This document presents a 3-sentence summary of a presentation on indifference curves:
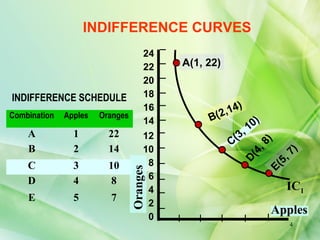
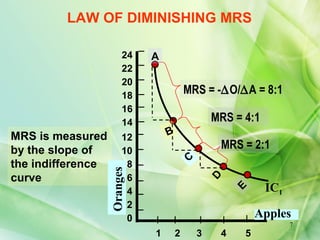
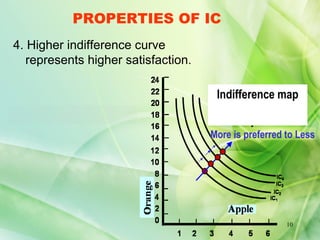
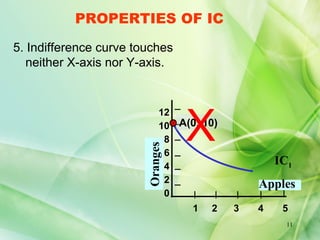
The presentation defines indifference curves as loci that represent combinations of two goods that provide the same level of satisfaction to a consumer. It discusses the properties of indifference curves including negative slope, convex shape, non-intersection, and representation of preference with higher curves indicating greater satisfaction. Examples are provided to illustrate concepts like marginal rate of substitution and the law of diminishing marginal rate of substitution.