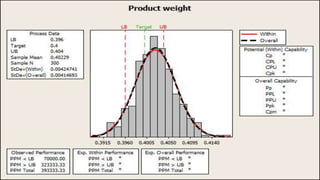
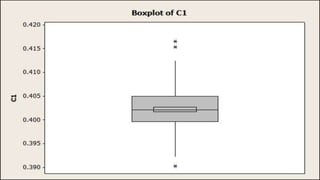
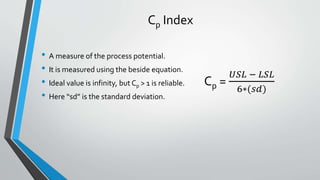
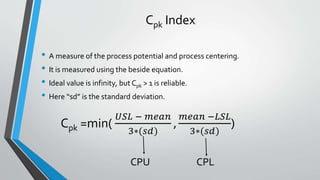
This document discusses process capability analysis. It defines tolerance as the maximum acceptable error for a component. For example, a shaft diameter between 49.5-50.5mm is acceptable. Errors can be common causes, reduced through improved machinery, or special causes that cannot be predicted. Data was collected from a food and drug company showing process testing and statistics. The Cp and Cpk indices measure process potential and centering, with values over 1 indicating a reliable process. Cpk is the minimum value to show where defects are prominent, such as towards the upper or lower specification limits. A centered process has Cp equal to Cpk.