6 sigma
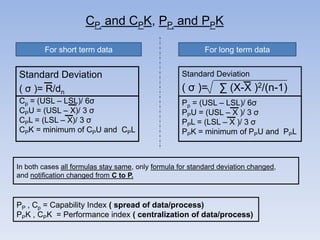
- 1. CP, and CPK, PP, and PPK For short term data For long term data Standard Deviation ( σ )= R/dn Standard Deviation Cp = (USL – LSL)/ 6σ CPU = (USL – X)/ 3 σ CPL = (LSL – X)/ 3 σ CPK = minimum of CPU and CPL Pp = (USL – LSL)/ 6σ PPU = (USL – X )/ 3 σ PPL = (LSL – X )/ 3 σ PPK = minimum of PPU and PPL ( σ )= ∑ (X-X )2/(n-1) In both cases all formulas stay same, only formula for standard deviation changed, and notification changed from C to P. PP , Cp = Capability Index ( spread of data/process) PPK , CPK = Performance index ( centralization of data/process)
- 2. All of 1st understand CP and CPK Graphically Upper specified limit CP LSL 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 CPU Center line Axis Title CPL USL Lower specified limit Desired location of data, centralized. good Cp K 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1011121314151617181920 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10111213141516171819 Axis Title All Data looks to be inside of this yellow curve, mean good spread of data. Mean good CP. But all data is not centralized, it is towards LSL , So we can get high number of rejections, mean – CPK is not good.
- 3. To study, Cp, CpK, Pp , PpK you must know HISTOGRAM . If you don’t know , then 1st study it, and next 4-slides will explain it. And if you already know, then that’s great, just skip, next 4 -slides.
- 4. HISTOGRAM It is used to observe that , how is the process going. Or we can say, use to predict future performance of a process. Any change in process. It is simply a bar chart, from which we get, info of the process- how its going, it is in limits or not. 10 Lower limit Upper limit HISTOGRAM 8 6 4 Trend line 2 0 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
- 5. How to build HISTOGRAM in Excel.(with example) 1.) 1st we have to Study/Collect specifications like -diameter (Data) for 24 products. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 D DIA 6 5 7 10 9 8 4 7 5 6 7 7 8 6 8 7 5 7 8 6 7 7 8 8 2.) Calculate RANGE. RANGE= Maximum value - Minimum value So here , maximum value= 10, Minimum value = 4 So RANGE = 10- 4 =6 3.) Now decide the NUMBER OF CELLS. We have 24 data points , and it fall in 1st group , so- No of cells = 6 Data Points 20 -50 51-100 101-200 201-500 501-1000 Over 1000 Number of Cells 6 7 8 9 10 11-20 4.) Calculate the approximately cell width. Cell width= RANGE/ NO OF CELLS = 6/6 =1 5.) Round Off the cell width. If cell width come in a complicated manner, like 0.34, 0.89 or else , then round off it to , one you want, like : 0.50 or 1 or else.
- 6. 6.) Now construct the Cell Groups with keep in mind cell width( cell width=1) 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Cell width=1 Cell width same for all cell groups =1 7.) Now find number of data values/ Frequencies in each Cell Group. You can do this manually , by counting itself or by using formula .(frequency formula) Mean how many values fall in each group. A B C cell groups frequency 1 2 3 0 2 3 4 1 3 4 5 3 4 5 6 4 5 6 7 8 6 7 8 6 7 8 9 1 8 9 10 1 9 10 11 0 10 11 12 0 (D1:D24) values are on previous page) Go to yellow block, type, =frequency( D1:D24, B1:B10), and press Enter. Then select yellow block and all sky blue blocks, press F2, and press CTRL , SHIFT, ENTER. ( frequency formula will get implement in all sky blue blocks as in yellow block ) And you will get frequency of data values in each group, As in group (7 – 8) , frequency is 6.
- 7. 8.) Now we got frequency data in each group, now we can build Histogram. frequency data is our final data. now select this data a build a bar chart. That’s it. 10 Frequency 8 6 4 2 0 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Dia (mm) Group 4 - 5, show values from 4.1 to 5 Group 5 - 6, show values from 5.1 to 6 So this rule for all groups. Trend line – also give an visual idea of moving process.
- 8. LETS FIND , CP, AND CPK FOR SHORT TERM DATA. sample lot 2 1 2 3 4 5 1 5.5 5.1 5 5.2 5.4 3 5.4 5 5.1 5.3 5.4 4 5.2 5.2 5.4 5.5 5.4 5 5.1 5 5 5.1 5.1 6 7 5.1 5.4 5.2 5 5 5 5.2 5.5 5.5 5 8 5.5 5.1 5 5.4 5.2 5 5 5.5 5.1 5.2 Range(R ) 0.5 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.1 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.1 sample sample sample sample sample 5 5 5 5.5 5.1 9 10 11 12 5 5.2 5.7 5.1 5.4 5 5.1 5 5.2 5 5.3 5.5 5 5.1 5.4 0.4 0.7 13 5.4 5 5.4 5.2 5.4 14 5.2 5.2 5 5 5.1 15 5.2 5 5 5.1 5.4 0.4 0.2 0.4 0.4 average R dn = 2.326 ( for 5 samples, from table 1.1, last slide) σ = R/dn = 0.17196 USL = 6.2, and LSL = 4.2 ( GIVEN) Data Points 20 -50 51-100 101-200 201-500 501-1000 Over 1000 Number of Cells 6 7 8 9 10 11-20
- 9. RANGE = (max-min ) = 0.7 NUMBER OF CELLS = 7 CELL WIDTH = 0.7/7 = 0.1 ROUND OFF = 0.2 CELL GROUP frequency USL = 6.2, and LSL = 4.2 30 0 4 4.2 0 4.2 4.4 0 4.4 4.6 0 15 4.6 4.8 0 10 4.8 5 24 5 5.2 27 5.2 5.4 15 5.4 5.6 8 5.6 5.8 1 5.8 6 0 6 6.2 0 6.2 6.4 0 6.4 6.6 0 USL 4 LSL 3.8 25 20 standard deviation σ = R/dn = 0.171969046 5 0 4 4.2 4.4 4.6 4.8 5 5.2 5.4 5.6 5.8 6 6.2 6.4 6.6 3.8 4 4.2 4.4 4.6 4.8 5 5.2 5.4 5.6 5.8 6 6.2 6.4 • Cp = (USL – LSL)/ 6σ = 1.938333333 • • • CPU = (USL – X)/ 3 σ = 1.957716667 CPL = (LSL – X)/ 3 σ = 1.91895 CPK = minimum of CPU and CPL = 1.9188
- 10. Lets find Pp and PpK for long term data 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 SUM AVERAGE X 5.5 5.1 5 5.2 5.4 5 5 5 5.5 5.1 5.4 5 5.1 5.3 5.4 5.2 5.2 5.4 5.5 5.4 104.7 5.235 (X - X ) (X - X )2 -0.26 0.07022 0.135 0.01823 0.235 0.05523 0.035 0.00123 -0.16 0.02722 0.235 0.05523 0.235 0.05523 0.235 0.05523 -0.26 0.07022 0.135 0.01823 -0.16 0.02722 0.235 0.05523 0.135 0.01823 -0.06 0.00422 -0.16 0.02722 0.035 0.00123 0.035 0.00123 -0.16 0.02722 -0.26 0.07022 -0.16 0.02722 0.6855 ∑(X-X )2 Standard Deviation ( σ )= ∑ (X-X )2/(n-1) Data Points 20 -50 51-100 101-200 201-500 501-1000 Over 1000 = 0.6855/(20-1) = 0.1899 Number of Cells 6 7 8 9 10 11-20
- 11. Range = (max – min ) = 0.5 Number of cells = 6 Cell width = 0.5/6 = 0.08 Round off cell width = 0.2 USL= 6.2 , LSL= 4.2 (GIVEN) cell group frequency 0 0 0 0 5 6 6 3 0 0 0 0 0 7 6 5 USL 4.2 4.4 4.6 4.8 5 5.2 5.4 5.6 5.8 6 6.2 6.4 6.6 LSL 4 4.2 4.4 4.6 4.8 5 5.2 5.4 5.6 5.8 6 6.2 6.4 4 3 2 1 0 4.2 4.4 4.6 4.8 5 5.2 5.4 5.6 5.8 6 6.2 6.4 6.6 4 4.2 4.4 4.6 4.8 5 5.2 5.4 5.6 5.8 6 6.2 6.4 Standard Deviation ( σ )= ∑ (X-X )2/(n-1) = 0.6855/(20-1) = 0.1899 Pp = (USL – LSL)/ 6σ = 1.75 PPU = (USL – X )/ 3 σ = 1.69 PPL = (LSL – X )/ 3 σ = 1.81 PPK = minimum of PPU and PPL = 1.81
- 12. CP 0.5 0.75 1 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 2 Ppk CPK PPM 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 2 133,614 24,449 2,700 967 318 96 27 7 2 0.34 0.067 0.012 0.0018 PPM – Parts rejected Per Million PPM PPM 500,000 382,089 274,253 184,060 115,070 66,807 35,930 17,864 8,198 3,467 1,350 483 159 48 13 3 1 0.170 0.033 0.006 0.001
- 13. Table 1.1 X-bar Chart Sample Size = N for sigma R Chart Constants LCL UPL S Chart Constants LCL UCL A2 A3 dn D3 D4 B3 B4 2 3 4 1.88 1.023 0.729 2.659 1.954 1.628 1.128 1.693 2.059 0 0 0 3.267 2.574 2.282 0 0 0 3.267 2.568 2.266 5 0.577 1.427 2.326 0 2.114 0 2.089 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 0.483 0.419 0.373 0.337 0.308 0.285 0.266 0.249 0.235 0.223 0.212 0.203 0.194 0.187 0.18 0.173 0.167 0.162 0.157 0.153 1.287 1.182 1.099 1.032 0.975 0.927 0.886 0.85 0.817 0.789 0.763 0.739 0.718 0.698 0.68 0.663 0.647 0.633 0.619 0.606 2.534 2.704 2.847 2.97 3.078 3.173 3.258 3.336 3.407 3.472 3.532 3.588 3.64 3.689 3.735 3.778 3.819 3.858 3.895 3.931 0 0.076 0.136 0.184 0.223 0.256 0.283 0.307 0.328 0.347 0.363 0.378 0.391 0.403 0.415 0.425 0.434 0.443 0.451 0.459 2.004 1.924 1.864 1.816 1.777 1.744 1.717 1.693 1.672 1.653 1.637 1.622 1.608 1.597 1.585 1.575 1.566 1.557 1.548 1.541 0.03 0.118 0.185 0.239 0.284 0.321 0.354 0.382 0.406 0.428 0.448 0.466 0.482 0.497 0.51 0.523 0.534 0.545 0.555 0.565 1.97 1.882 1.815 1.761 1.716 1.679 1.646 1.618 1.594 1.572 1.552 1.534 1.518 1.503 1.49 1.477 1.466 1.455 1.445 1.435
- 14. • That’s it . • I Hope you got it. • Have any question, please let me know.
