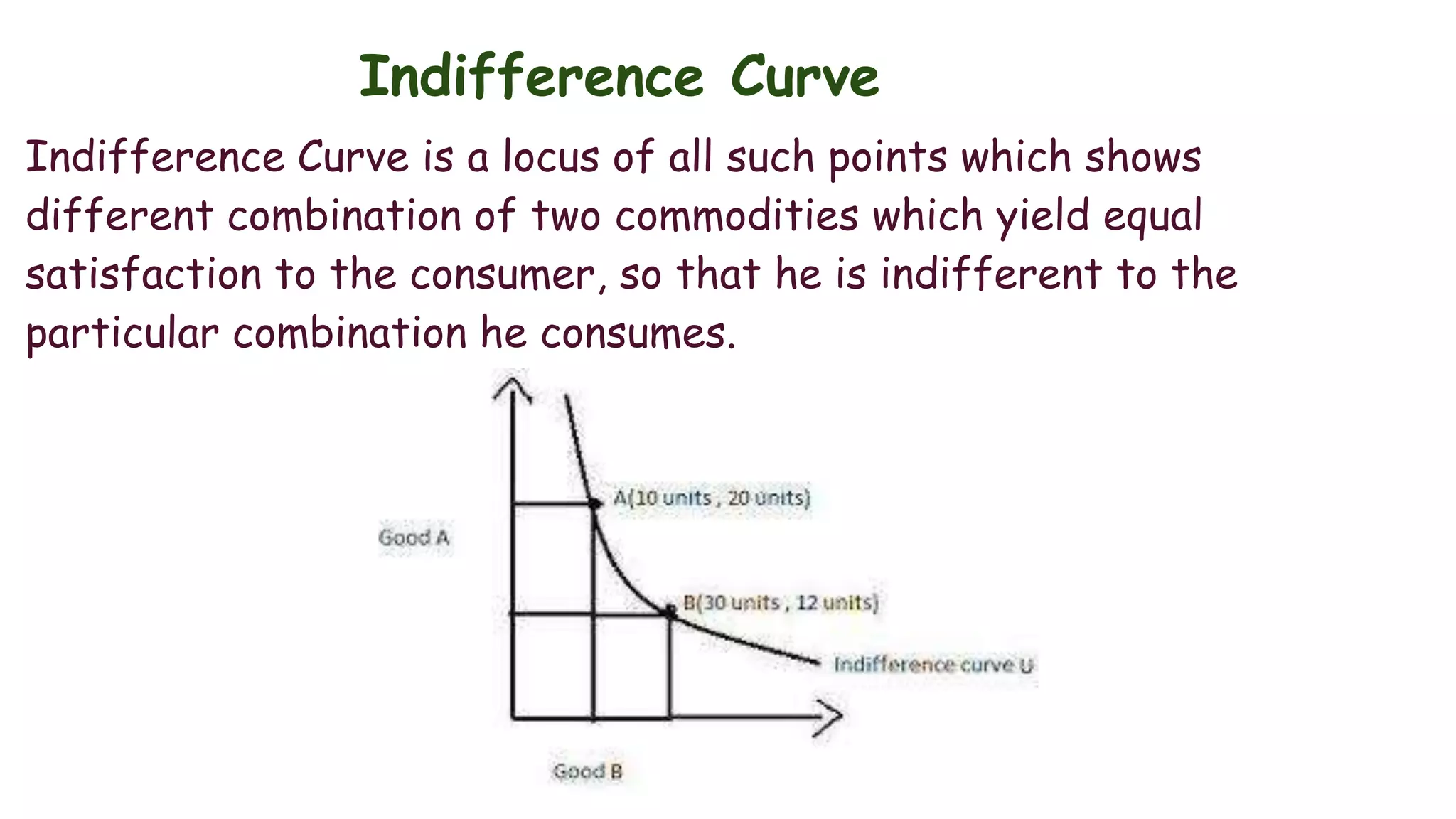
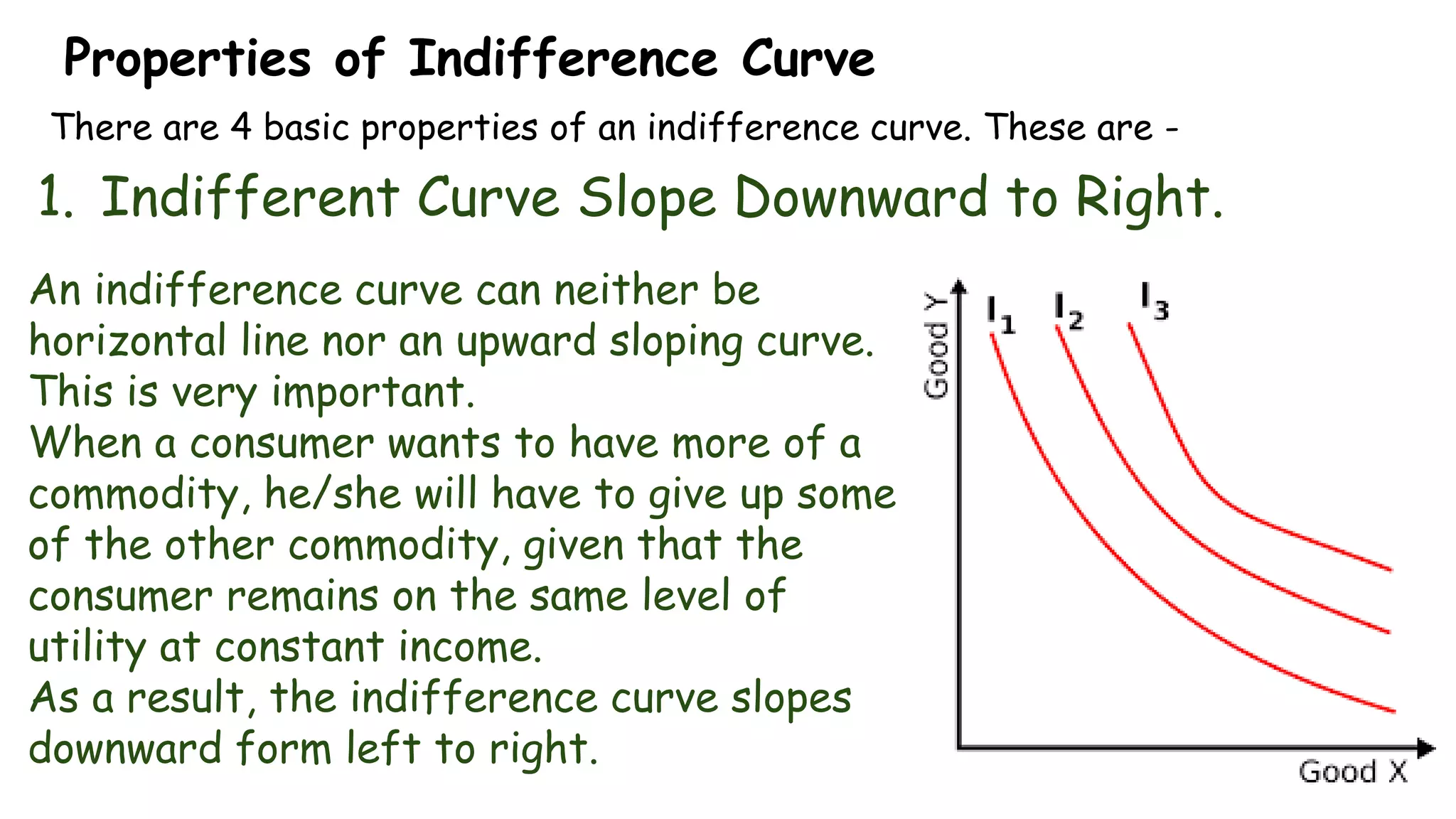
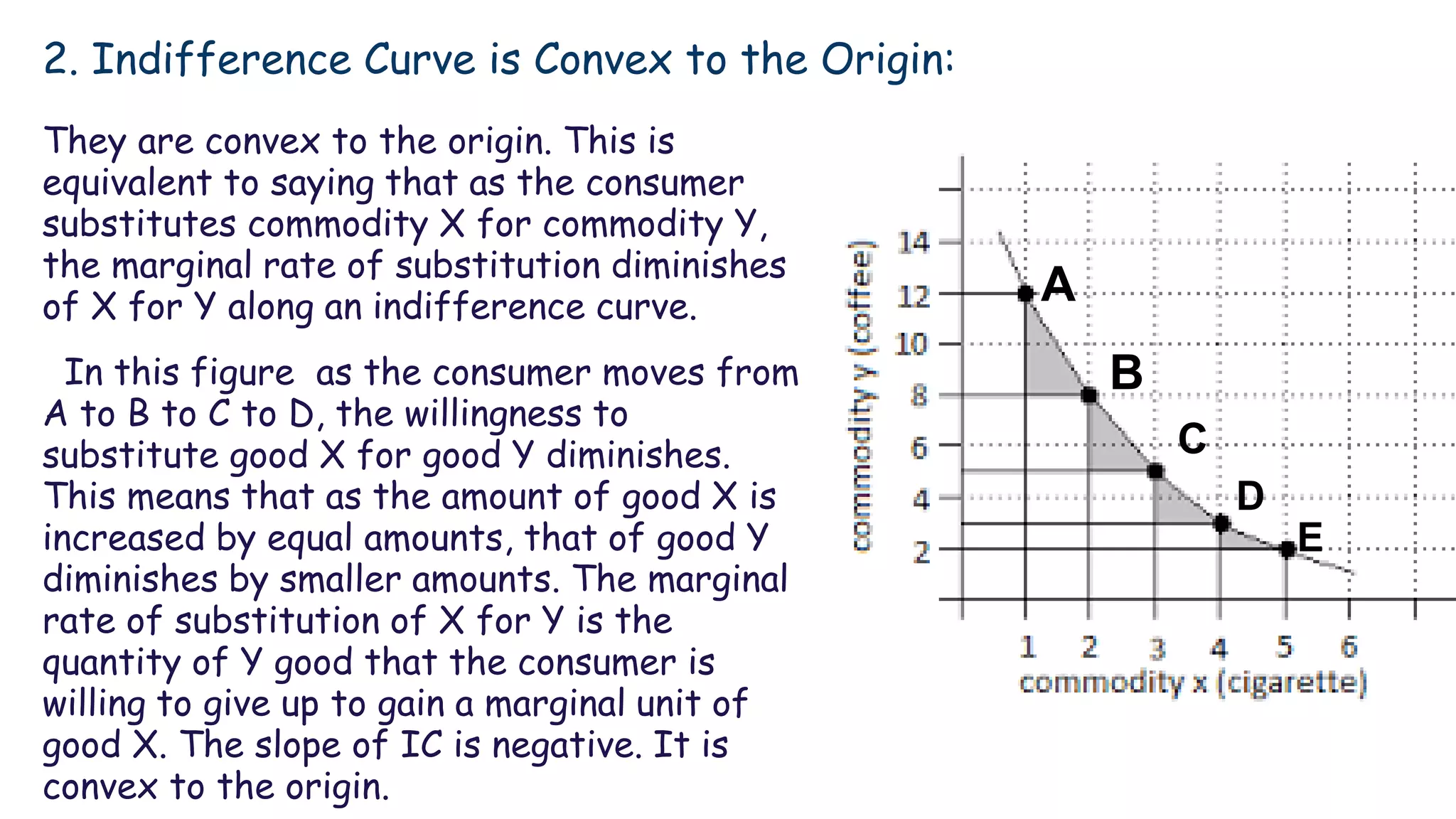
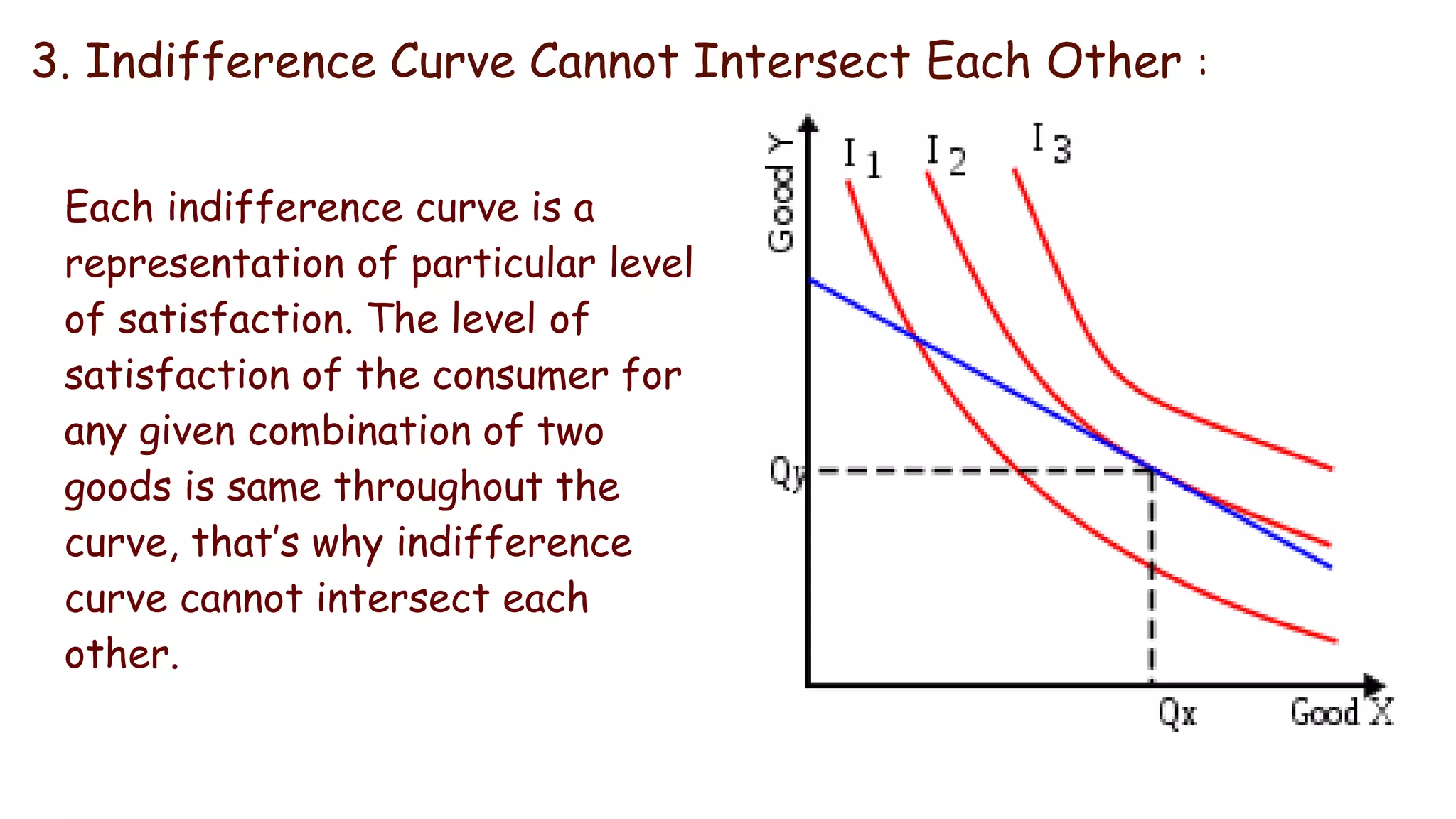
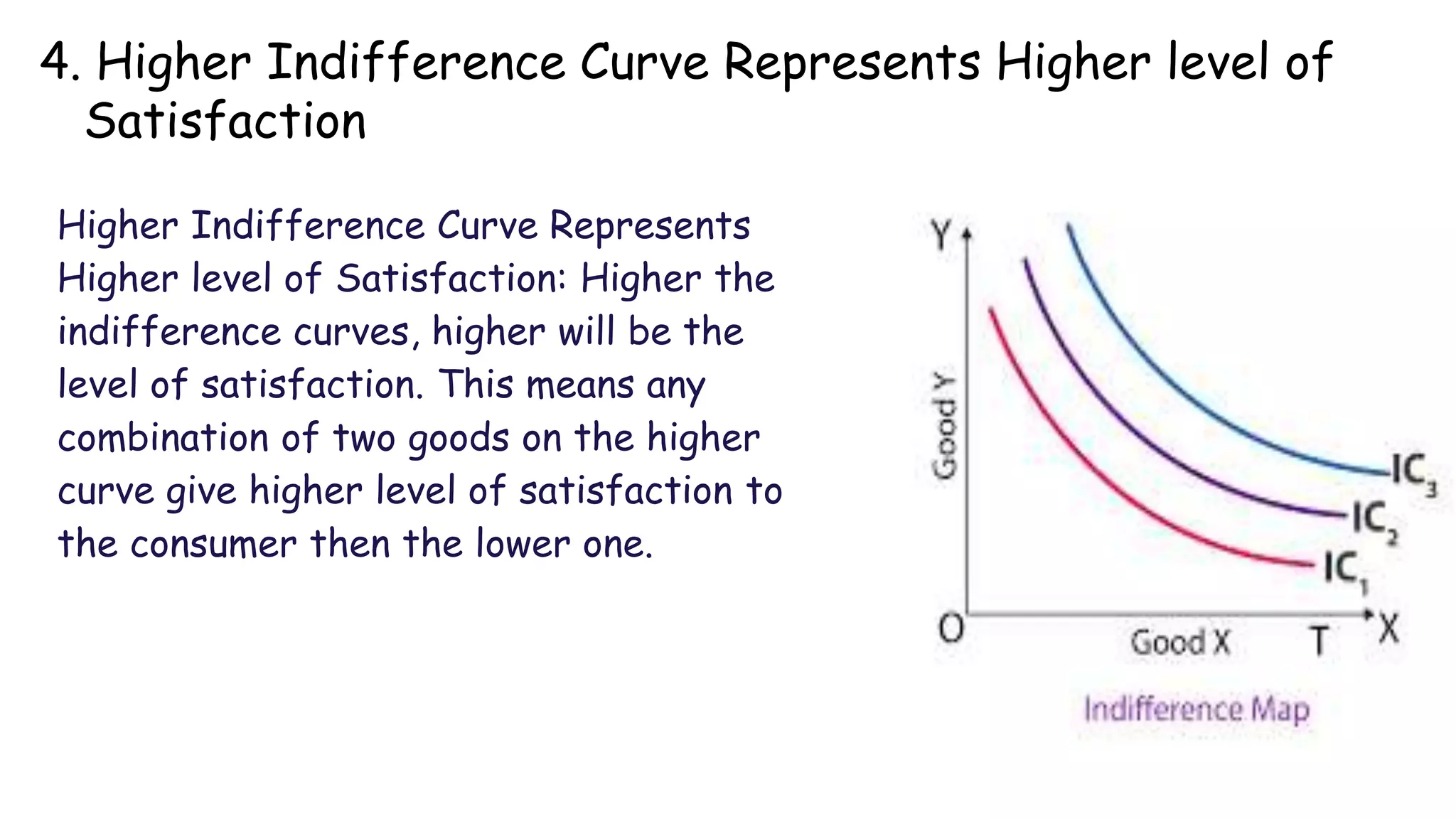
Indifference curve theory assumes that consumers will seek to maximize satisfaction when purchasing two goods given a fixed budget. An indifference curve represents all combinations of two goods that provide equal satisfaction. Properties of indifference curves include sloping downward to the right, being convex to the origin, and not intersecting, with higher curves representing greater satisfaction. The theory aims to explain consumer equilibrium when choosing between multiple options under scarcity.