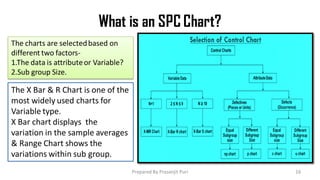
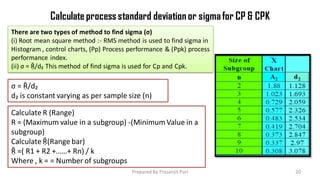
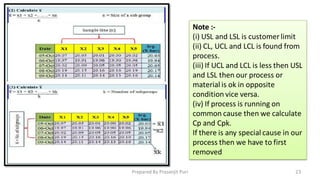
The document explains Statistical Process Control (SPC), a method used to reduce process variation through statistical techniques. It covers concepts like process capability (Cp and Cpk), variability, and the development of SPC by Dr. Walter A. Shewhart in the 1920s, highlighting its importance for continuous improvement in quality and efficiency. Additionally, it describes how to measure and analyze process performance using control charts and sigma levels.