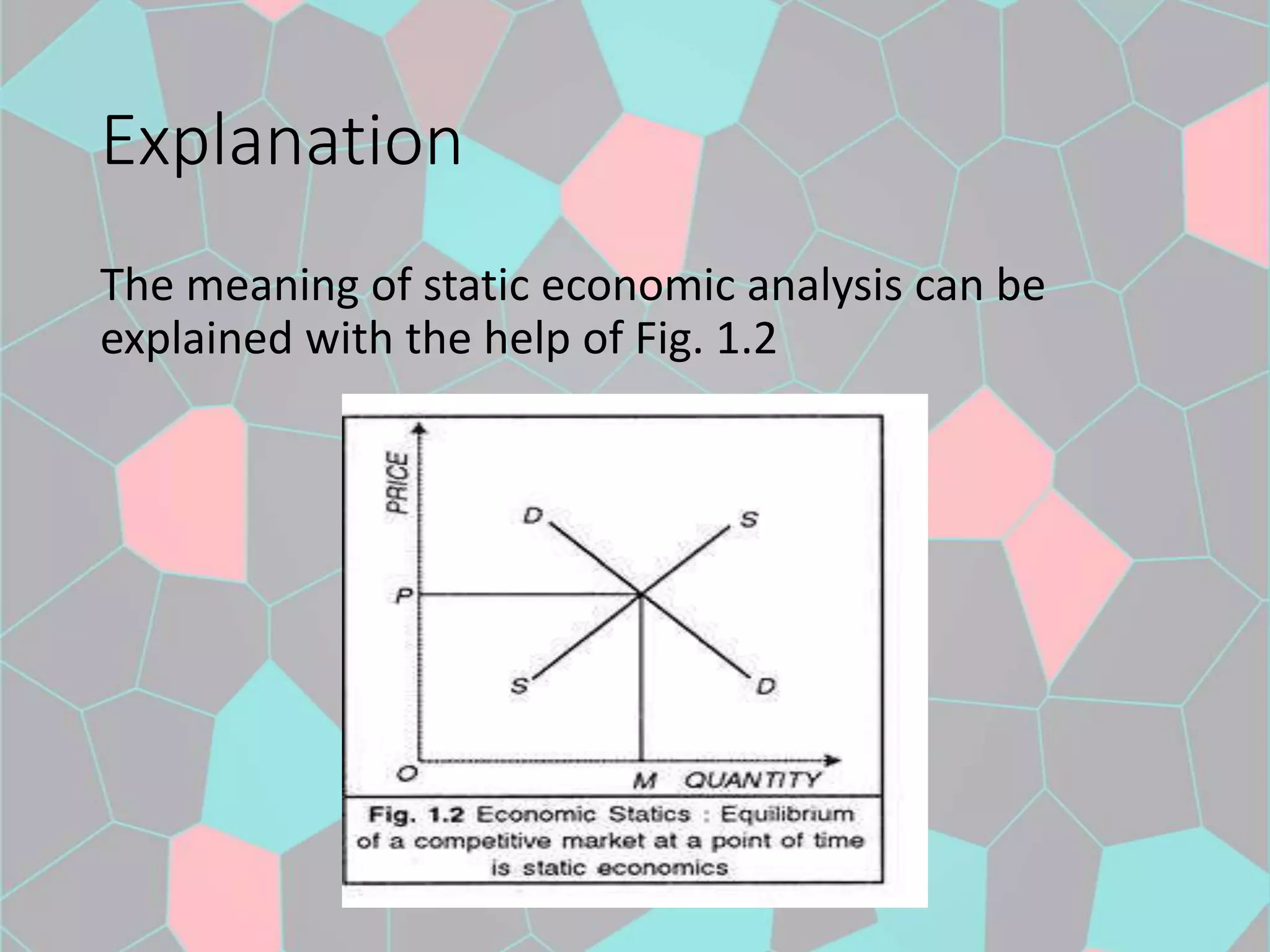
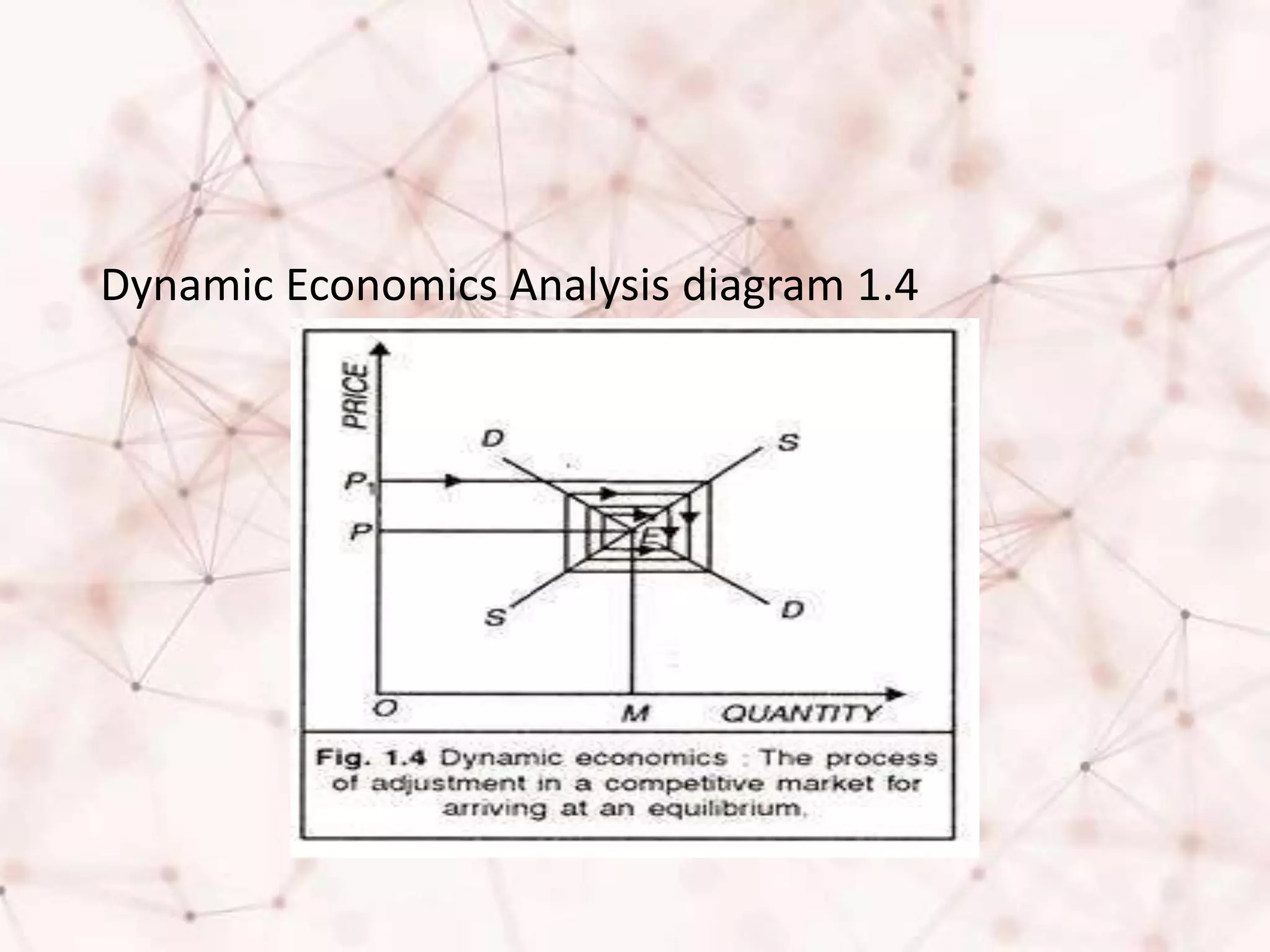
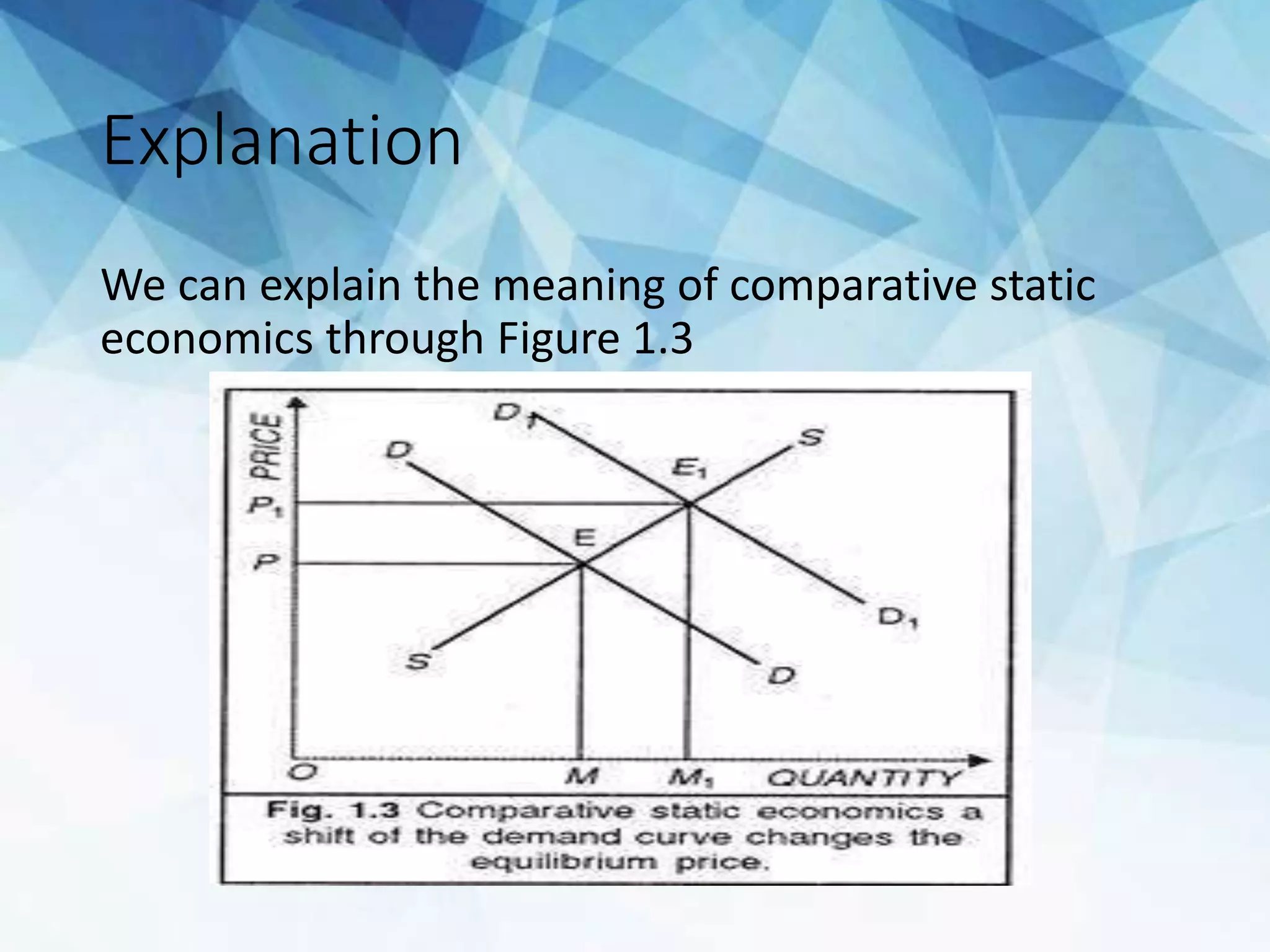
The document discusses the concepts of static, dynamic, and comparative static economics, highlighting their definitions, features, scope, and limitations. Static economics focuses on time-specific scenarios with constant variables, while dynamic economics addresses changes over time, providing a more realistic view of economic fluctuations. Comparative static economics serves to compare different equilibrium states without detailing the transition path between them.