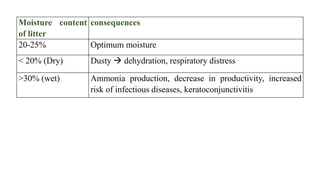
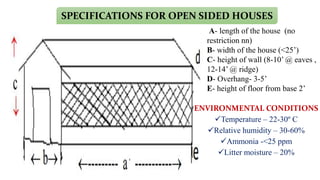
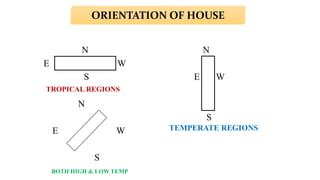
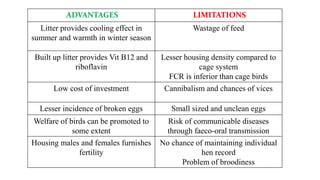
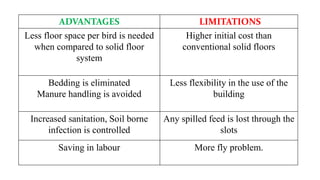
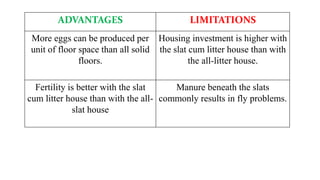
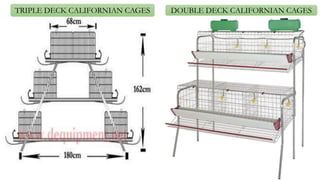
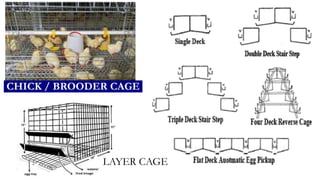
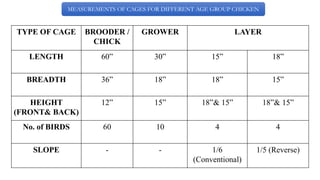
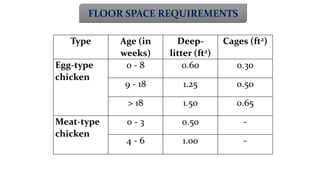
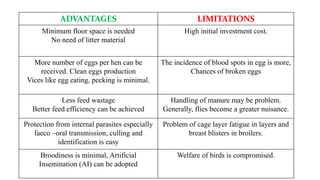
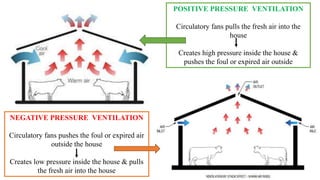
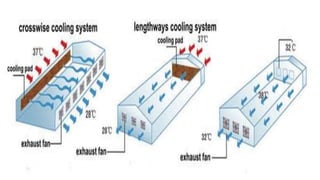
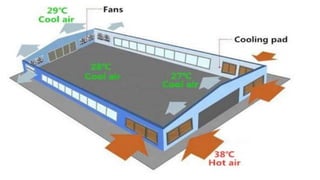
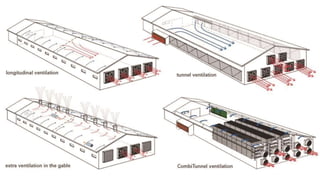
The document provides a comprehensive overview of various housing systems for intensive poultry rearing, including deep litter, slatted floors, and cage systems. It discusses the advantages and limitations of each system, emphasizing factors such as site selection, cost, management practices, and implications for bird welfare and productivity. The content also covers construction specifications, environmental conditions, and the importance of proper ventilation and moisture management in poultry housing.