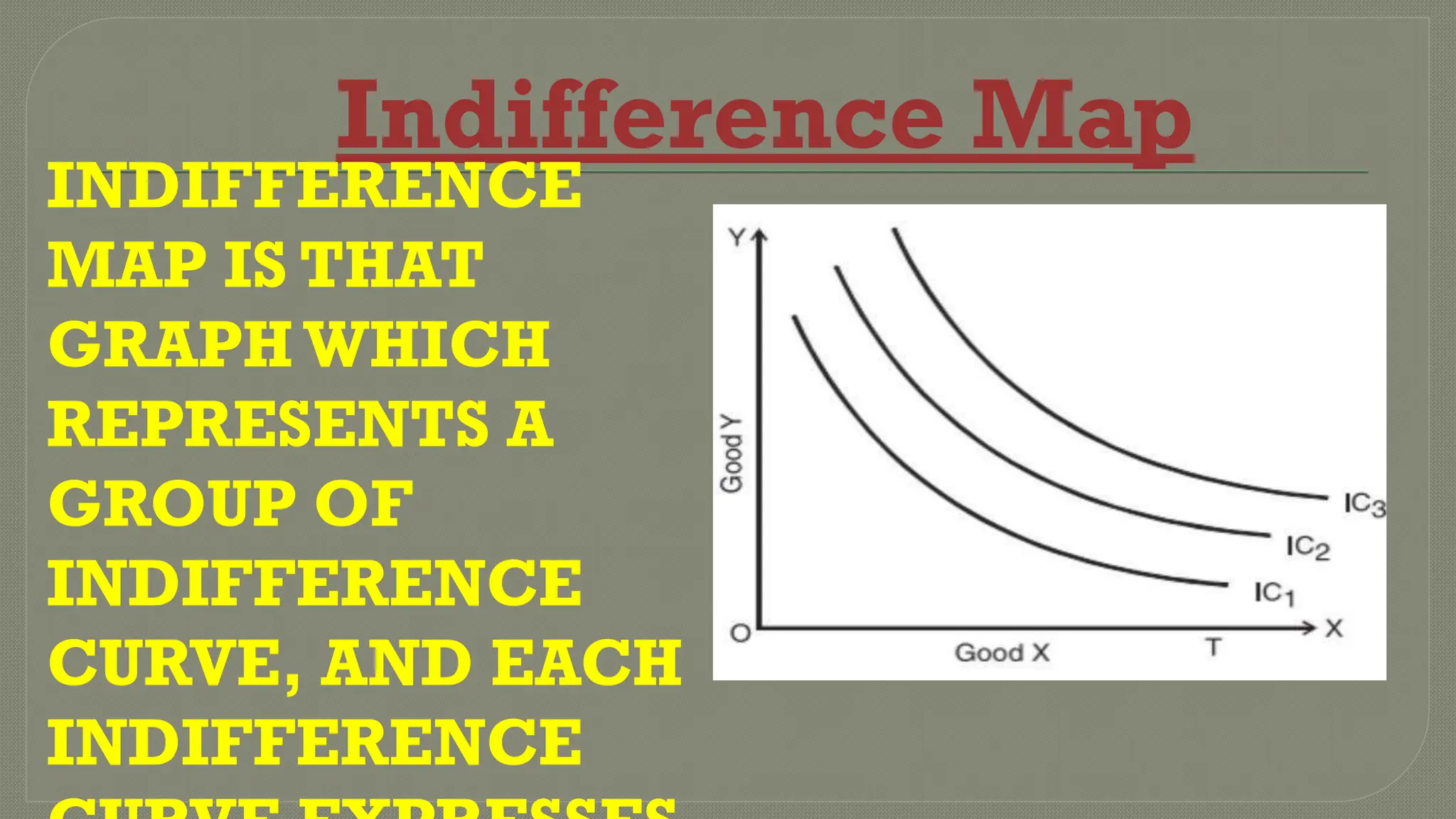
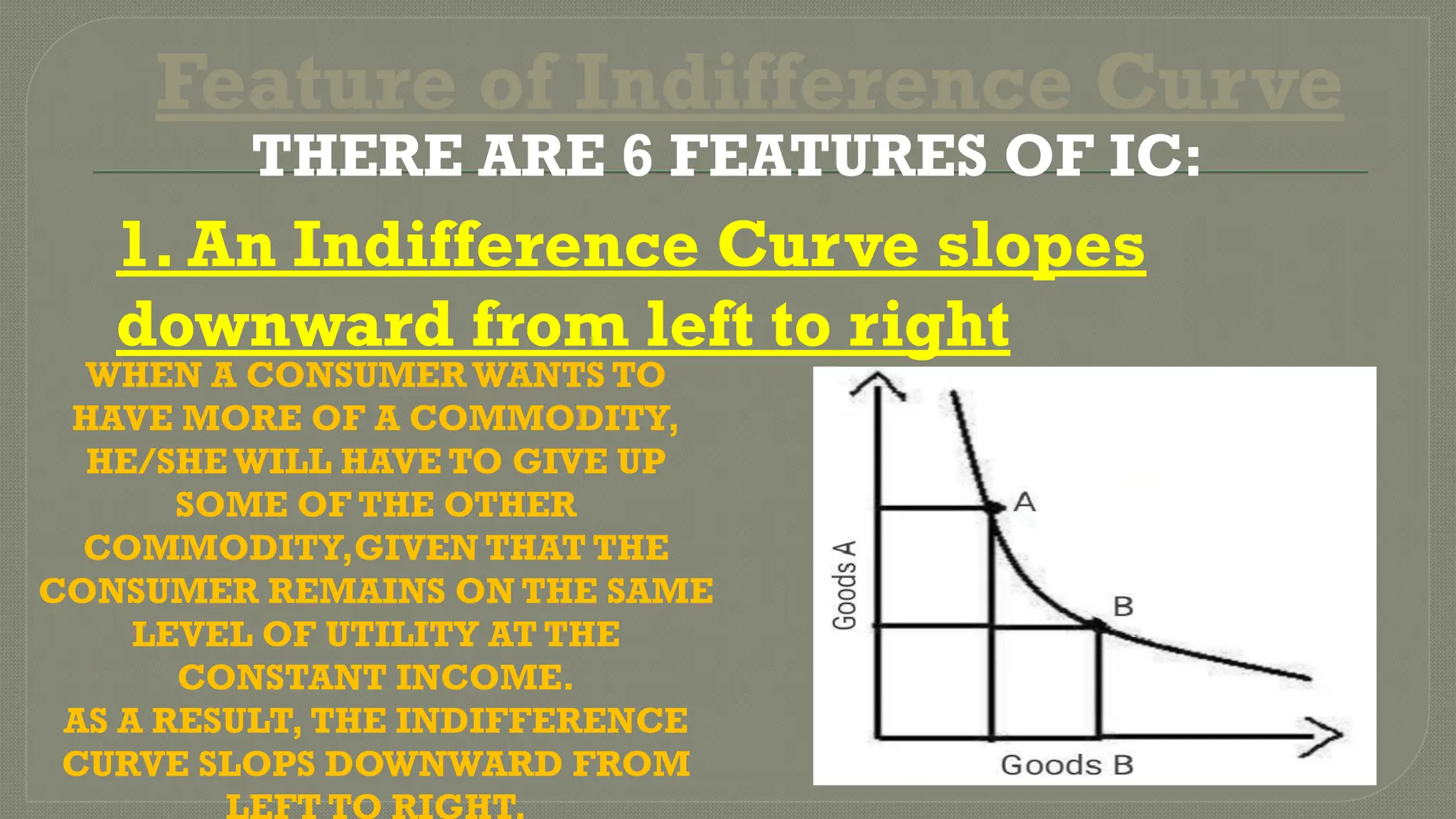
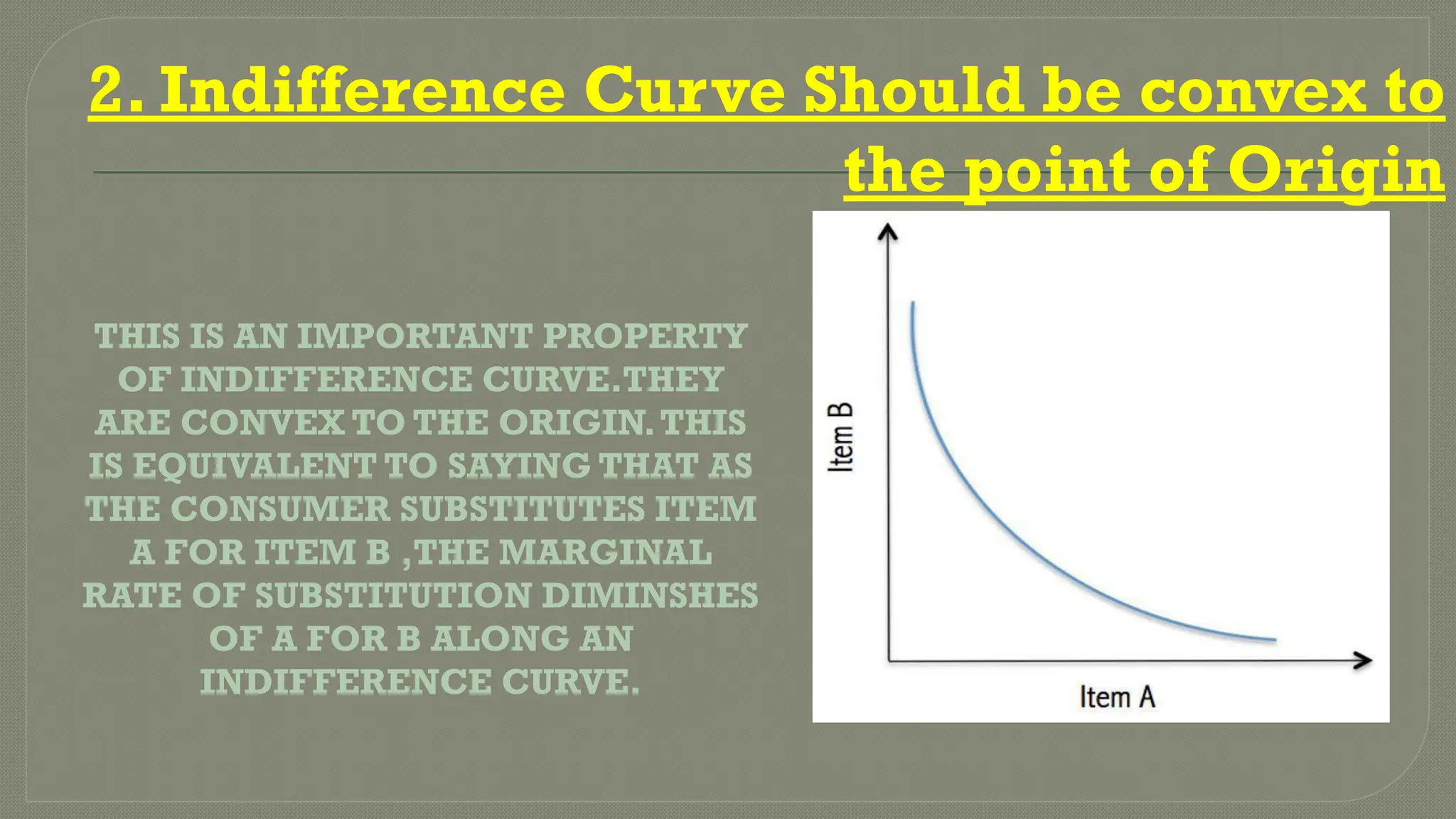
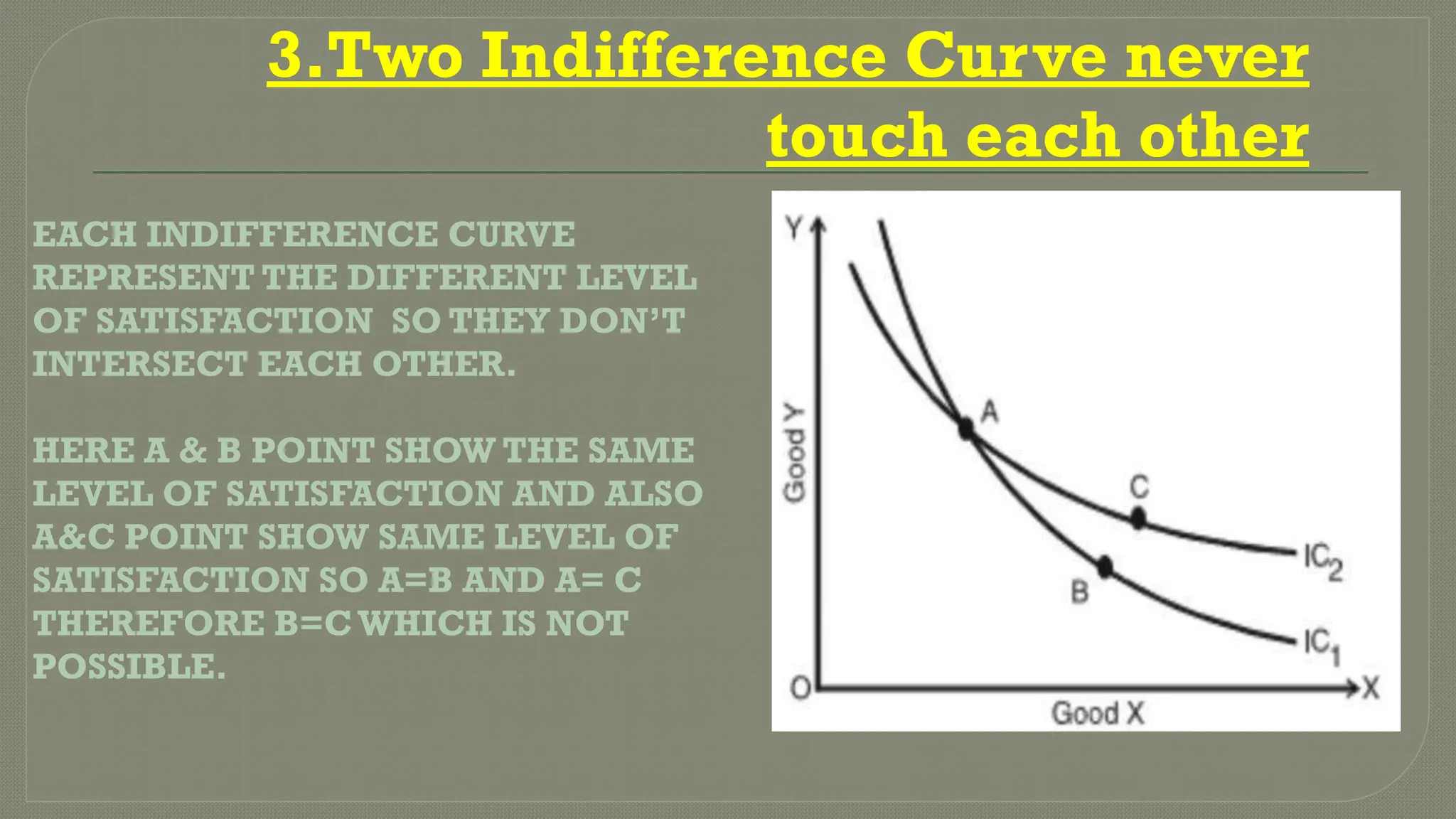
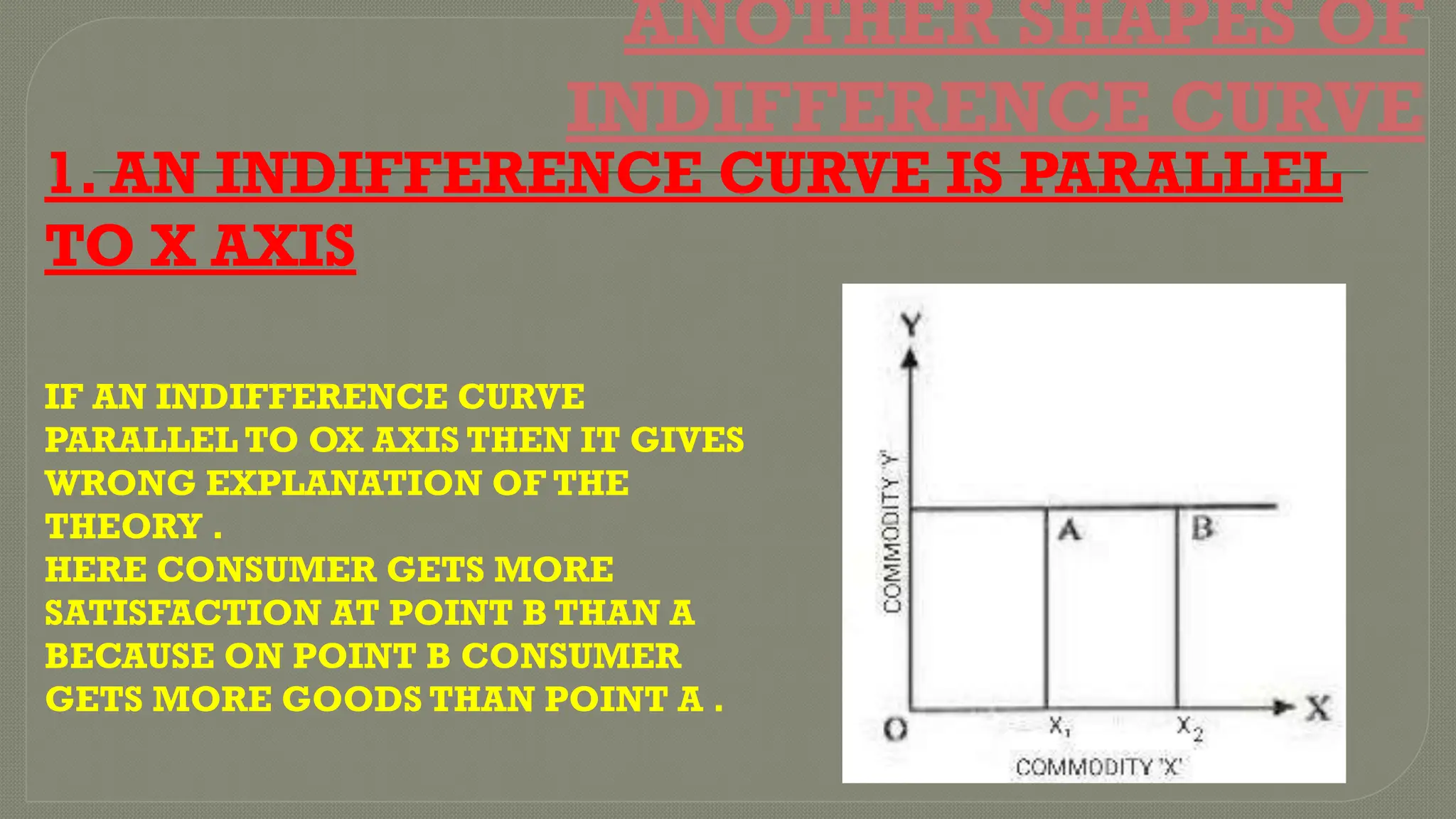
Indifference curve analysis illustrates various combinations of commodities that yield equal satisfaction to consumers, depicted through downward-sloping curves that are convex to the origin. Key features include the non-intersections of curves, higher curves representing greater satisfaction, and the curves never touching the axes. Additionally, indifference curves may not be parallel, and incorrect configurations include curves parallel to the axes or with a positive slope, which would misrepresent consumer satisfaction.