Embed presentation
Download to read offline




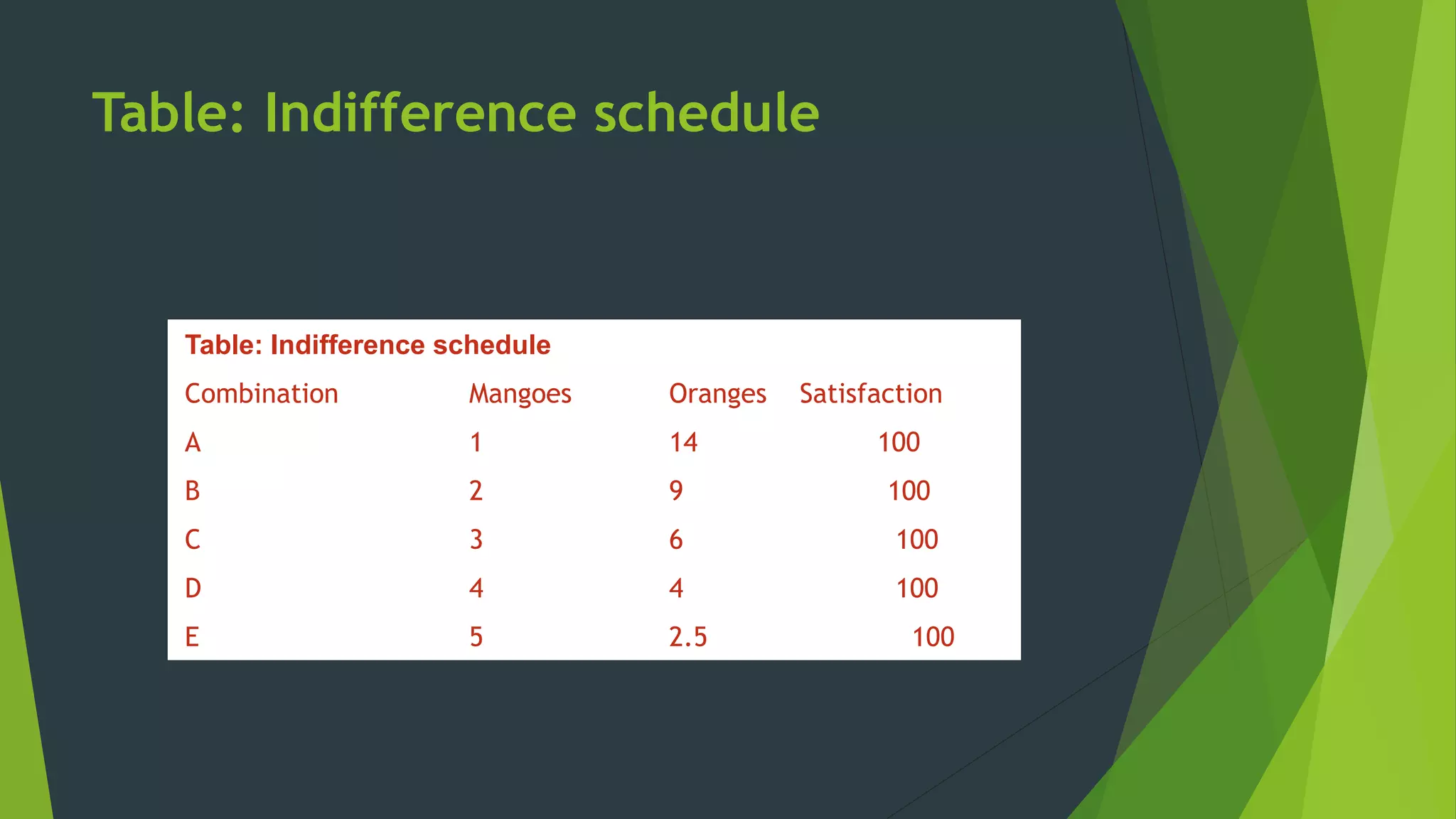
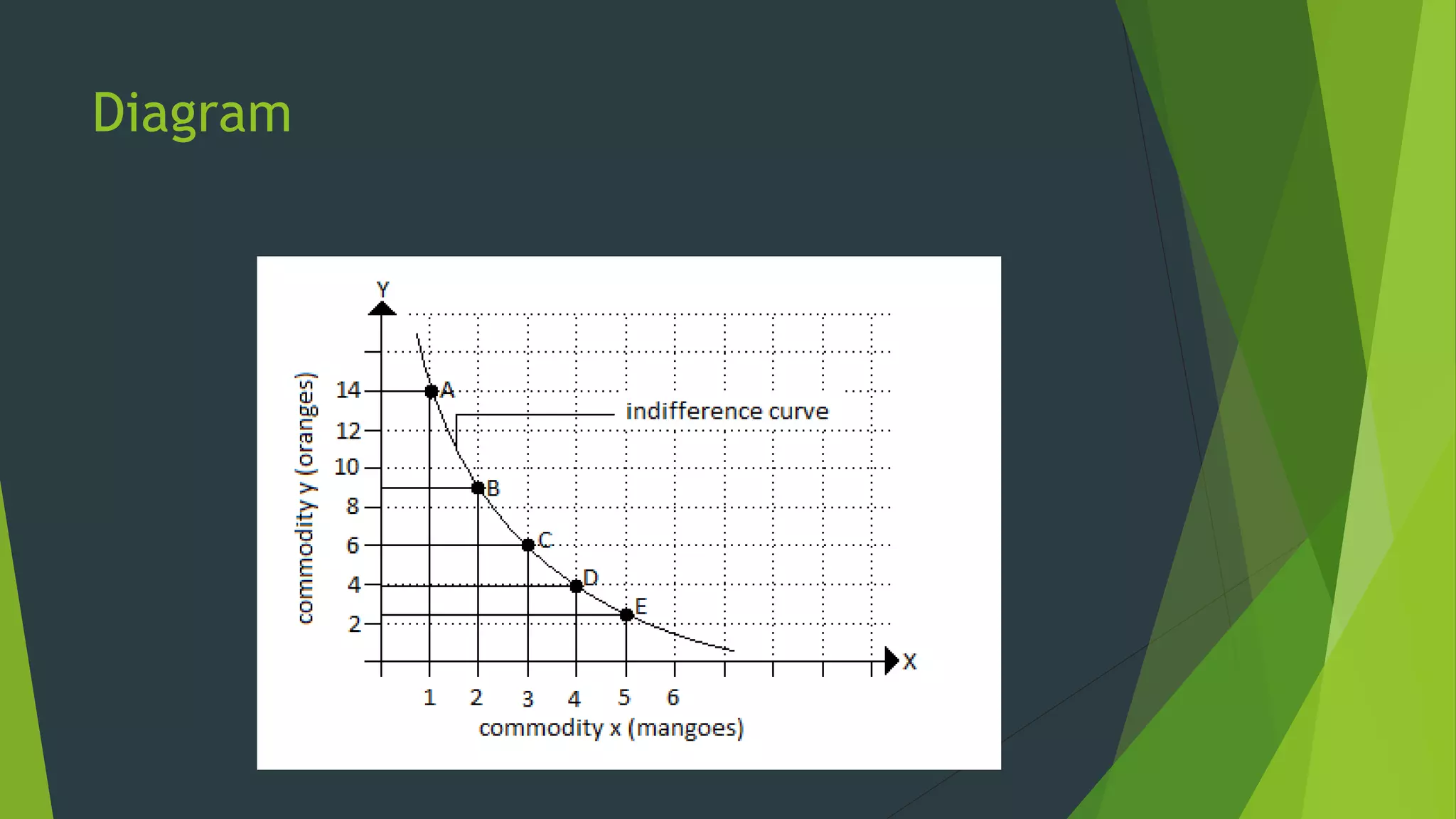
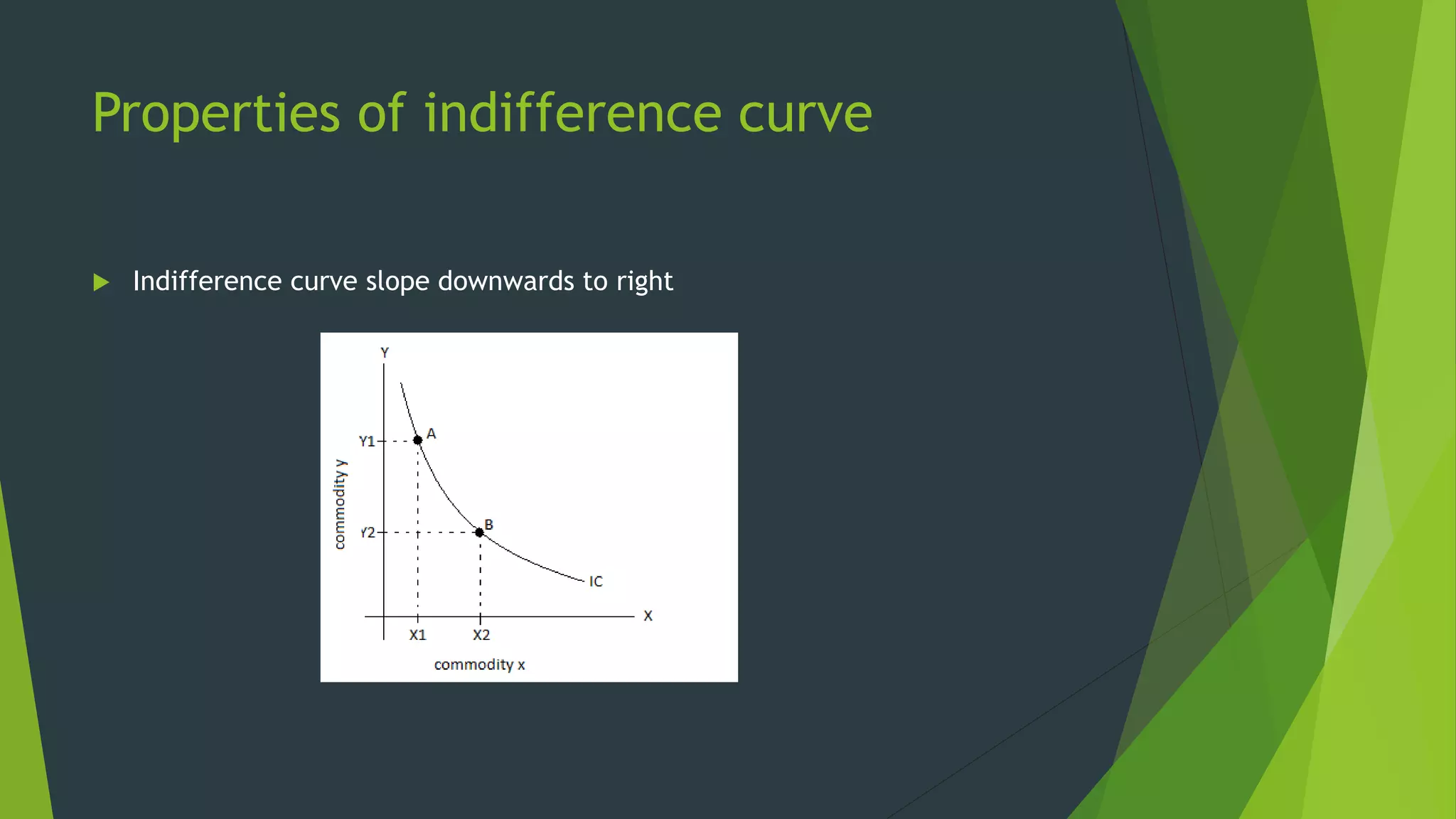
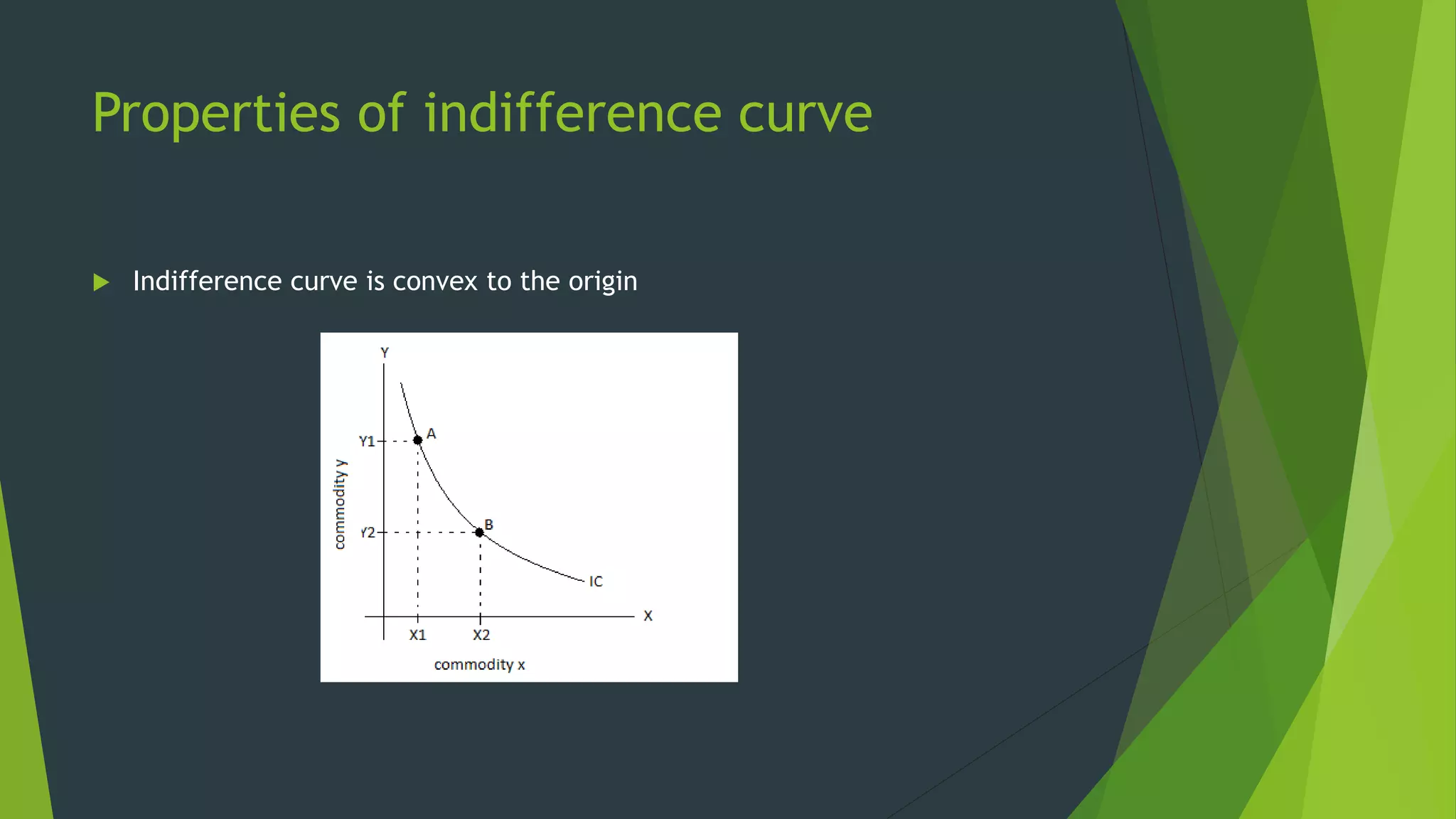
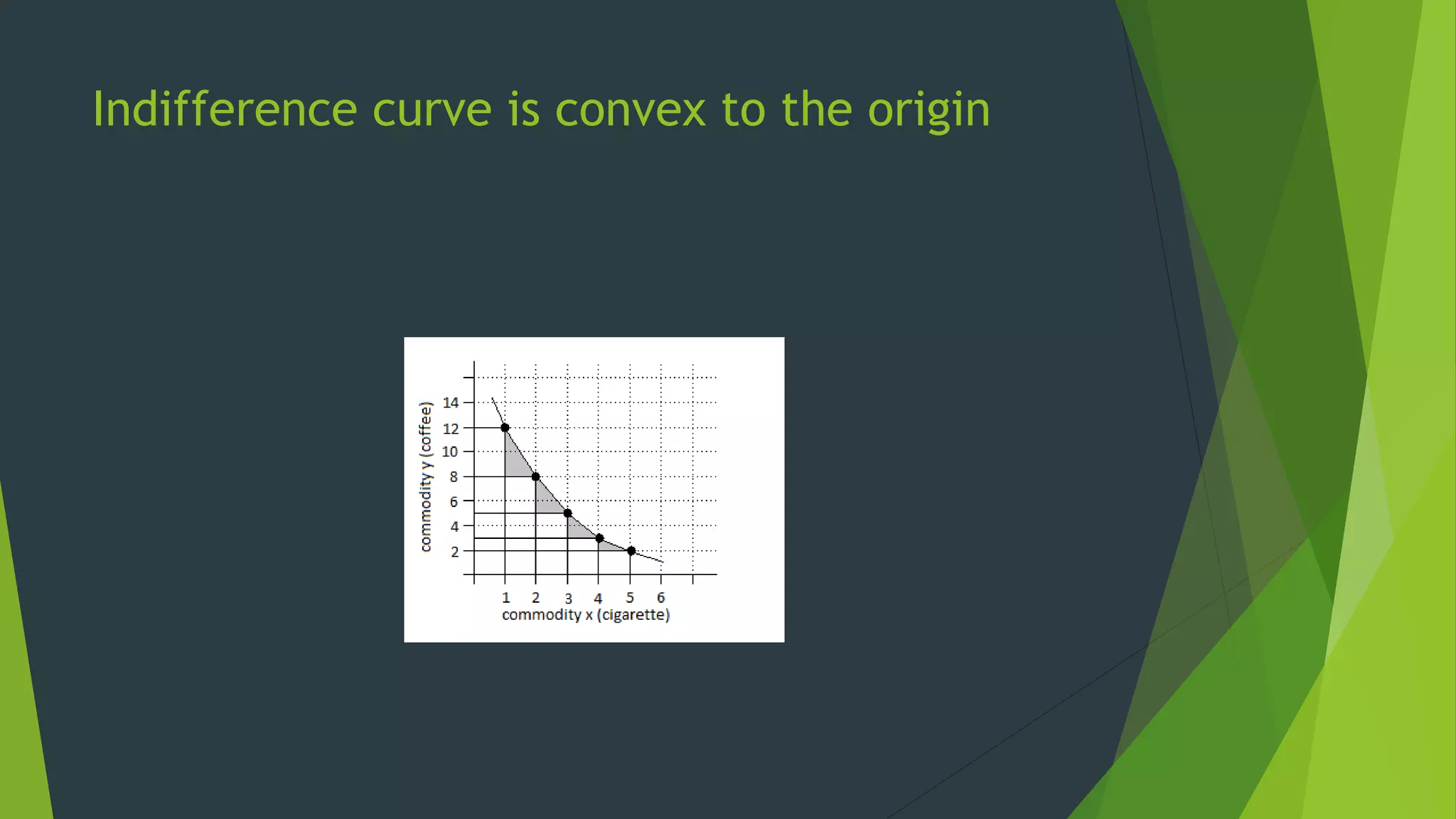
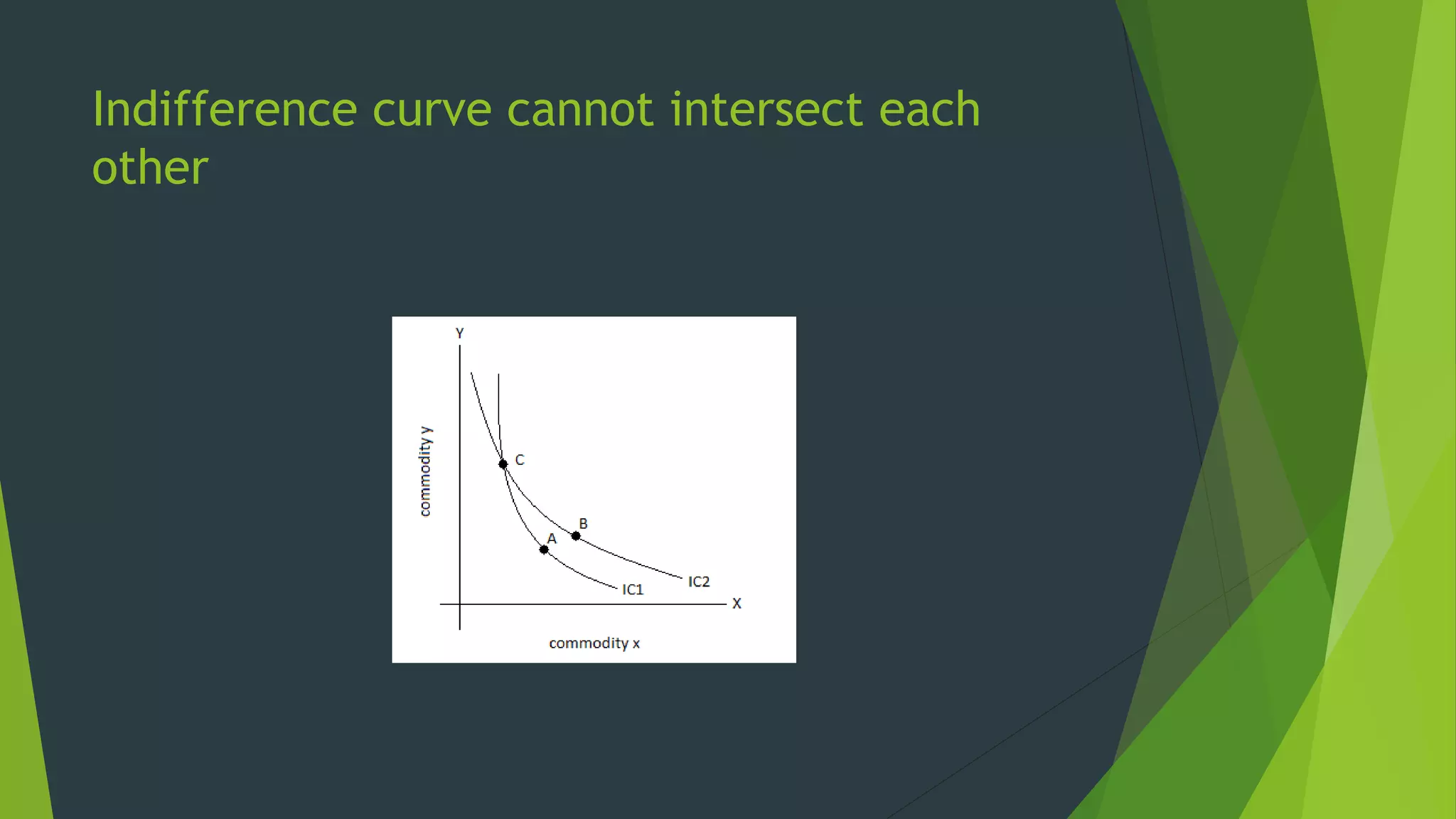
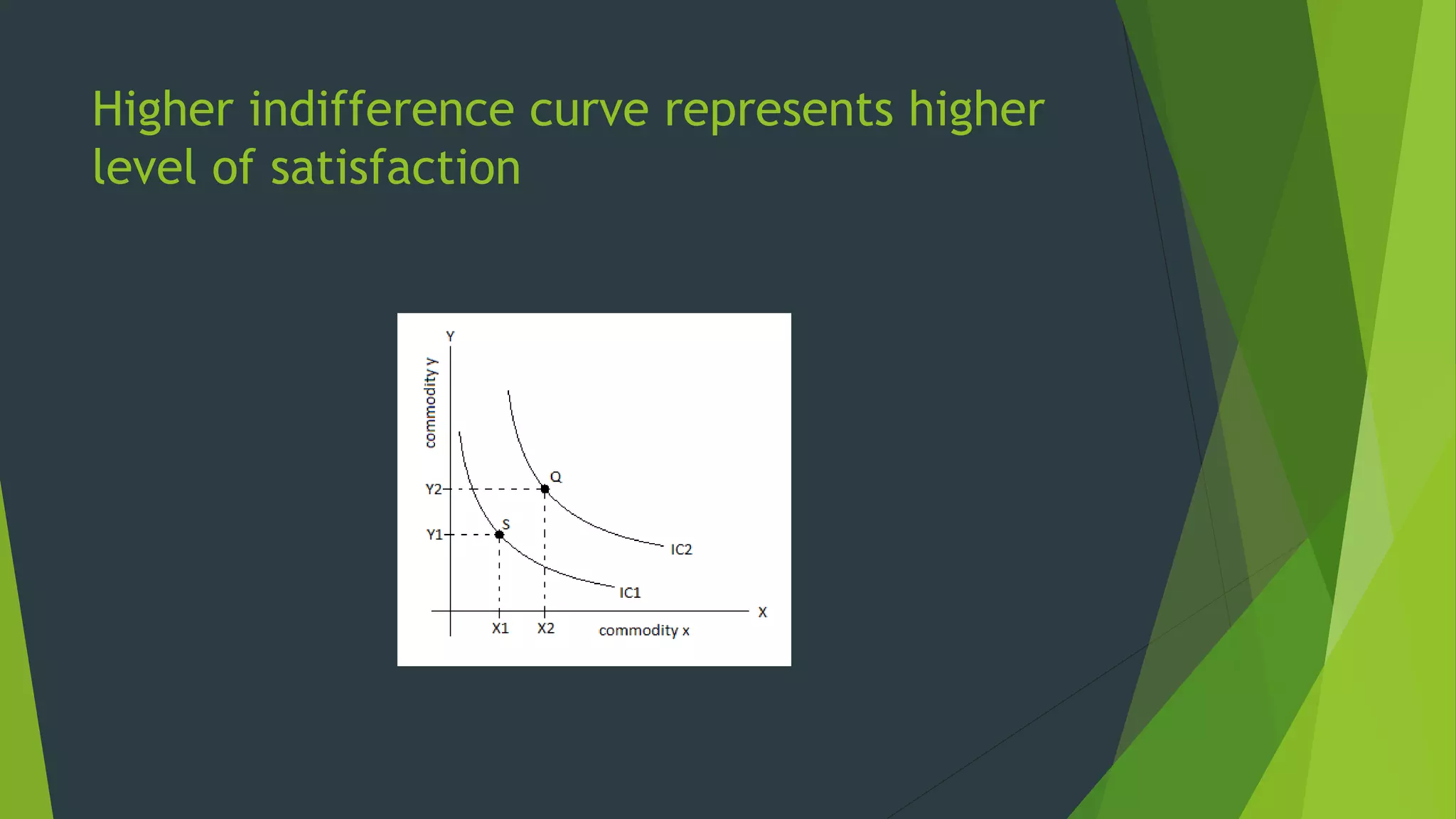


The document defines an indifference curve as a set of combinations of two goods that provide the same level of utility or satisfaction to a consumer. It assumes consumers have a fixed budget to spend on two goods with constant prices. Indifference curves depict combinations of goods that yield equal satisfaction based on ordinal utility. They have the properties of downward sloping, convex shape, and not intersecting, with higher curves representing greater satisfaction. The marginal rate of substitution along a curve diminishes as the consumer trades one good for another to maintain the same utility.












