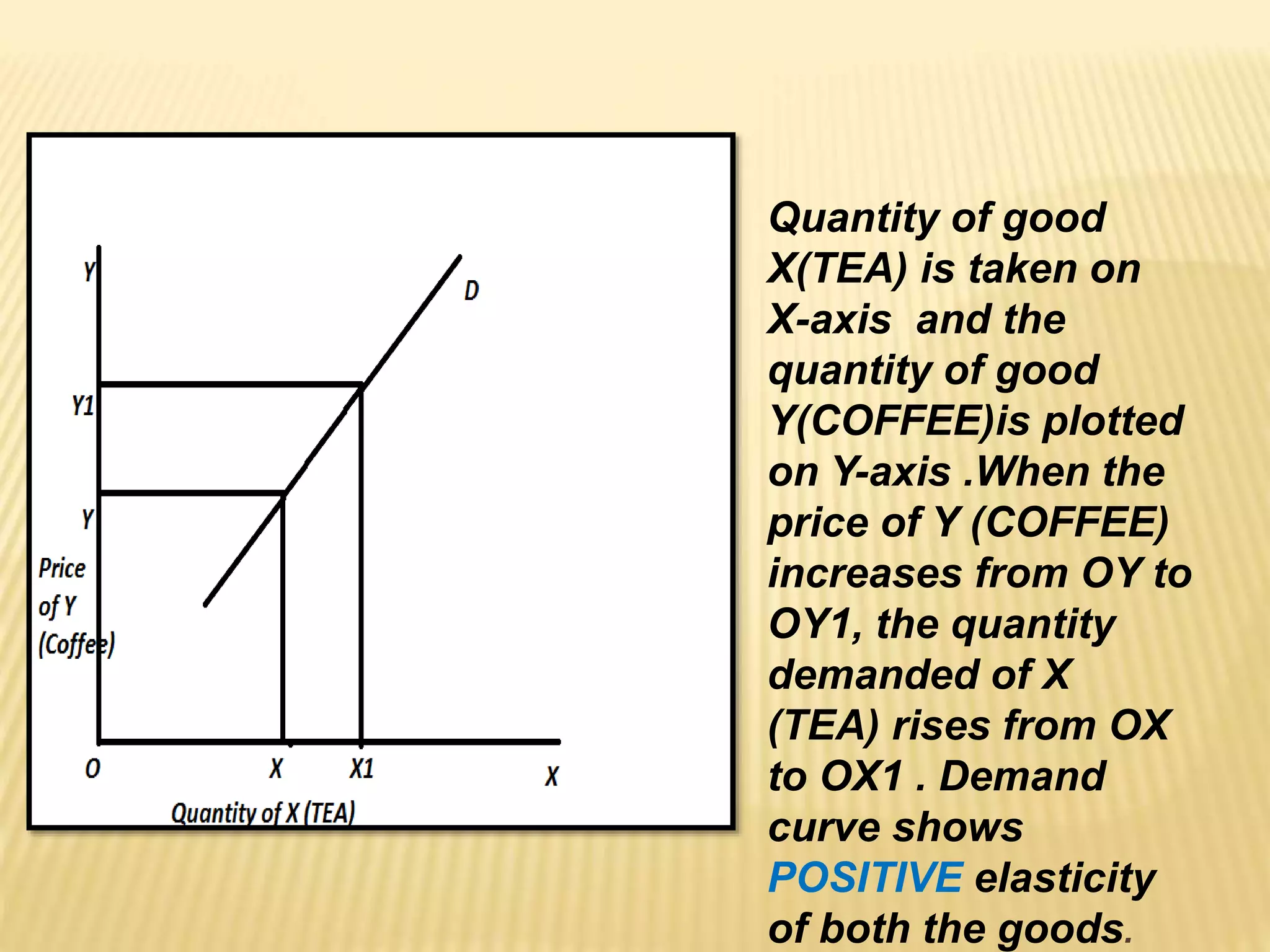
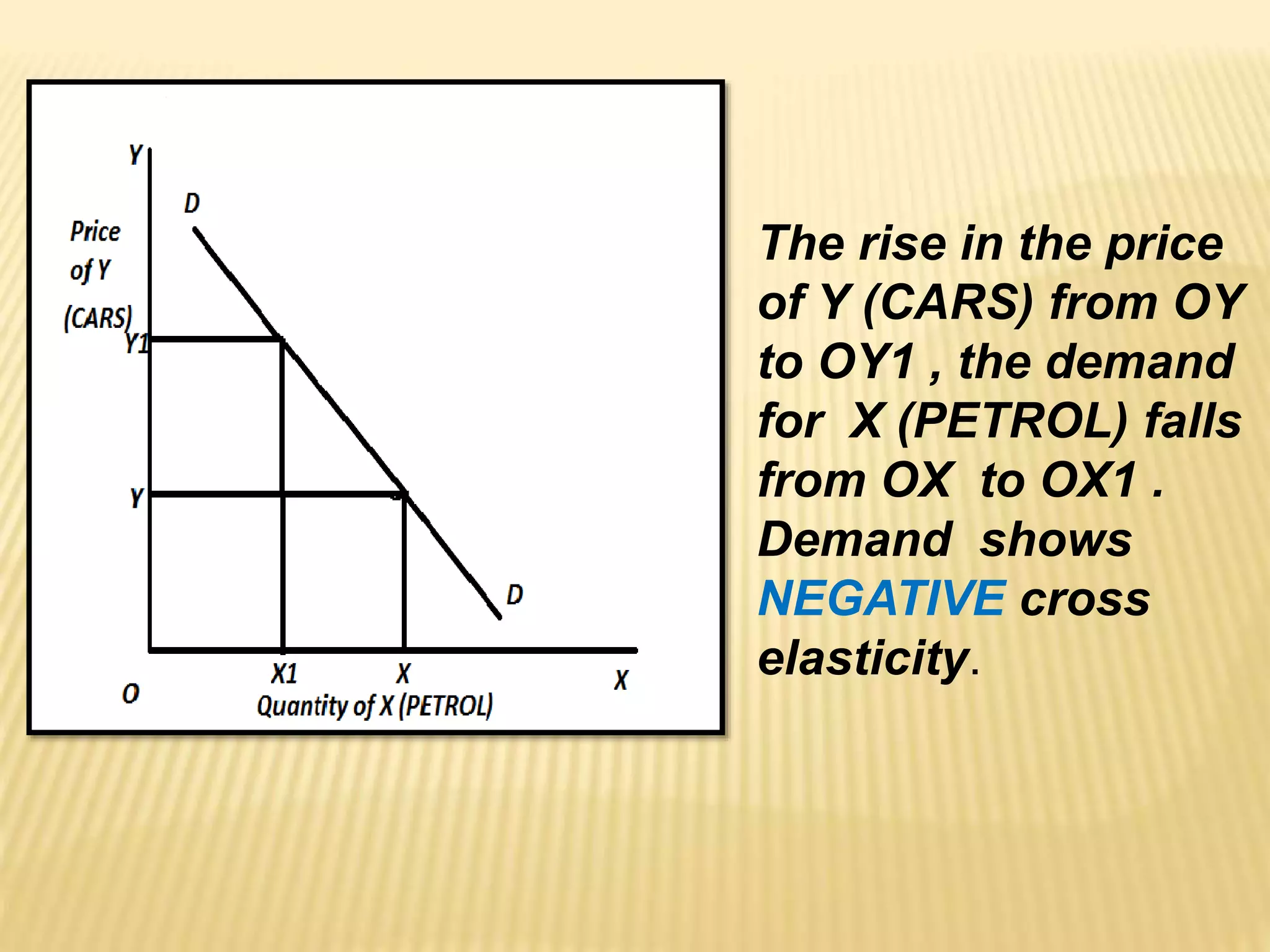
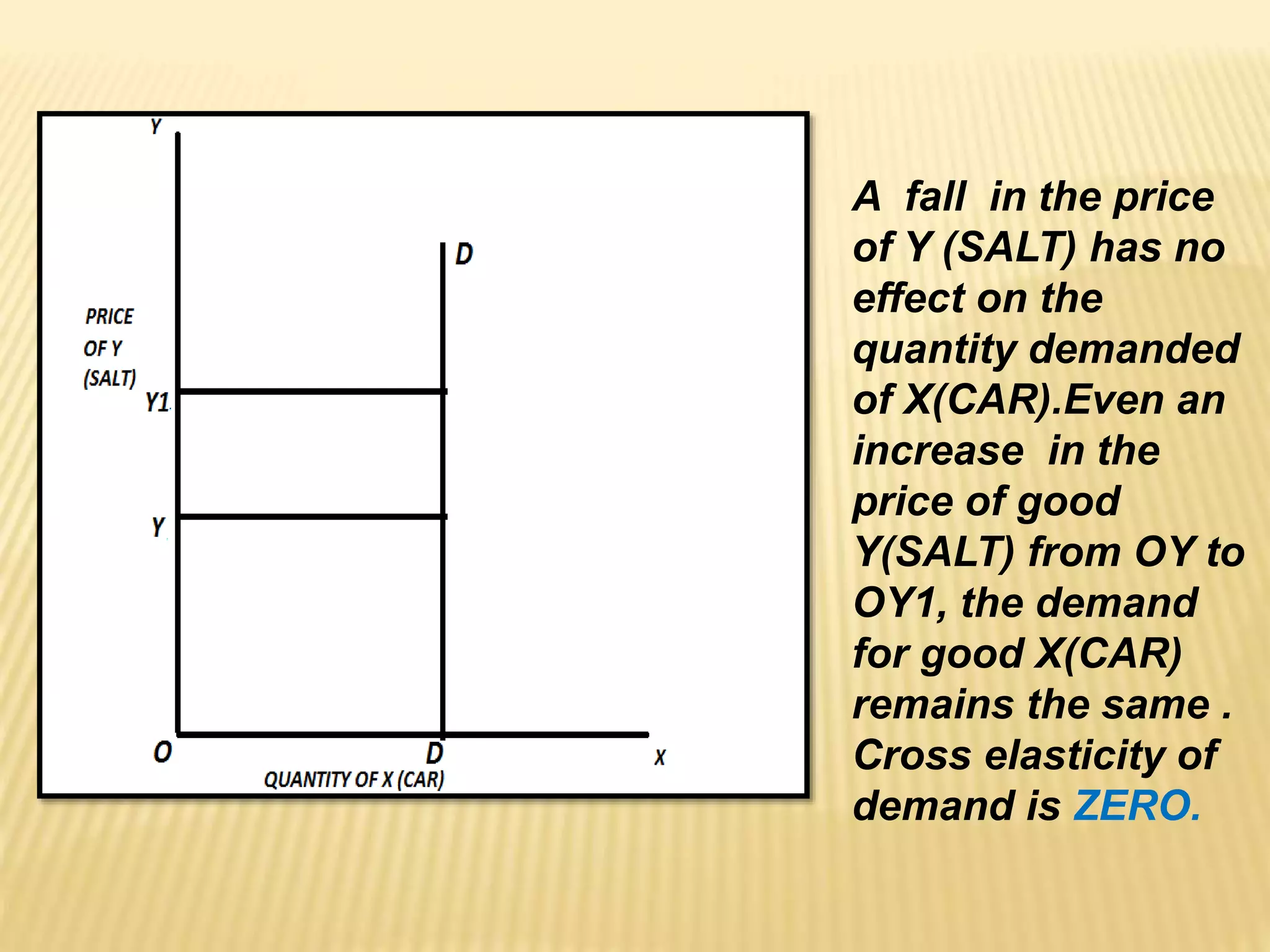
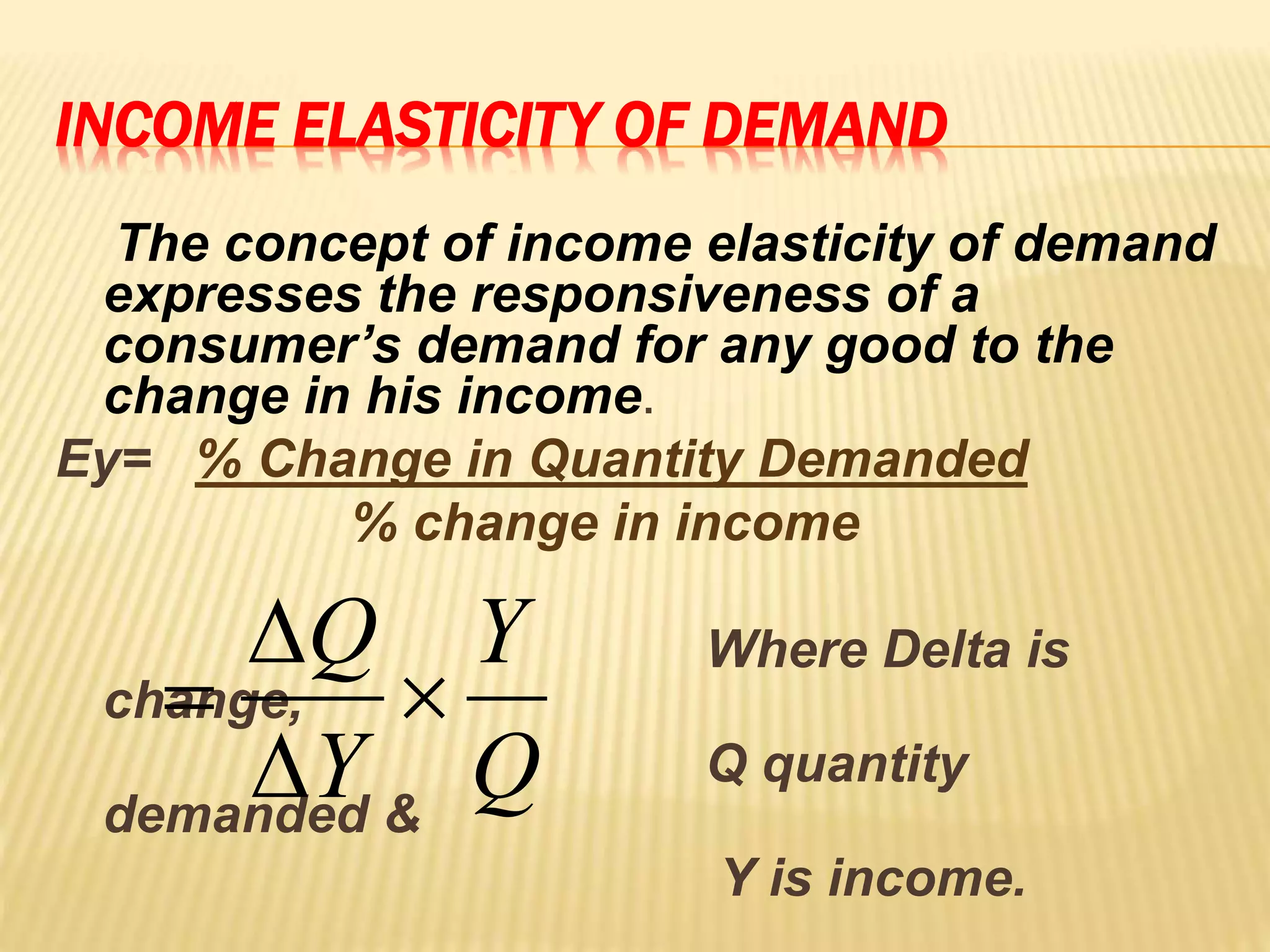
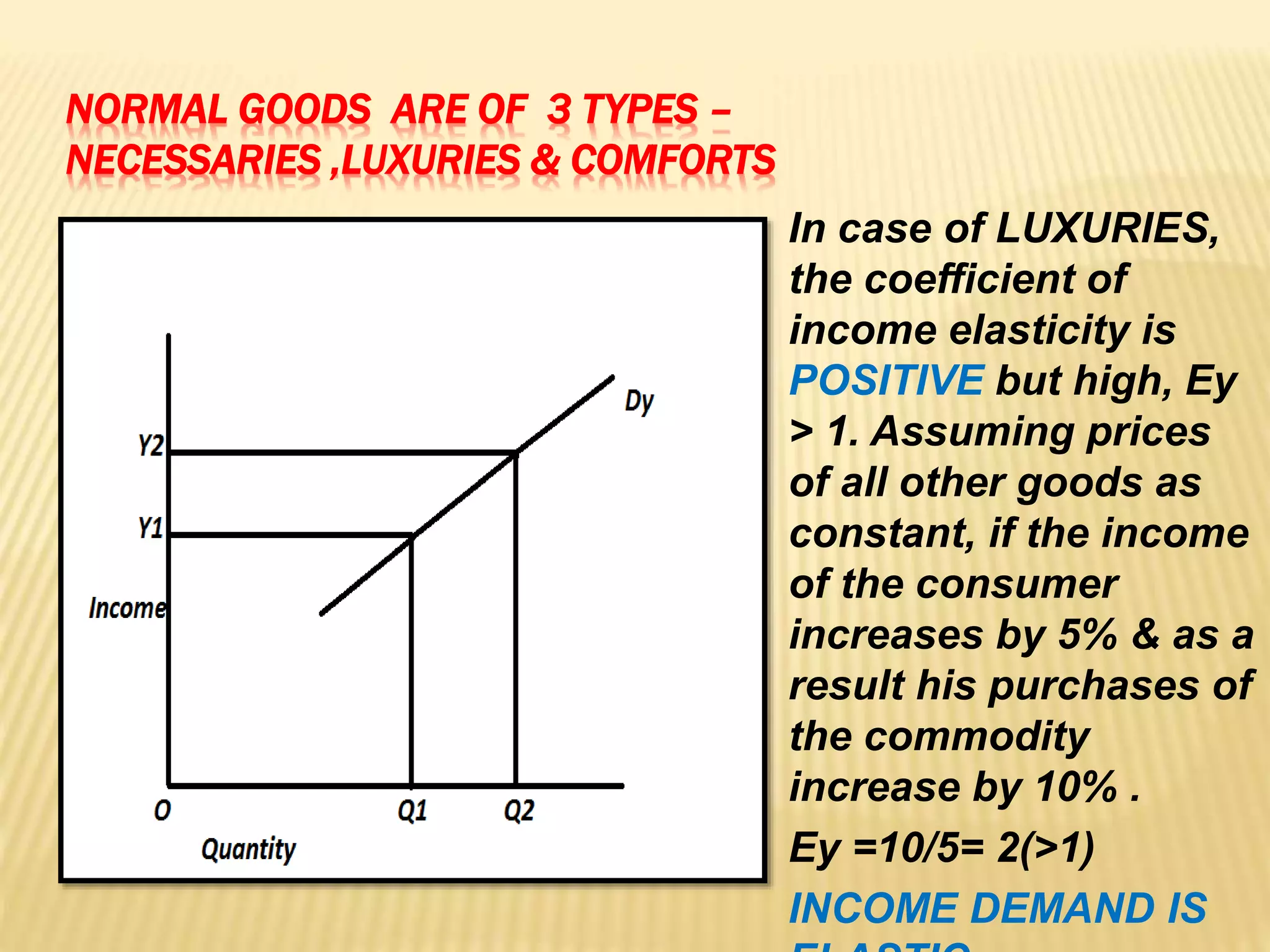
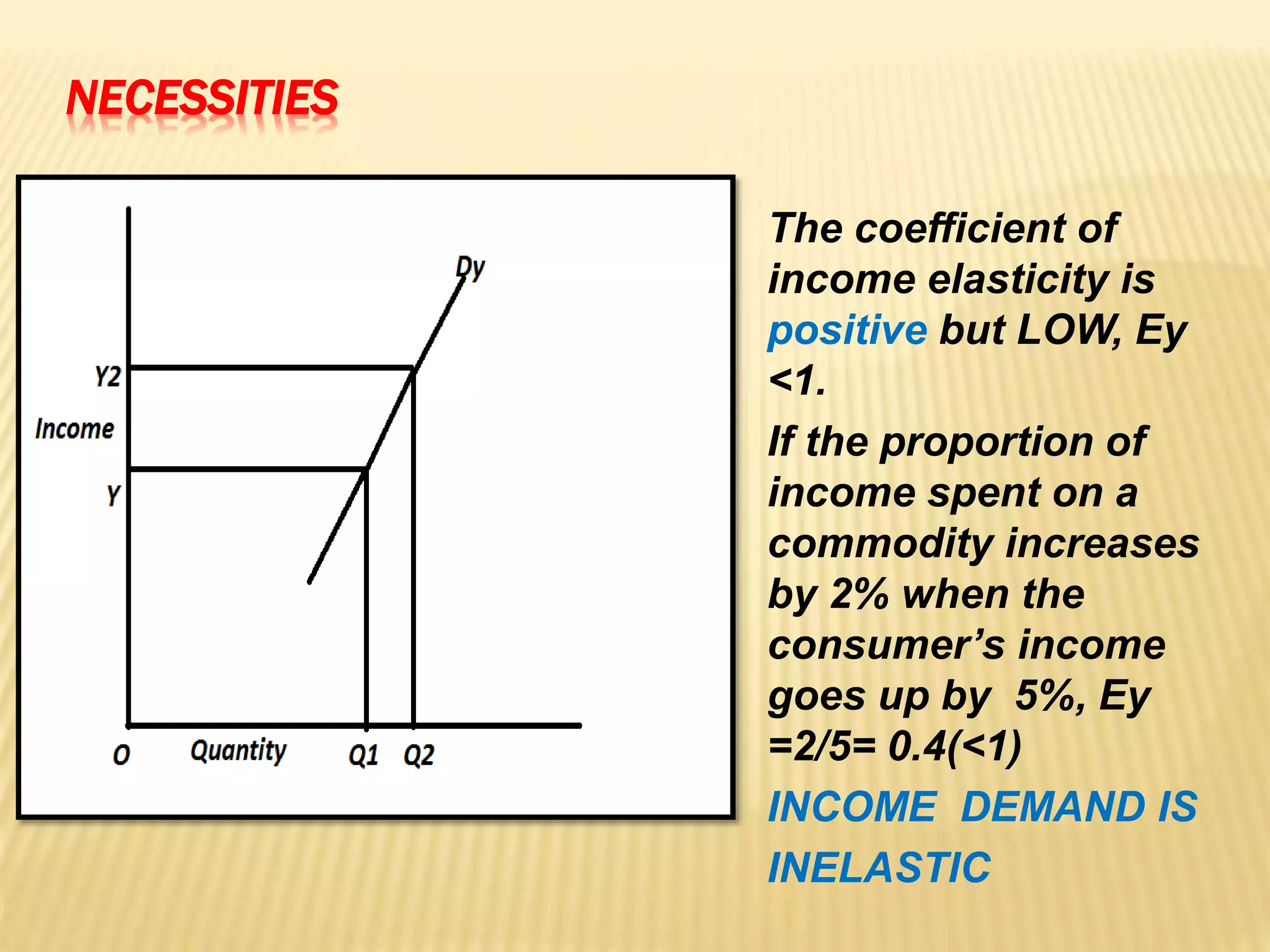
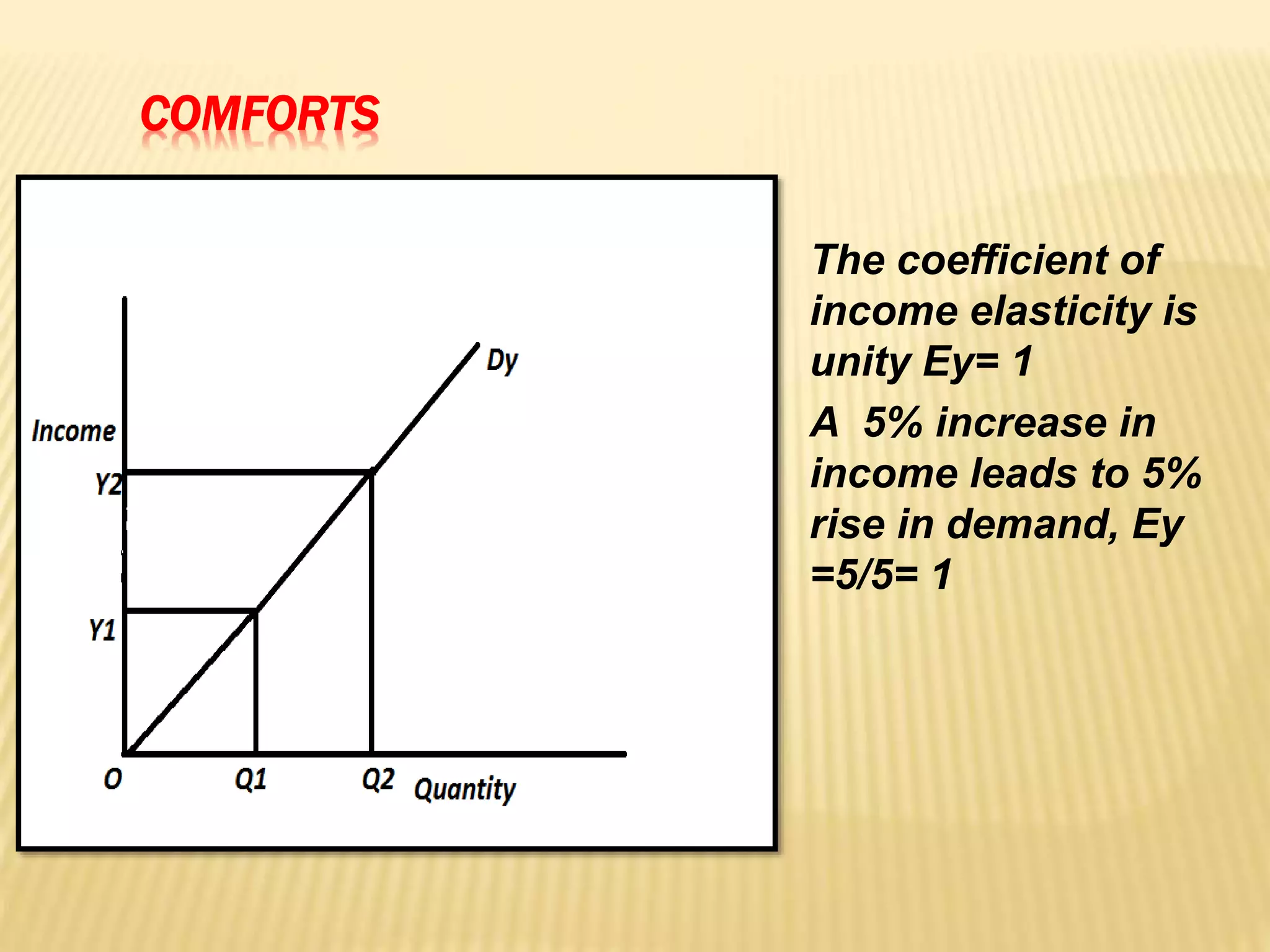
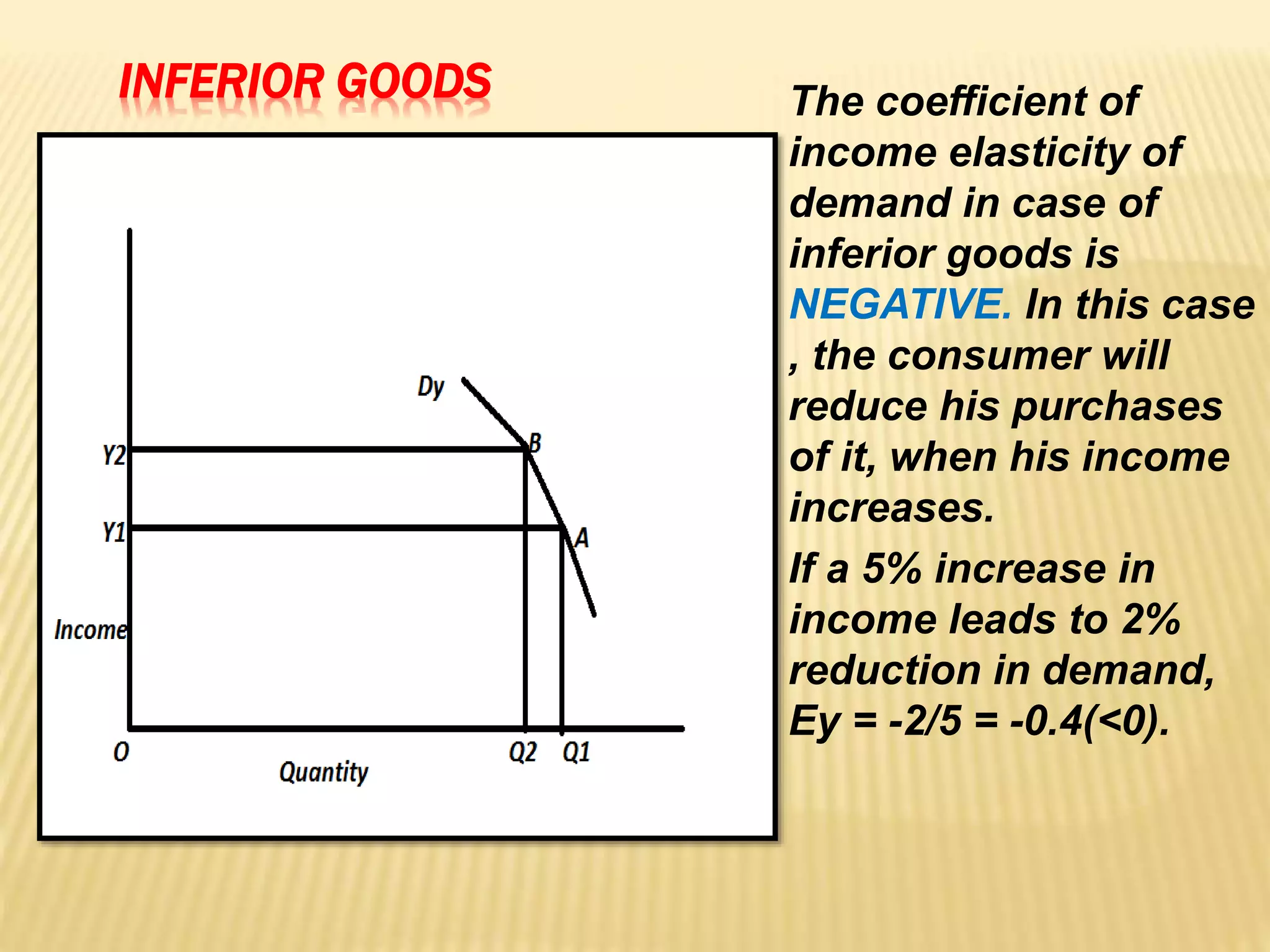
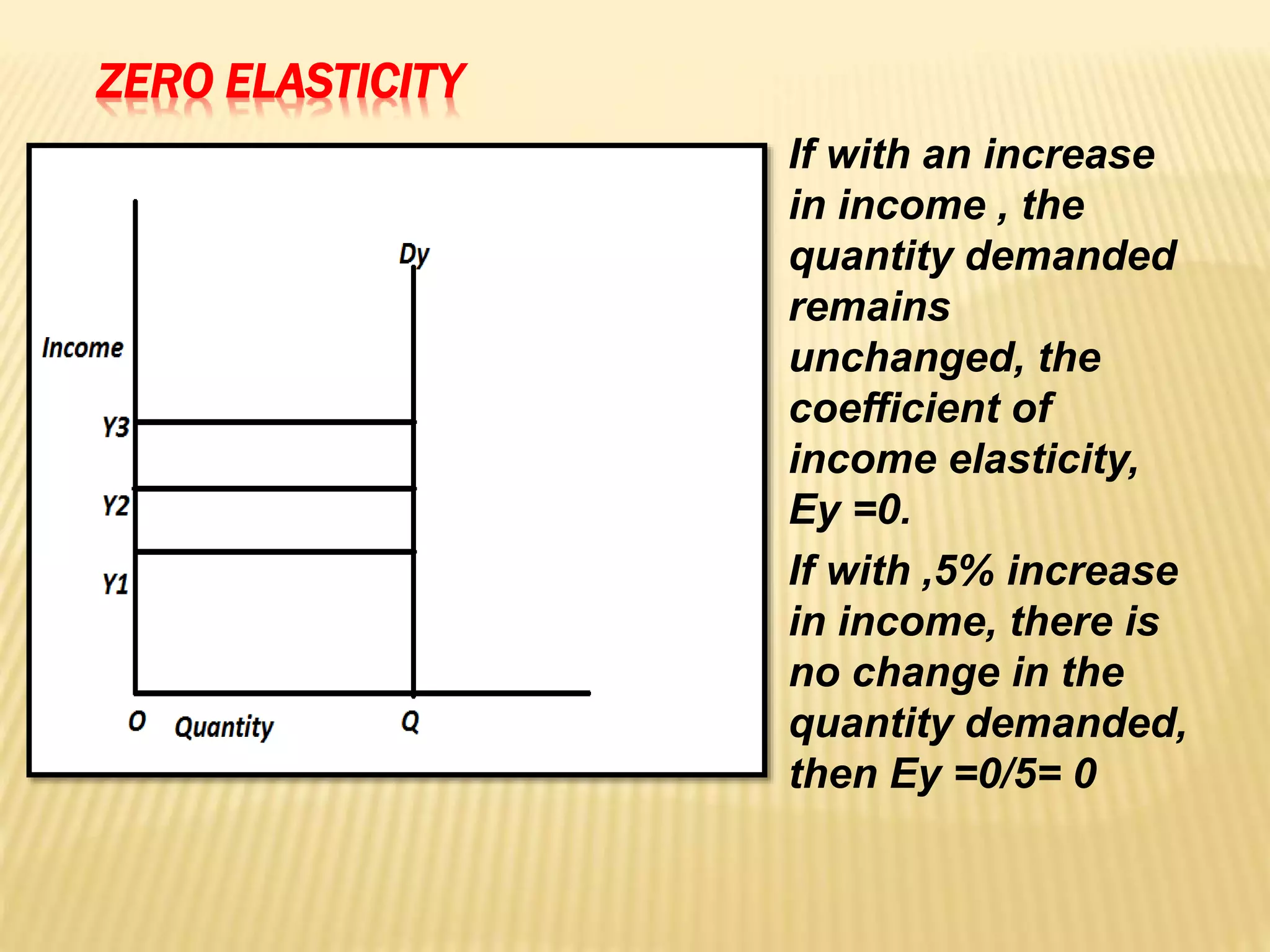
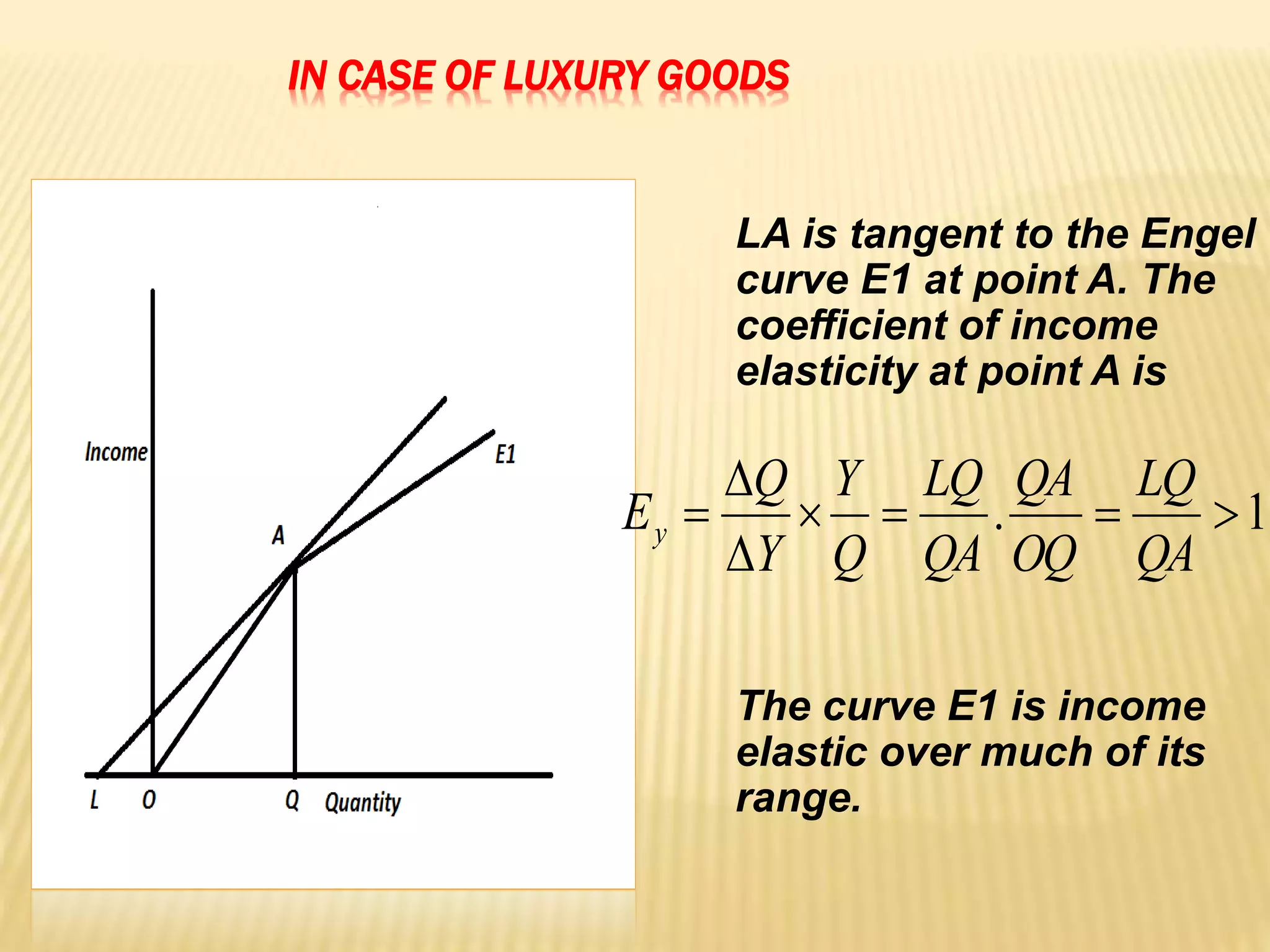
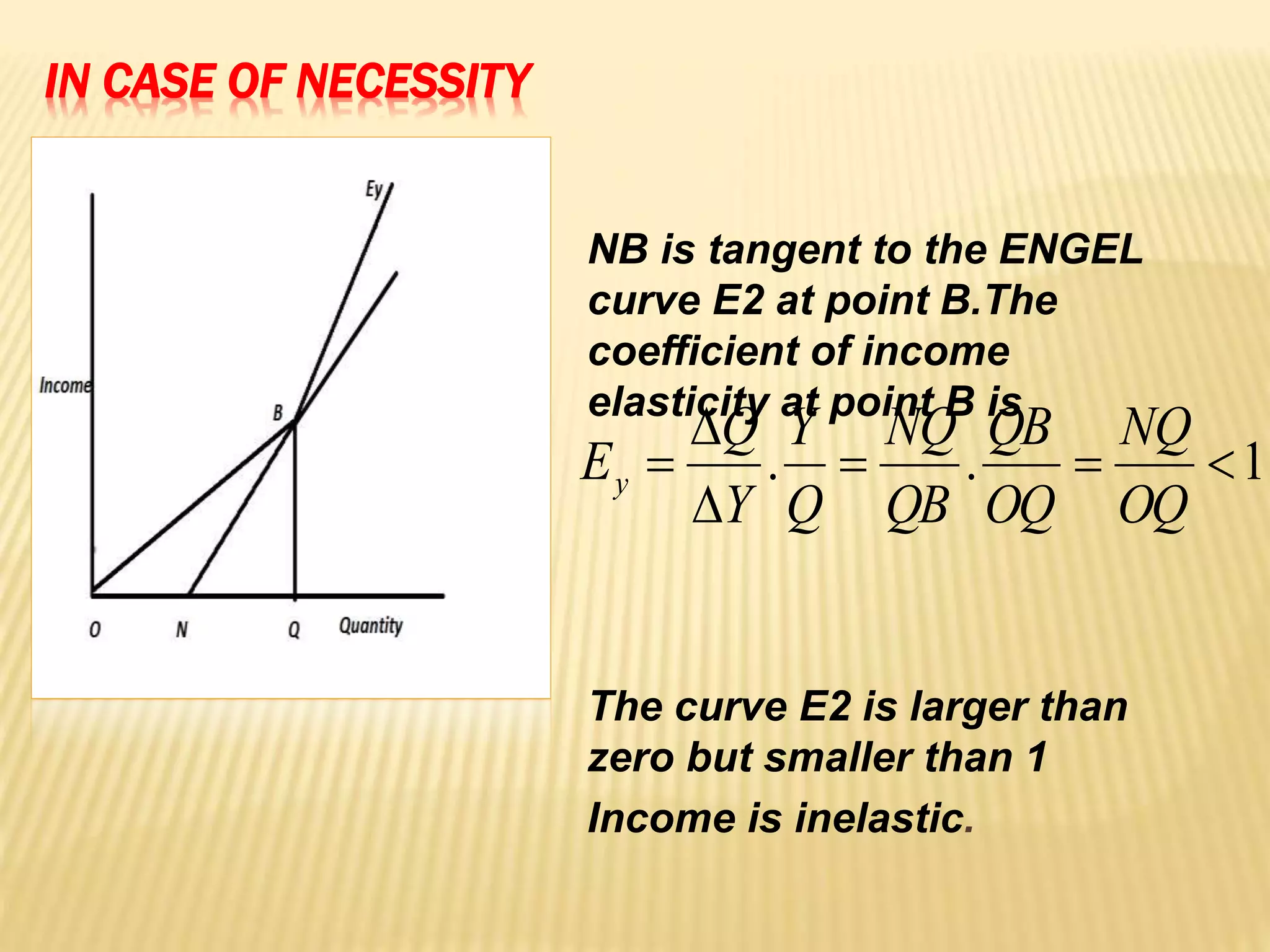
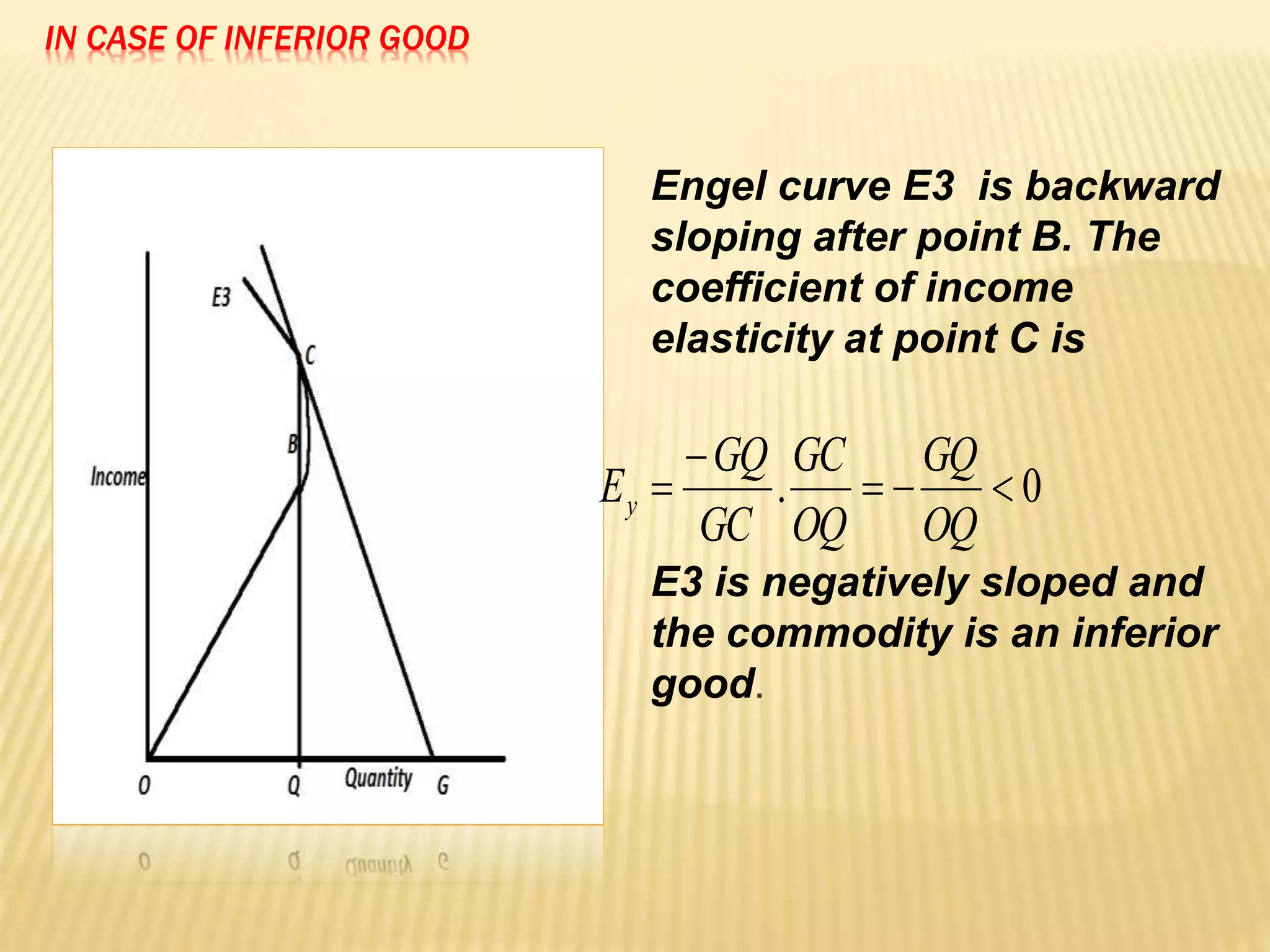
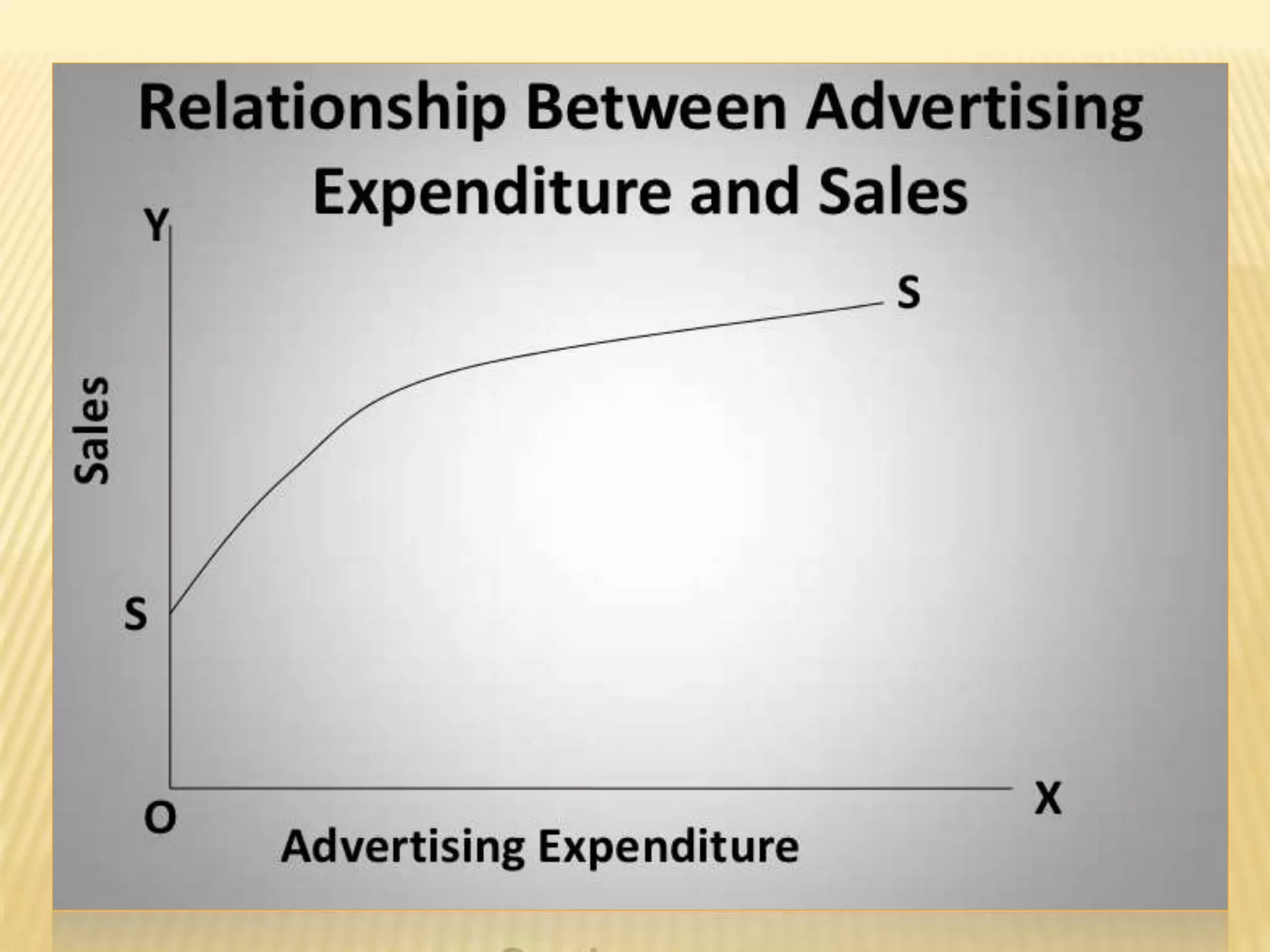
The document discusses four types of elasticity of demand: price elasticity, cross elasticity, income elasticity, and advertising elasticity. It provides details on cross elasticity, explaining that it measures the responsiveness of the quantity demanded of a good to a change in the price of a related good. Cross elasticity can be positive, negative, or zero depending on whether the goods are substitutes, complements, or unrelated. Income elasticity measures the responsiveness of demand for a good to a change in consumer income. It too can be positive, negative, or zero, depending on whether the good is normal, inferior, or if demand is unchanged by income changes. Advertising elasticity measures the responsiveness of demand