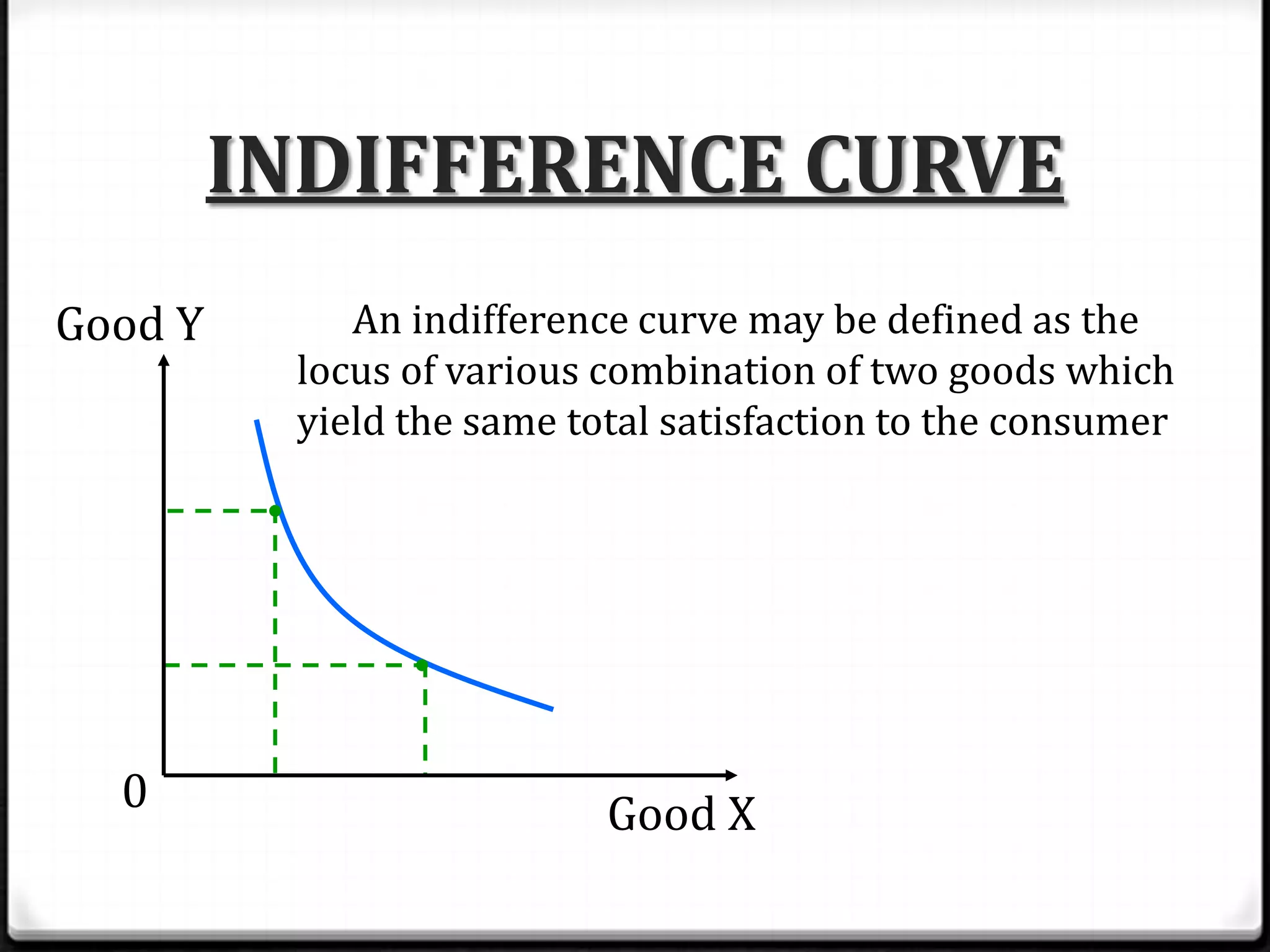
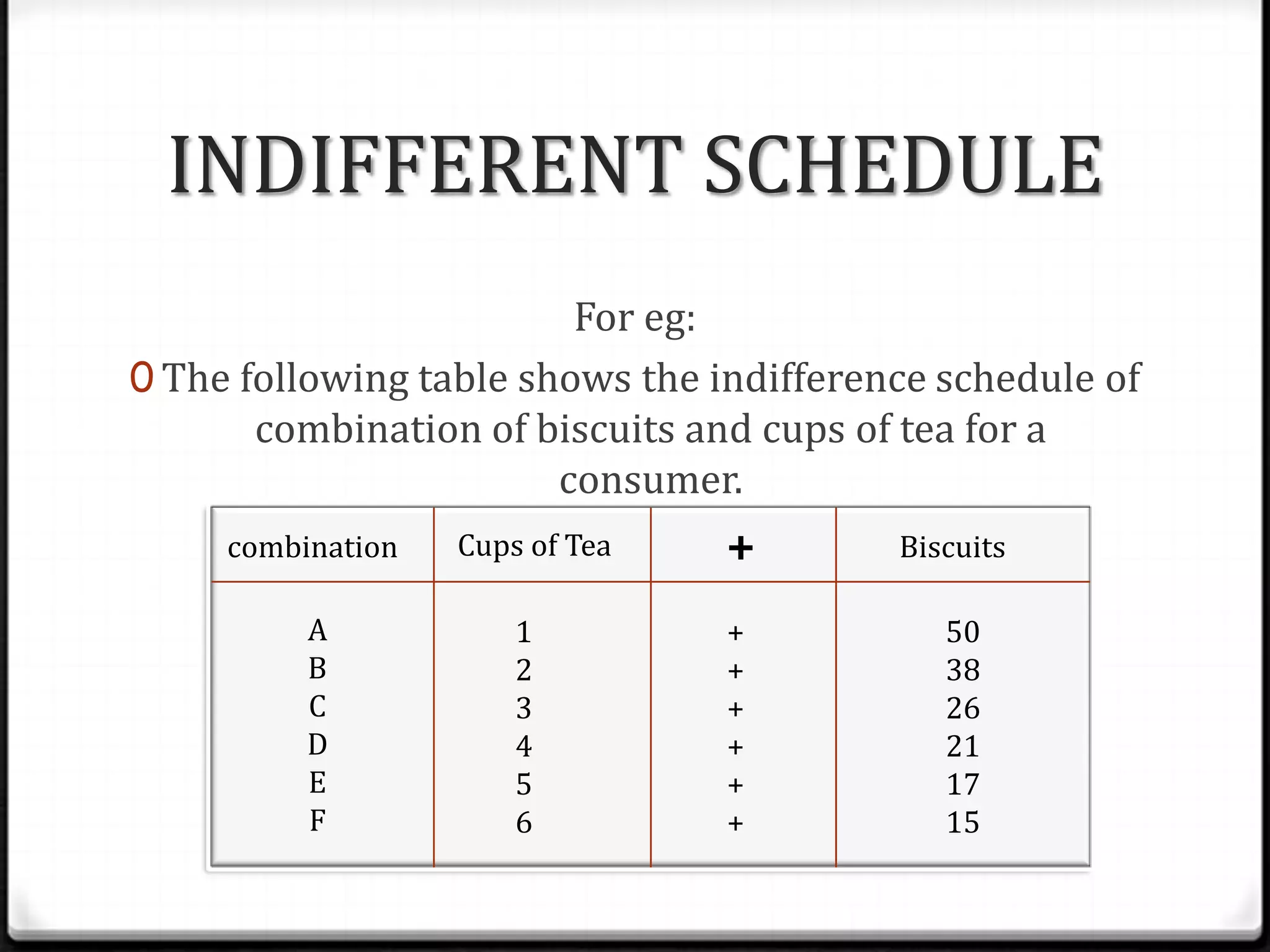
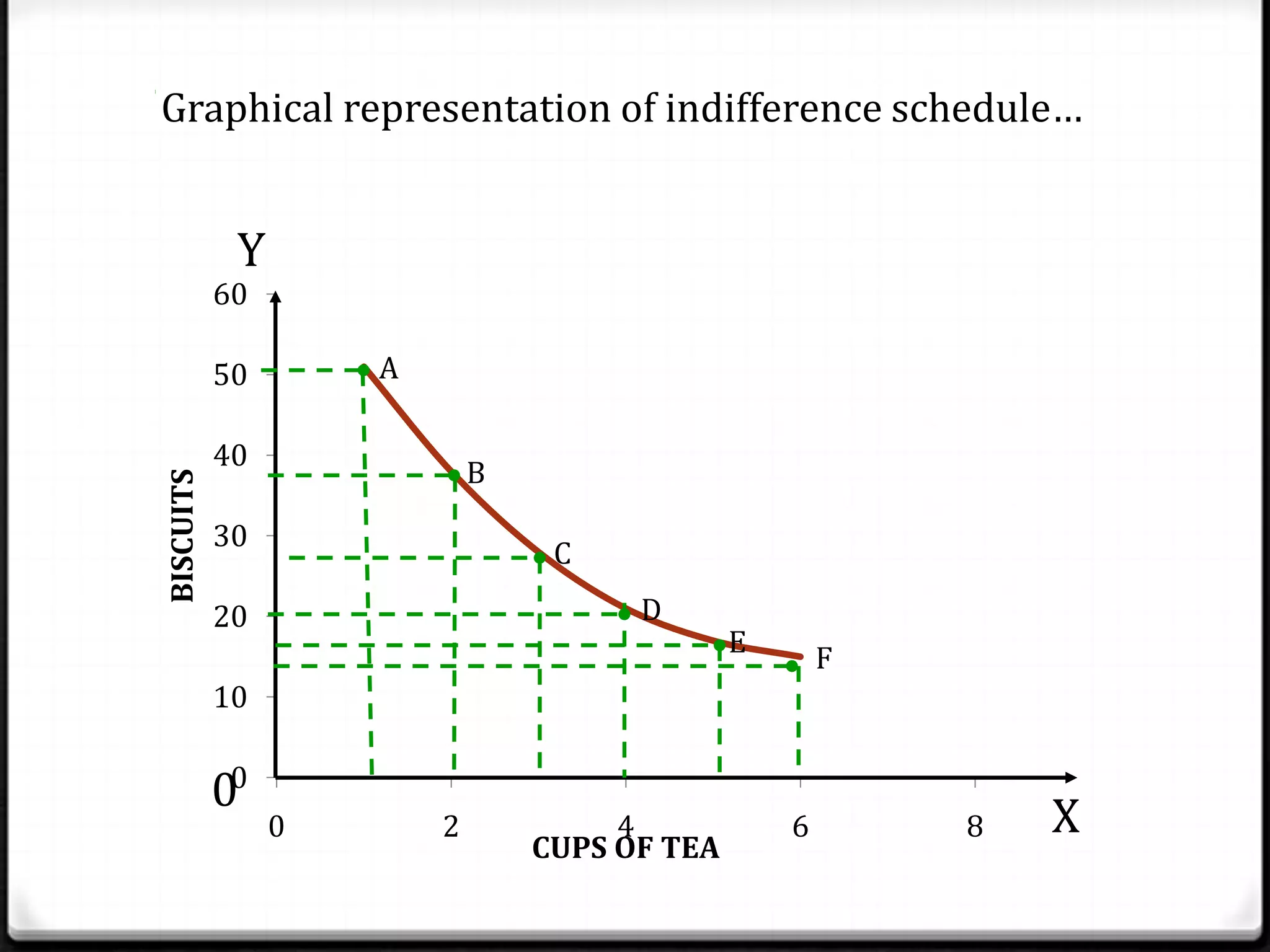
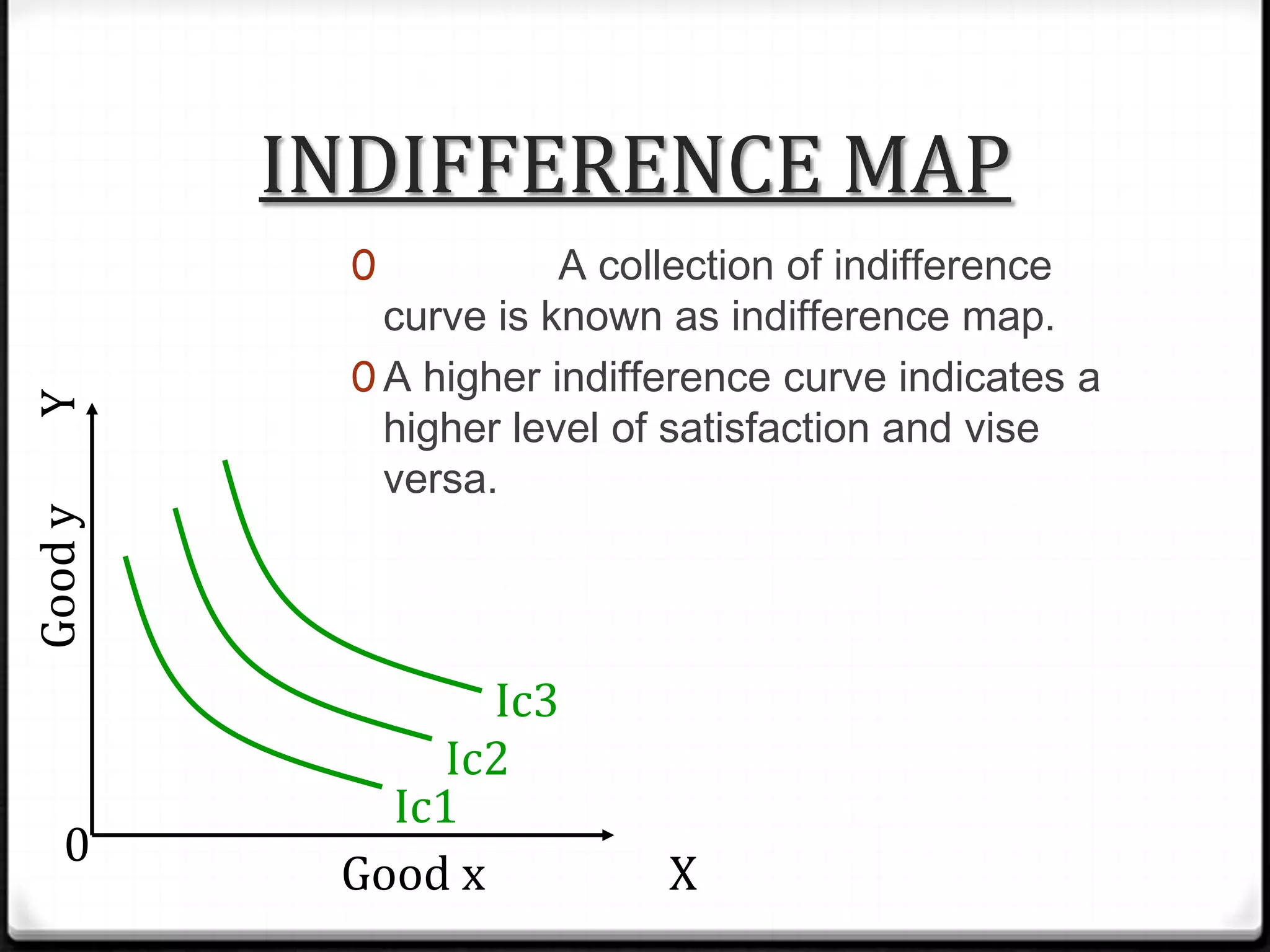
This document discusses indifference curve analysis, which is an approach to consumer choice developed by Edgeworth and later preferred by Hicks and Allen. It assumes consumers express preferences over bundles of goods rather than quantities. Consumers are assumed to be rational and choose the bundle that provides the highest satisfaction level. An indifference curve represents combinations of two goods that provide equal satisfaction. The document provides an example indifference schedule and shows how it can be represented graphically with indifference curves, with higher curves indicating greater satisfaction.