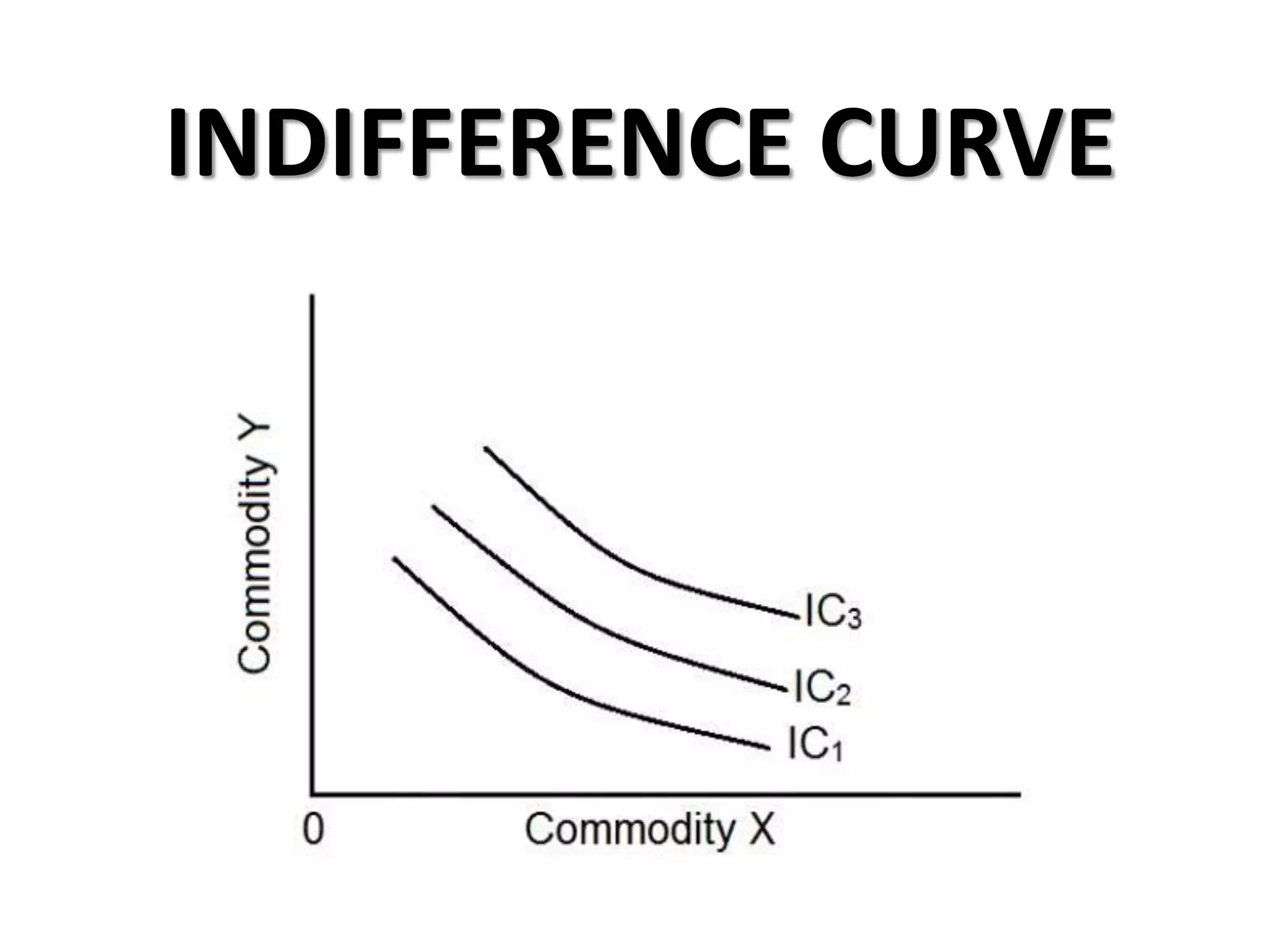
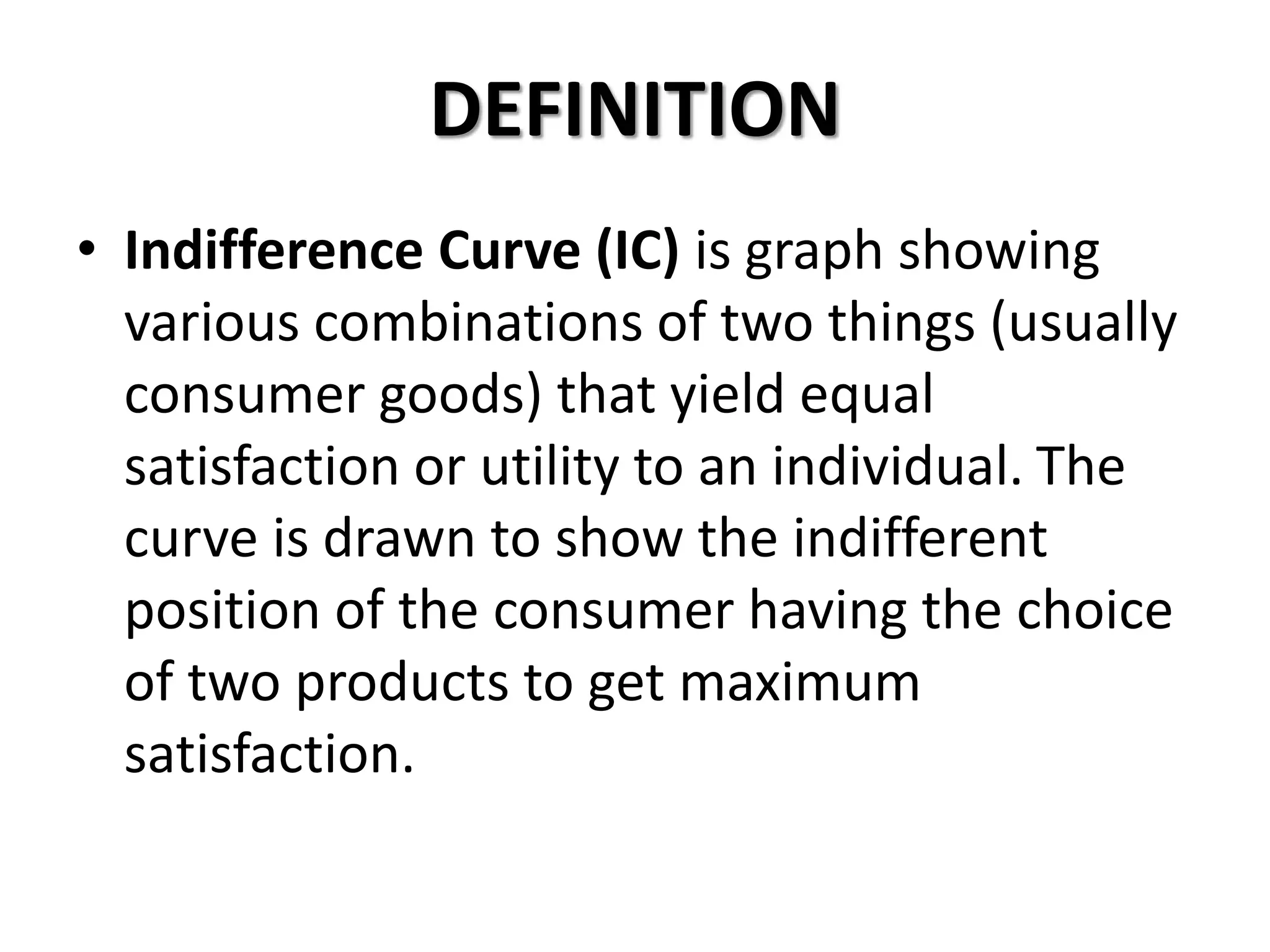
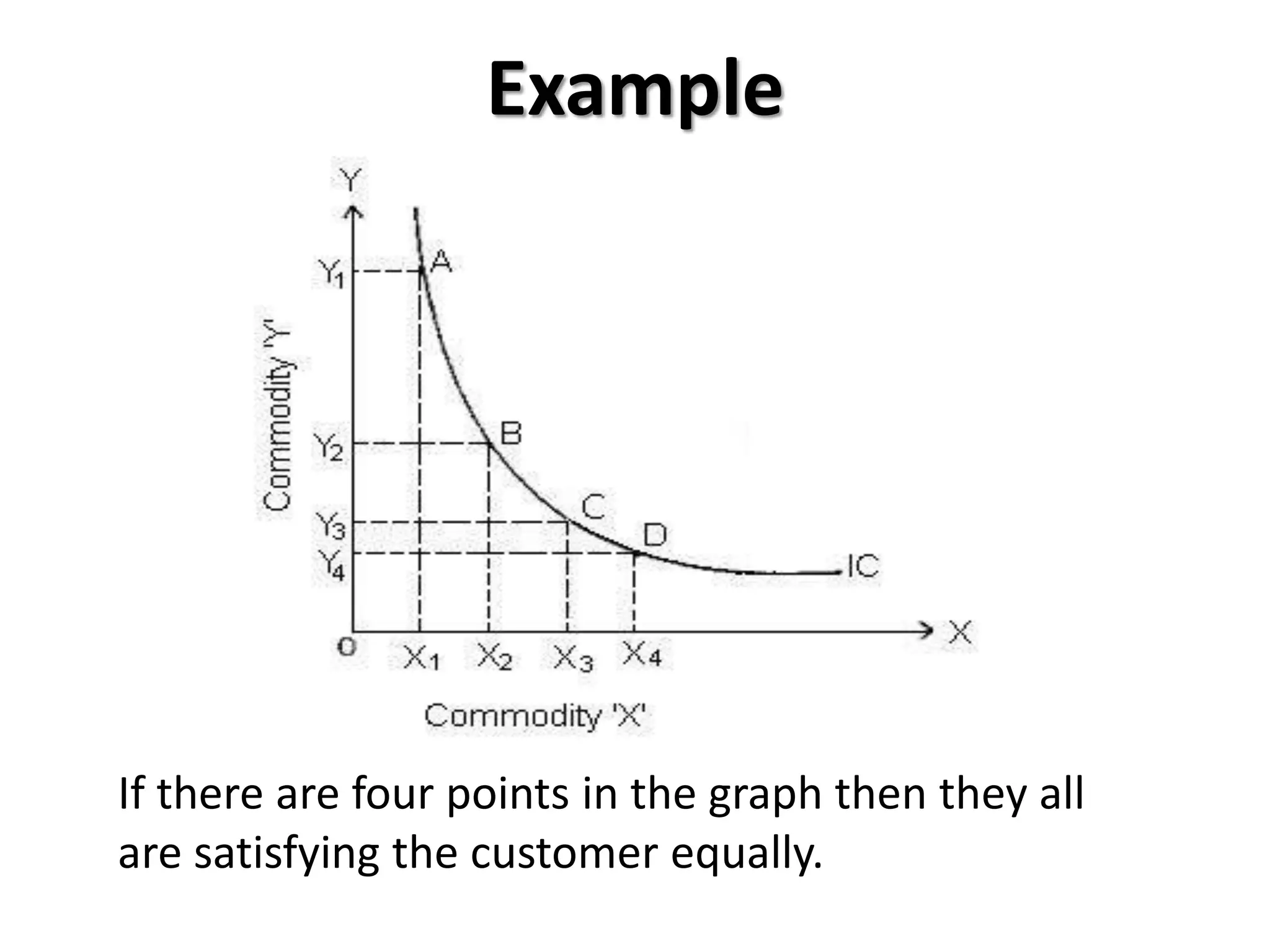
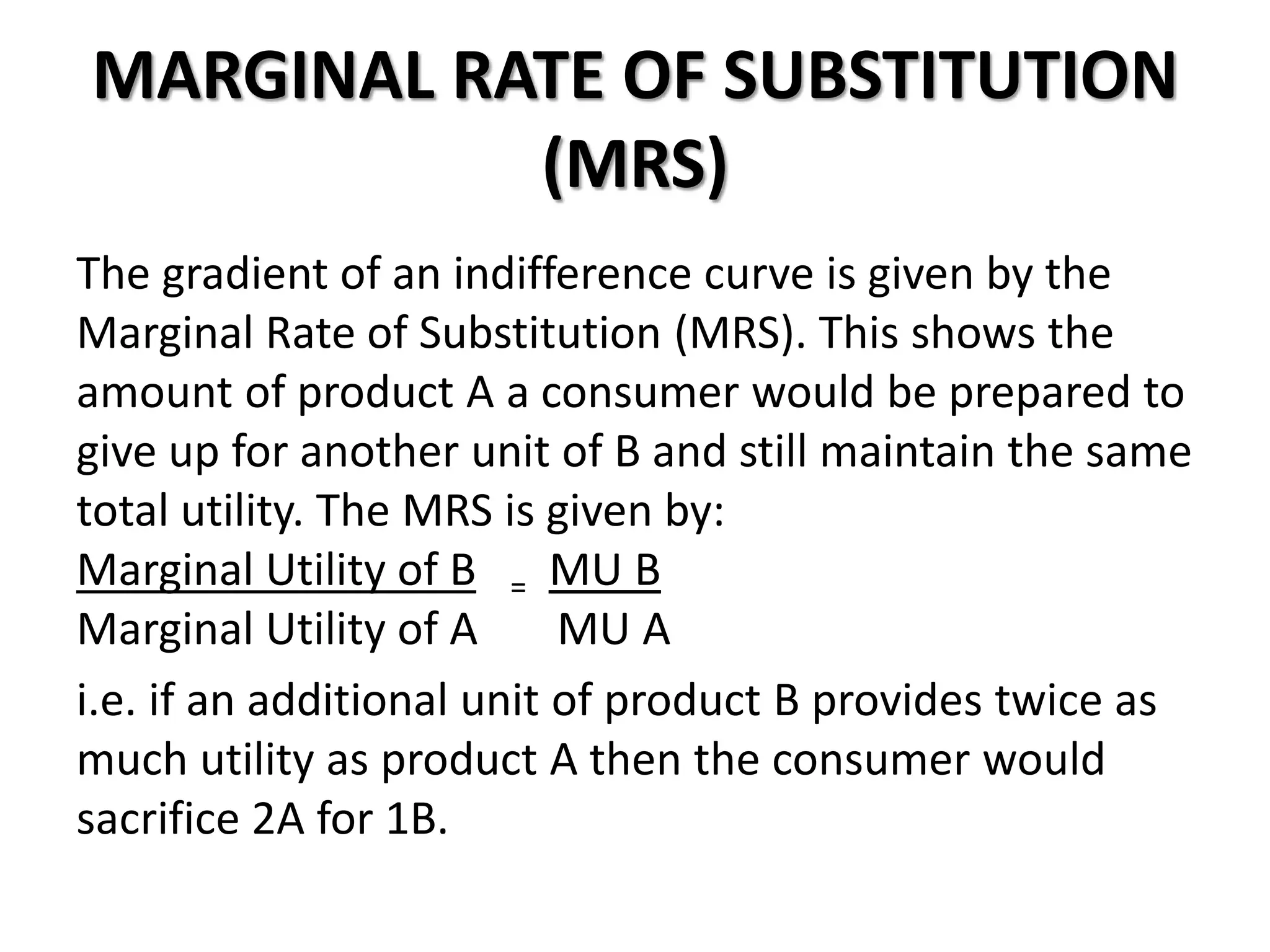
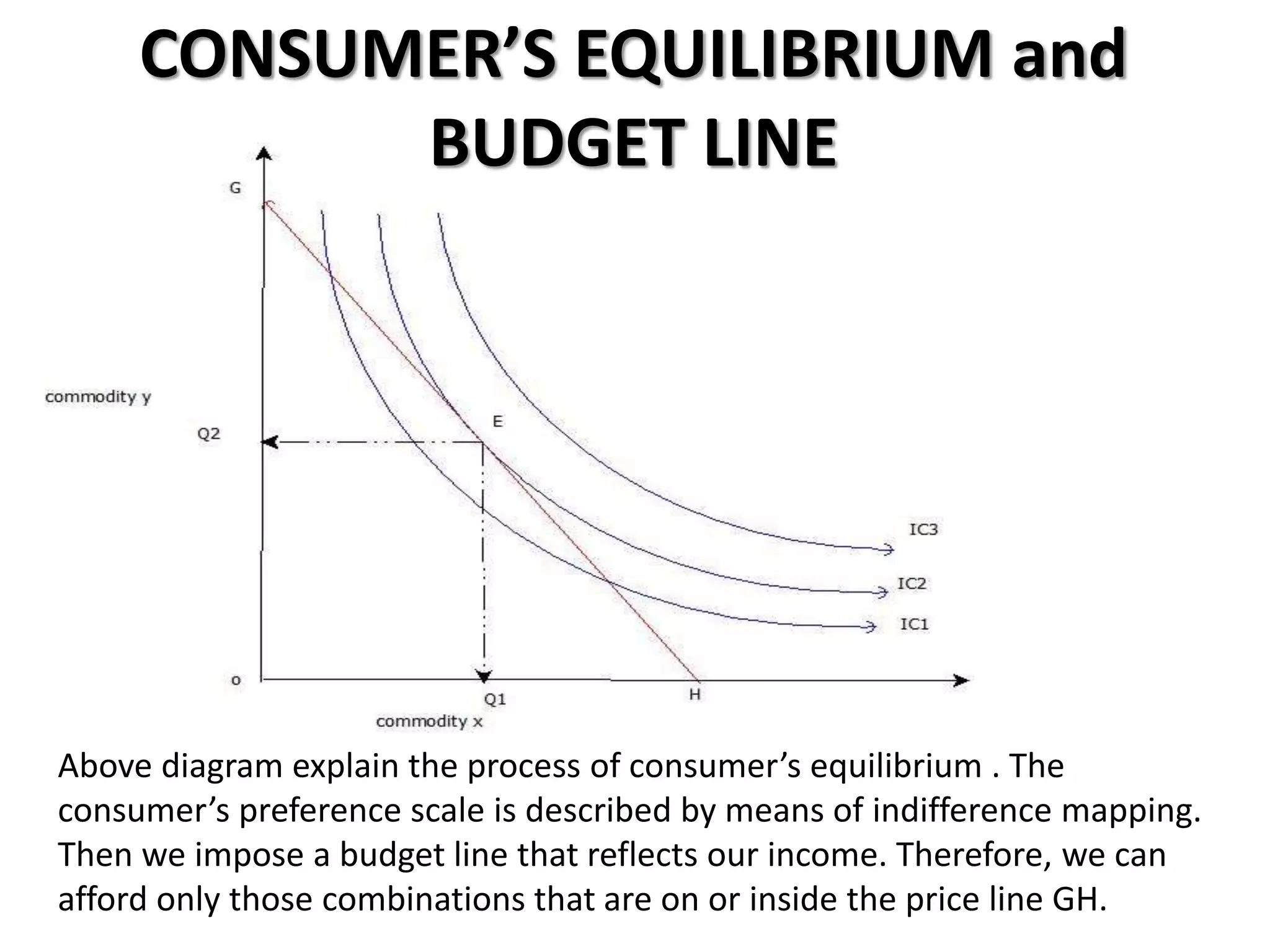
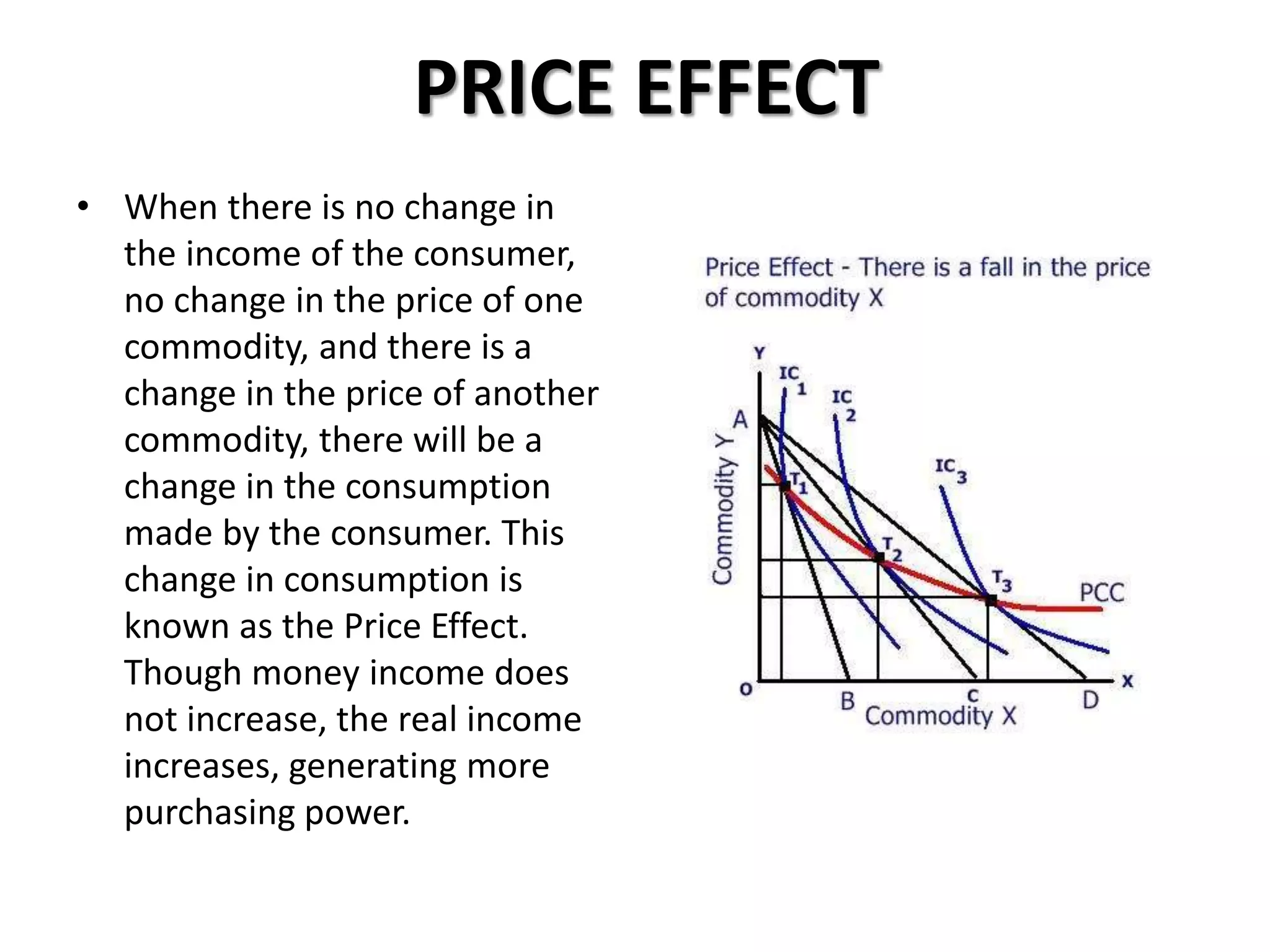
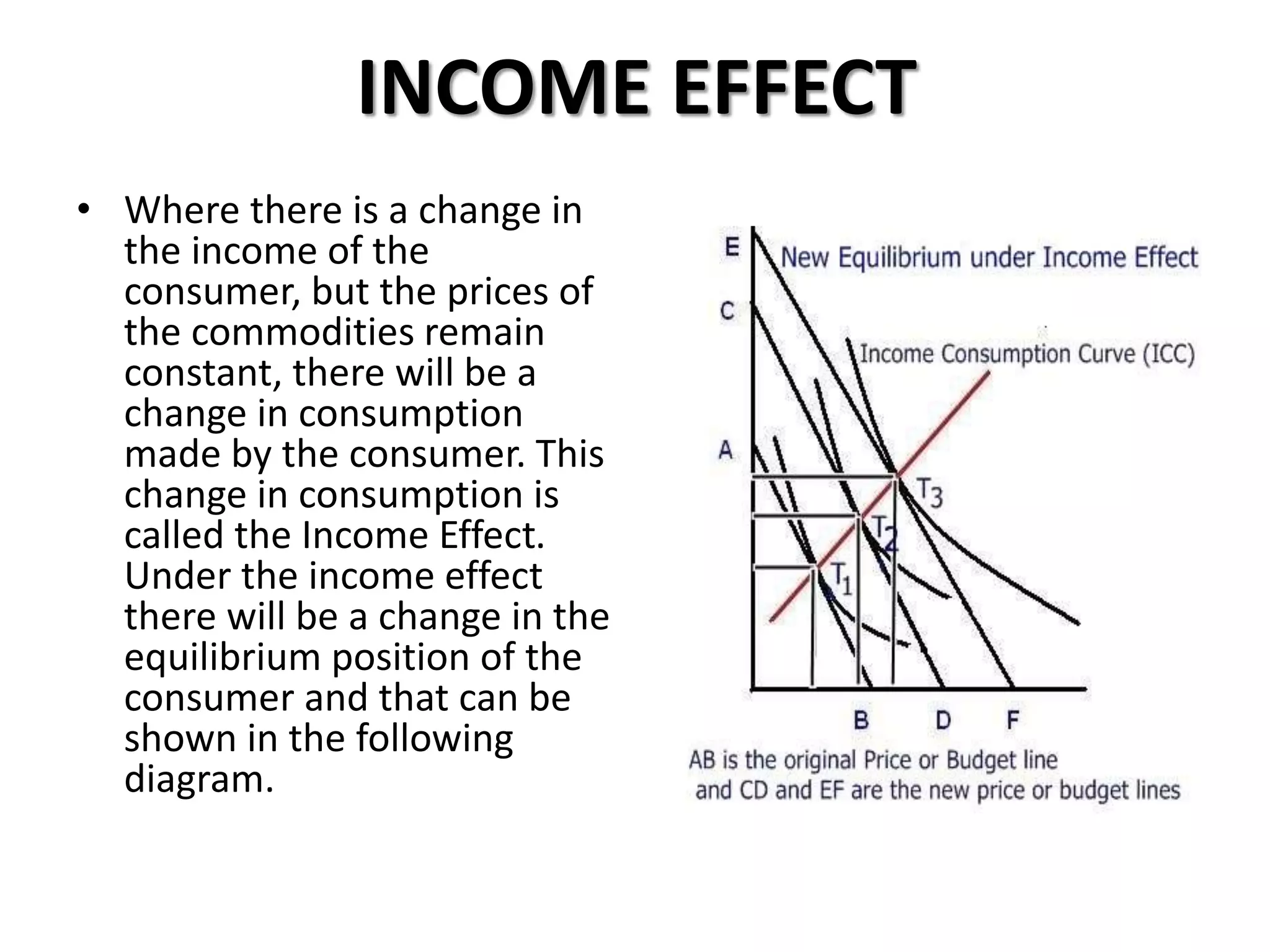
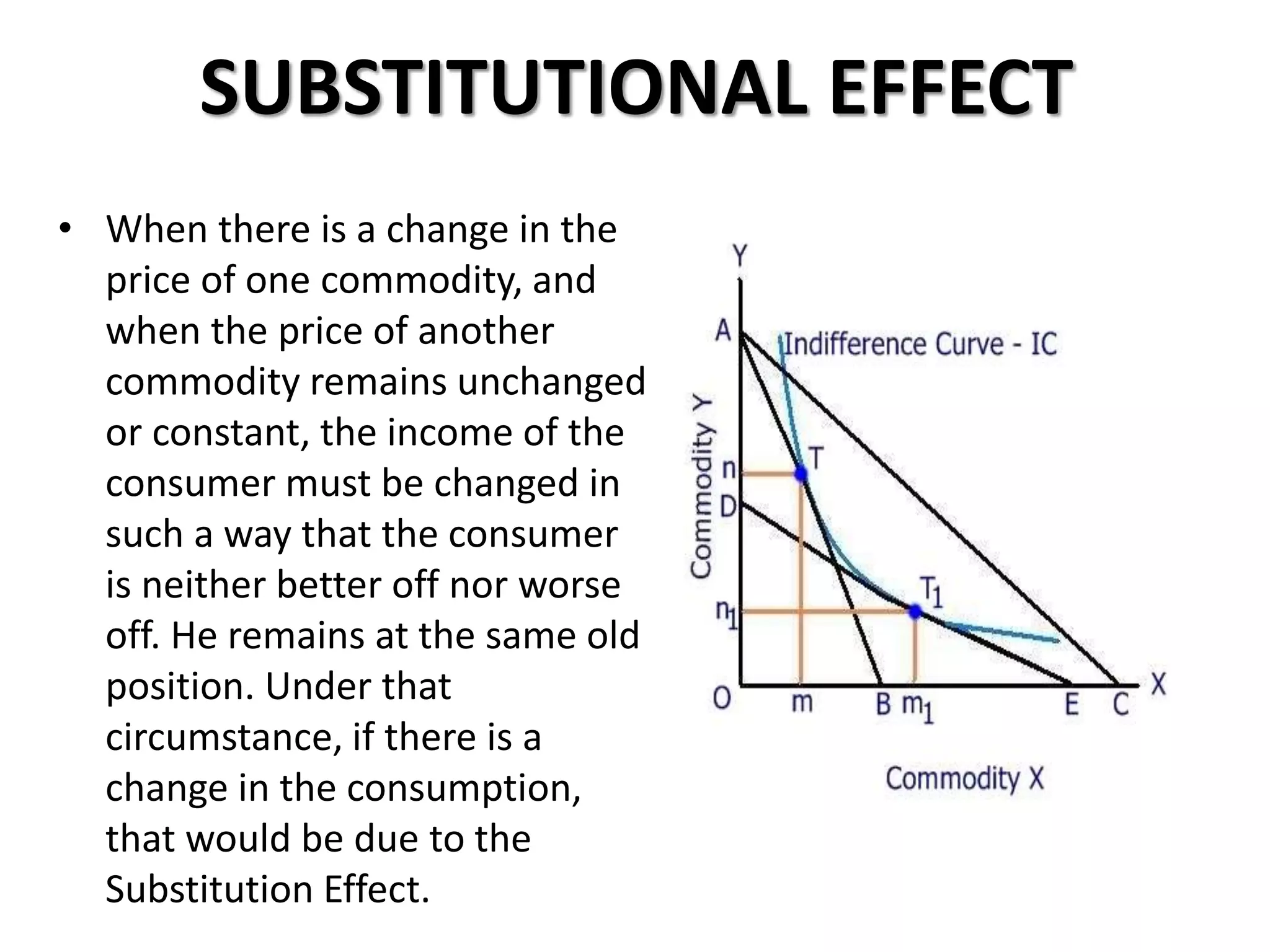
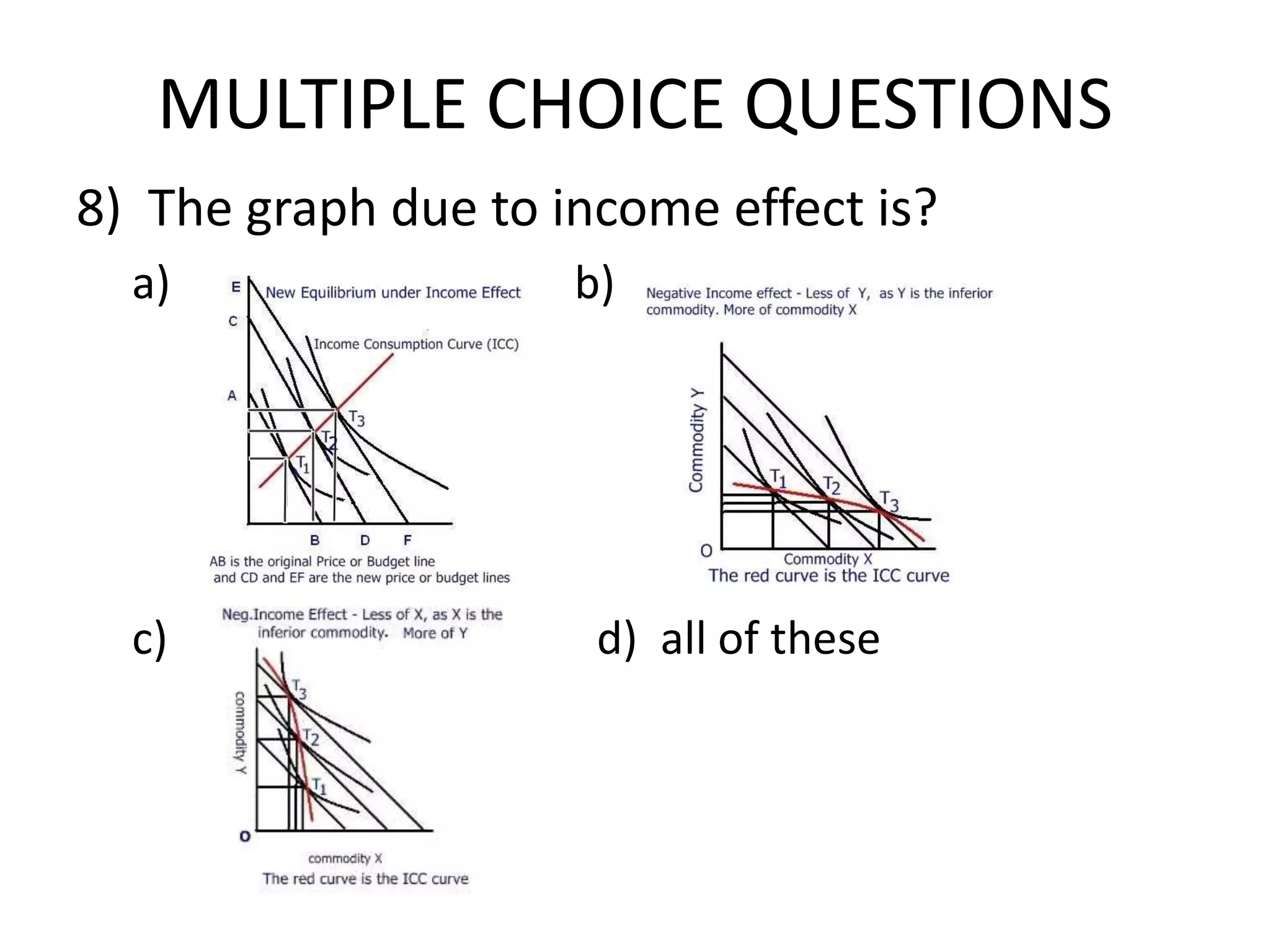
The document defines indifference curves as graphs showing combinations of two goods that provide equal satisfaction to a consumer. Indifference curves are convex and the marginal rate of substitution diminishes along the curve. The budget line shows affordable combinations given prices and income. At the point where the budget line is tangent to the highest indifference curve is the consumer's equilibrium. Price, income, and substitution effects cause the curve to shift as prices or income change.