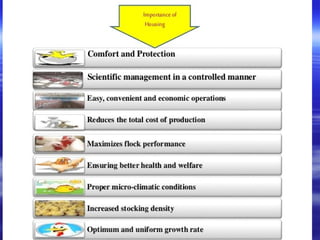
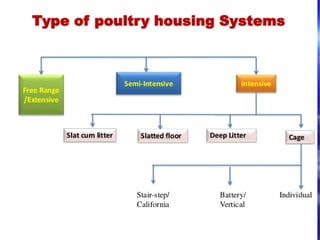
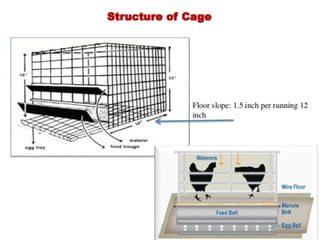
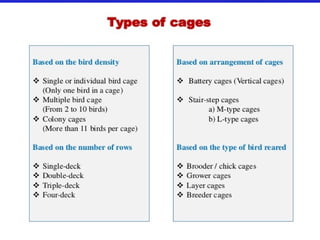
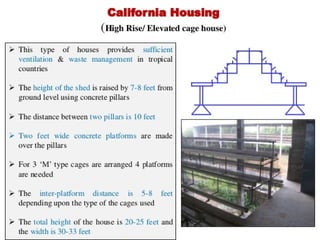
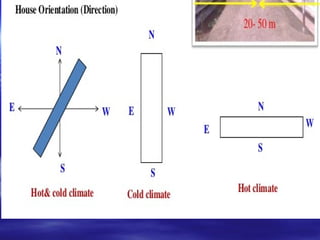
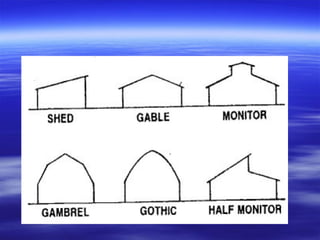
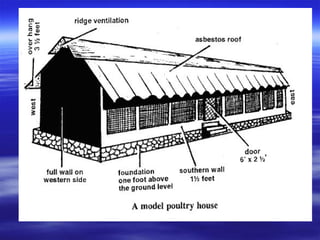
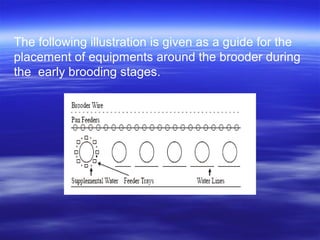
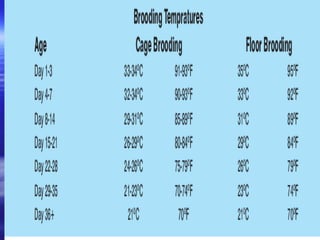
This document discusses different types of poultry housing systems and their characteristics. It describes brooder, grower, layer and breeder houses used for rearing chicks, growing birds, and egg-laying hens. Deep litter and cage systems are covered in detail, along with their advantages like disease control and easier management, and disadvantages such as lower density and foot problems. Factors in selecting a housing system include land costs and climate. The folding unit and intensive systems are also summarized briefly.