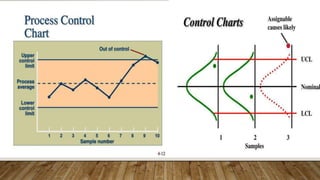
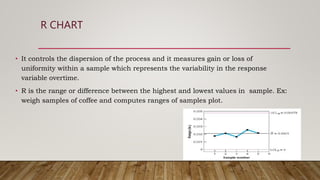
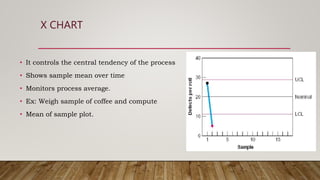
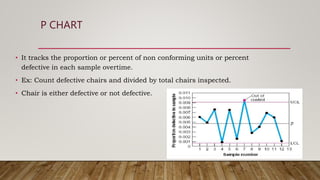
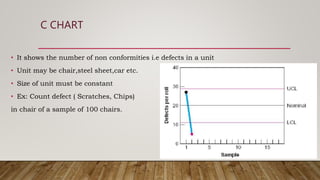
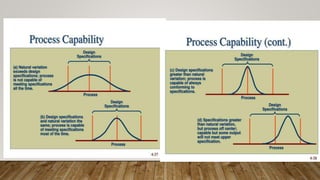
The document discusses Statistical Process Control (SPC), including its definition, importance, types of variations, and tools like control charts. It emphasizes SPC's role in measuring process quality and improving efficiency by reducing variability and inspection costs. Key components include control limits, process capability indices, and types of charts used to monitor and analyze manufacturing performance.