1. Eggs are formed in the ovaries of female animals and consist of an ovum surrounded by membranes and a shell. They provide nutrients like protein, vitamins, minerals, and fats.
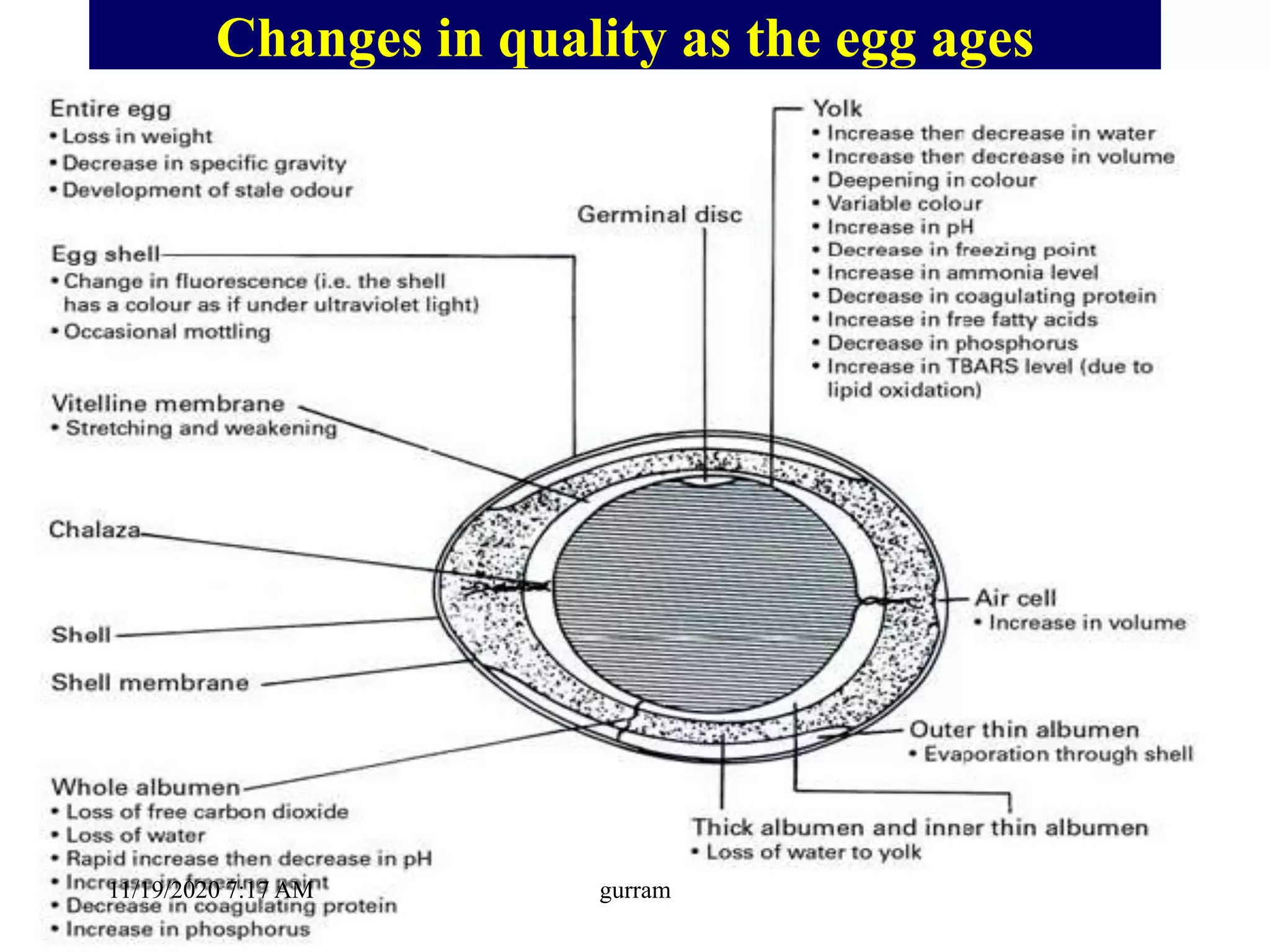
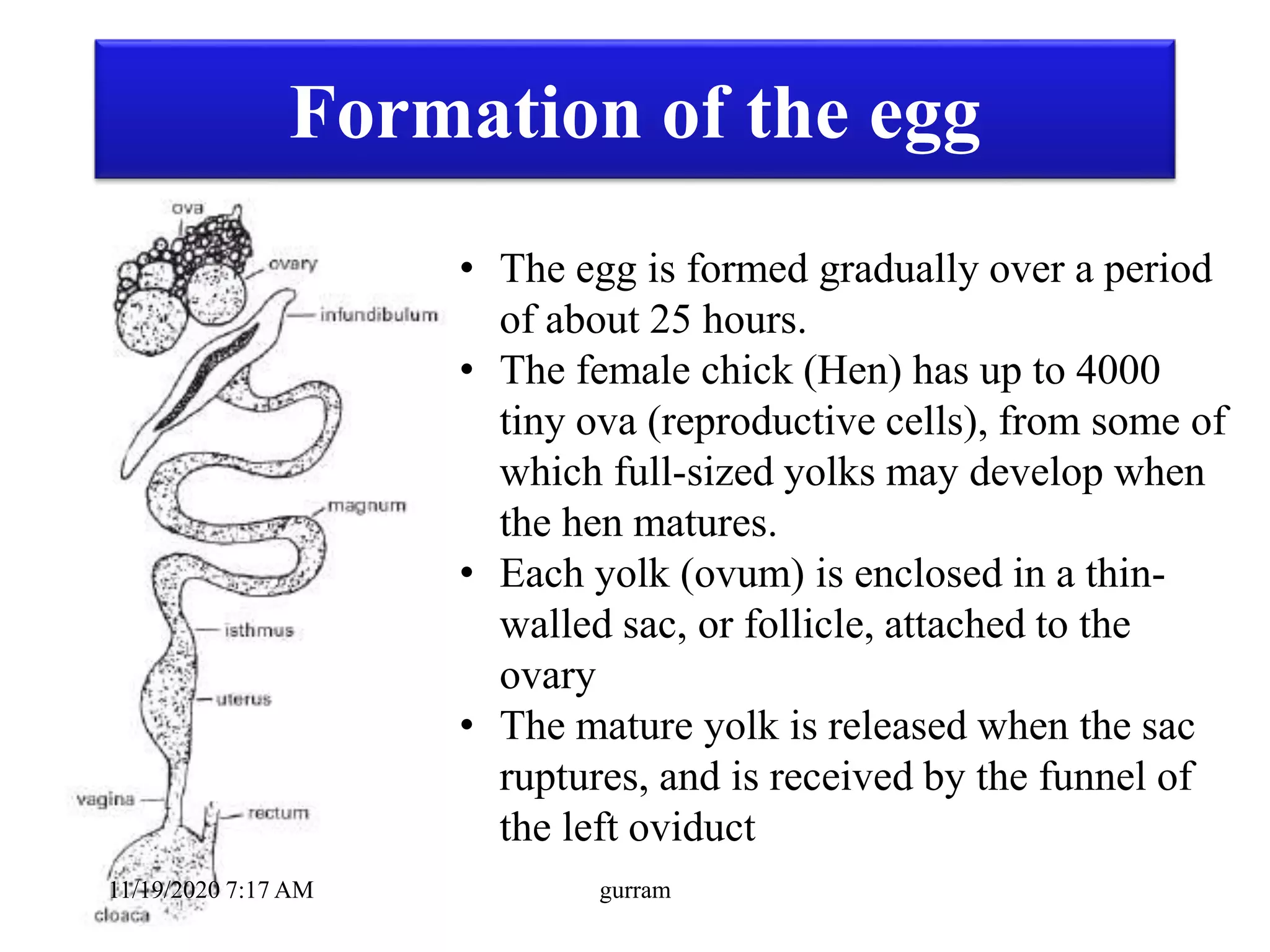
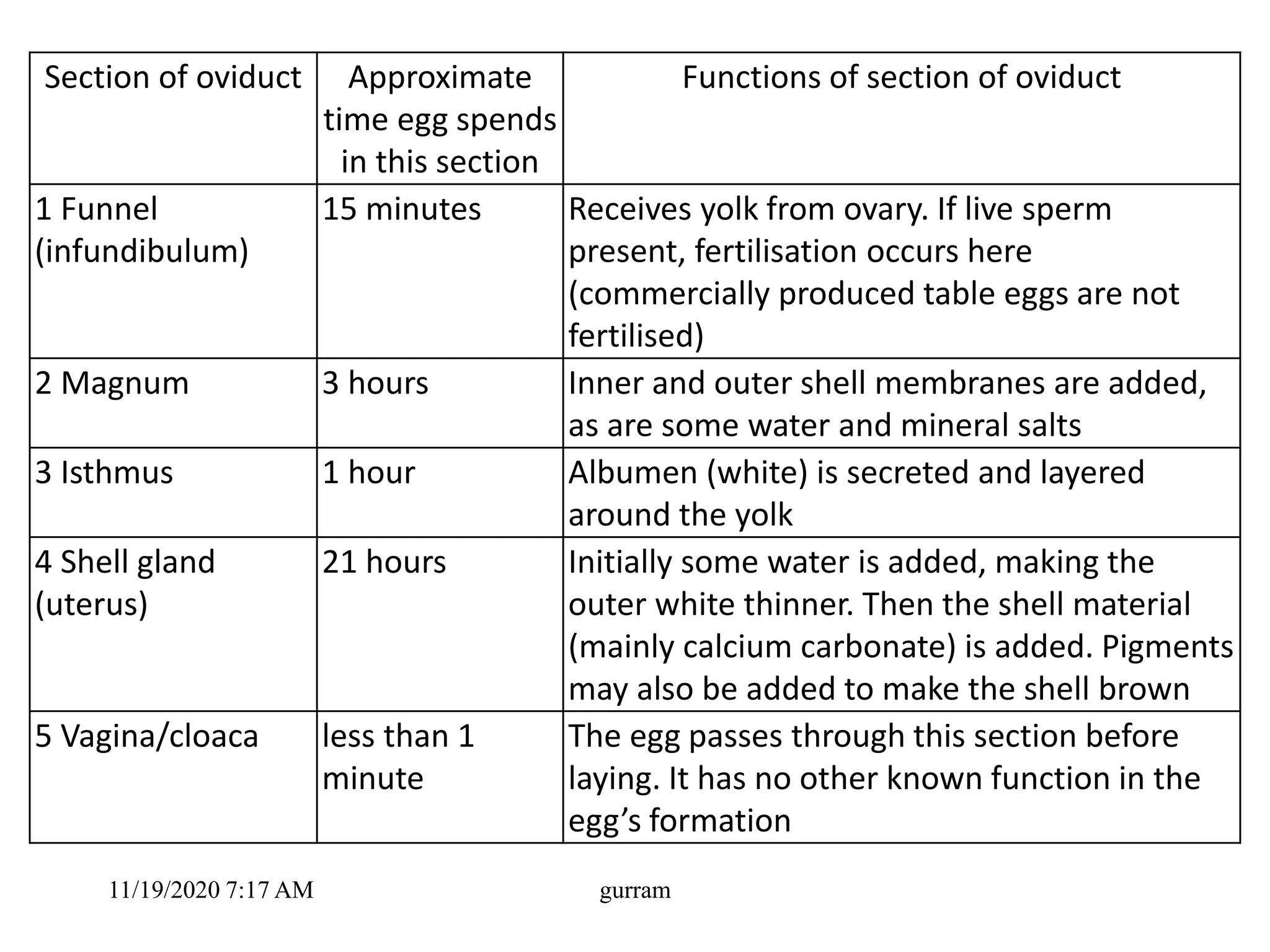
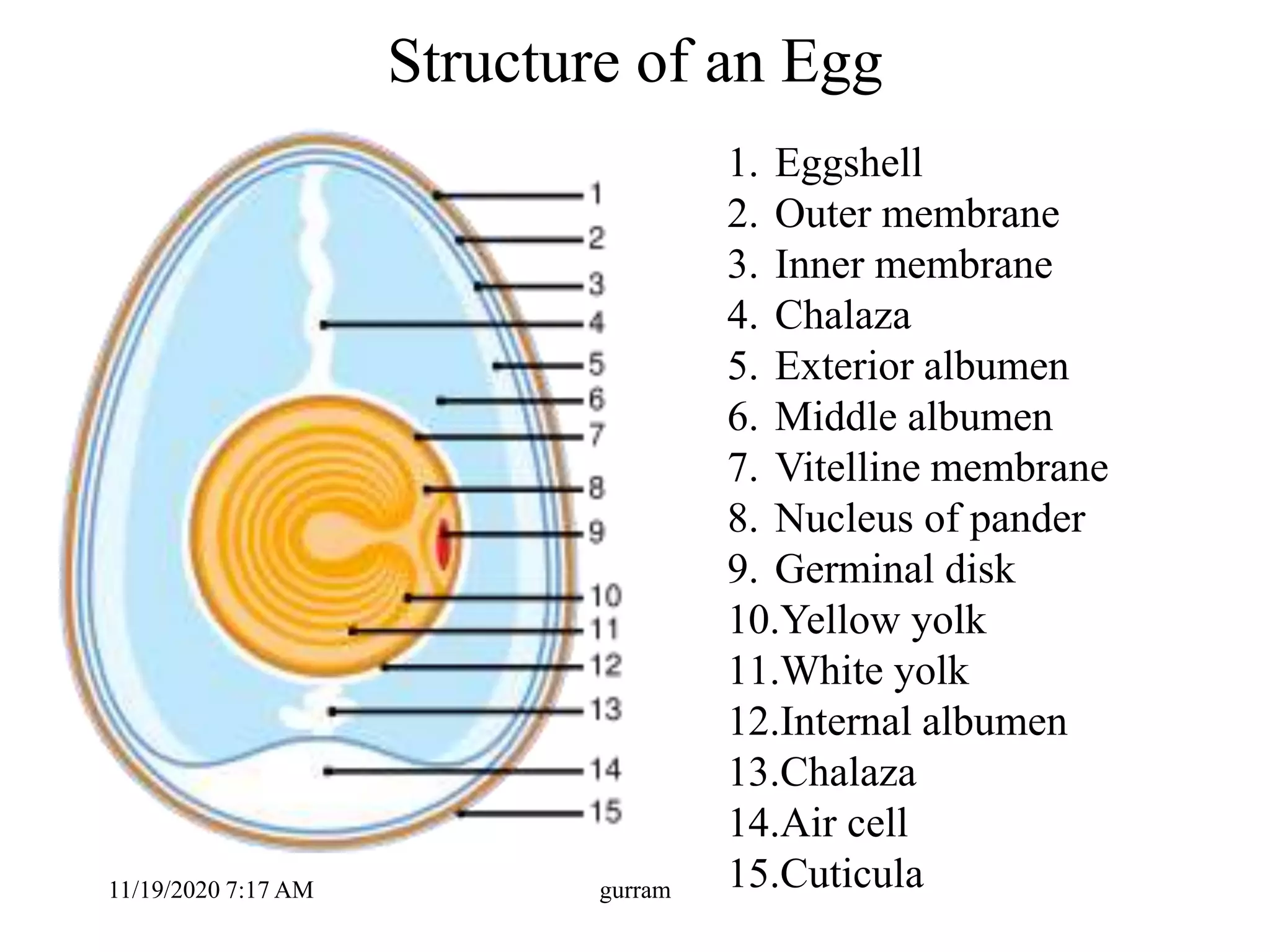
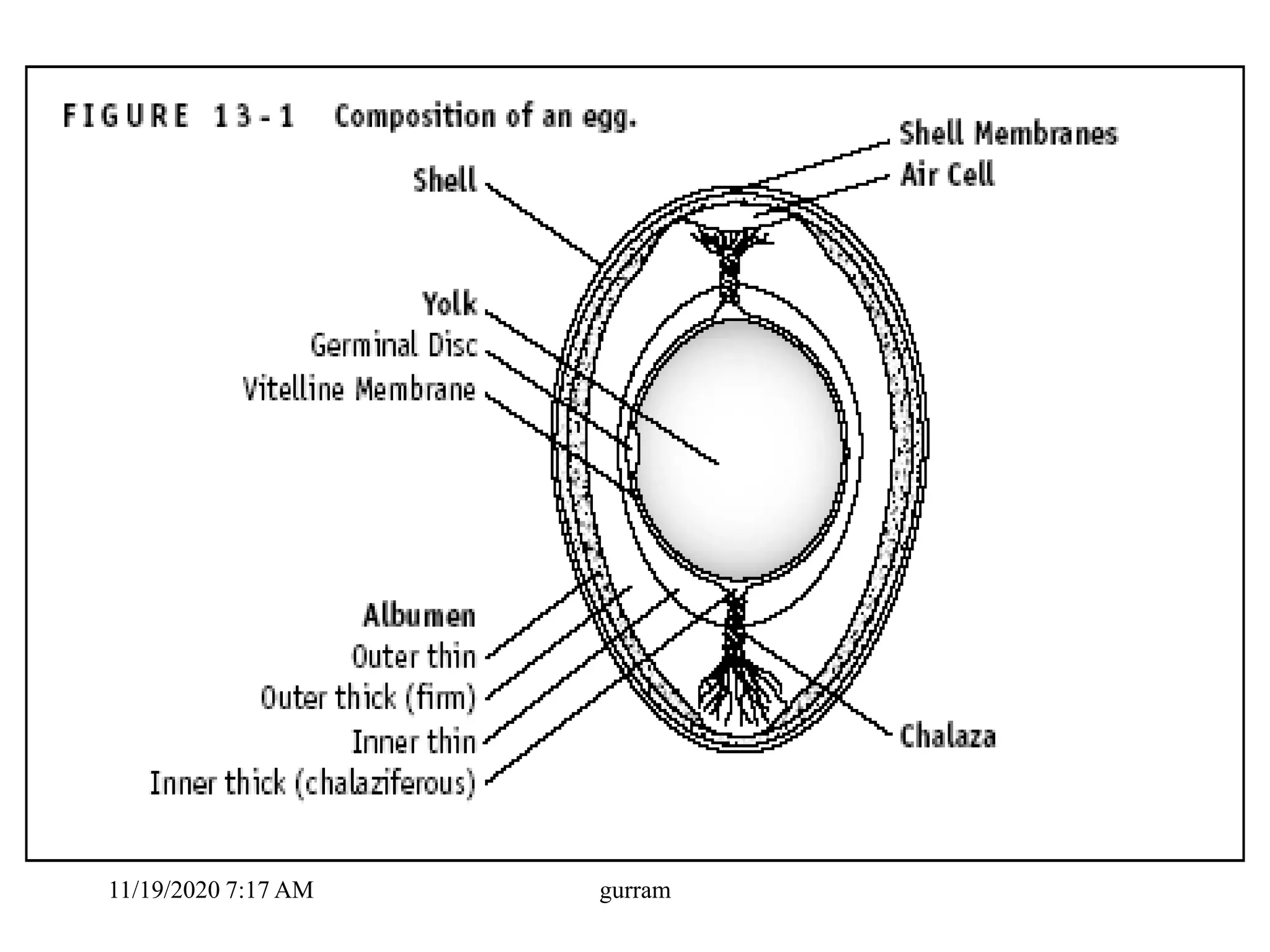
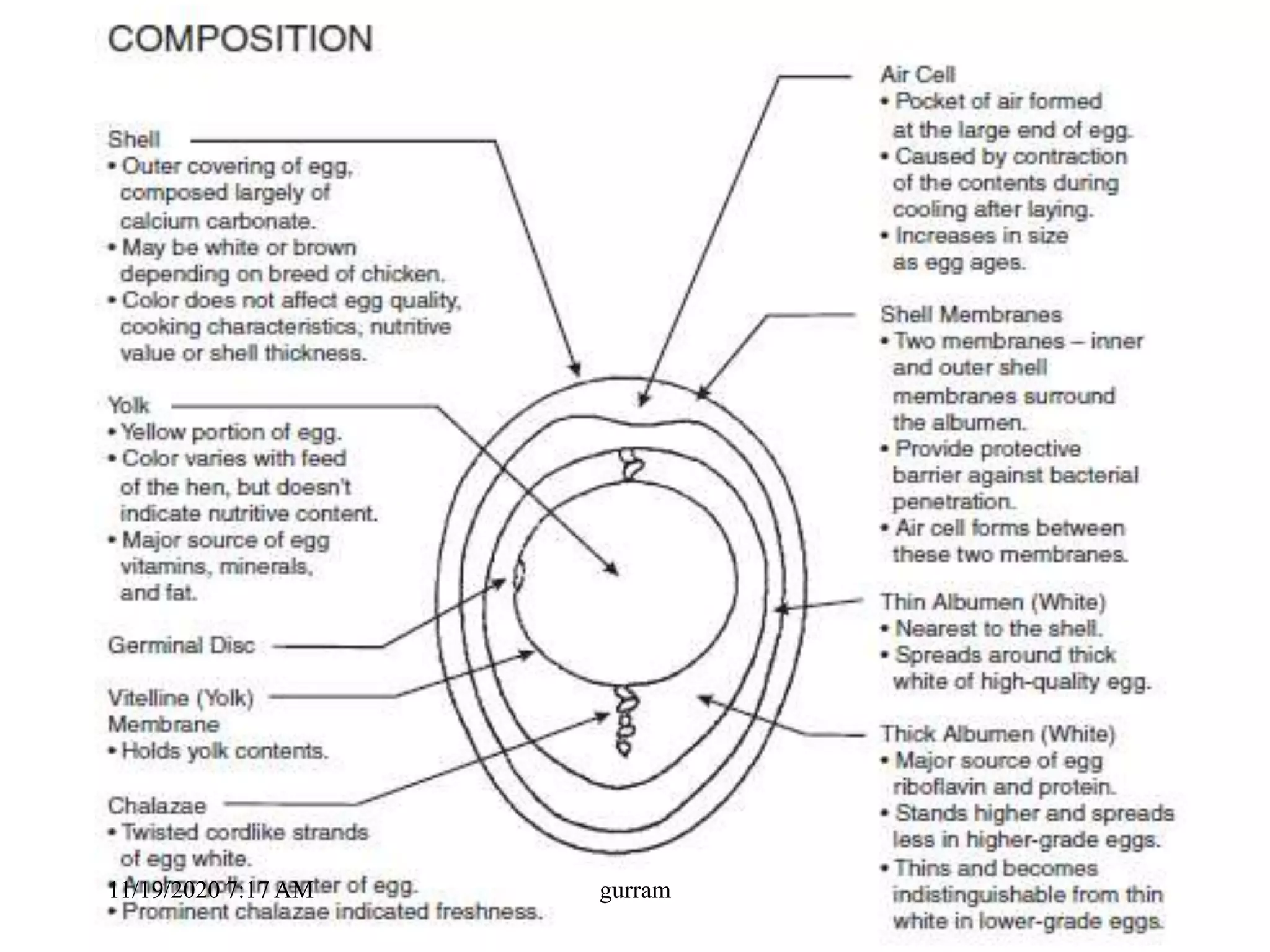
2. The key parts of an egg include the shell, membranes, albumen or egg white, yolk, and chalazae. The hen's oviduct adds different components over 25 hours to form the egg.
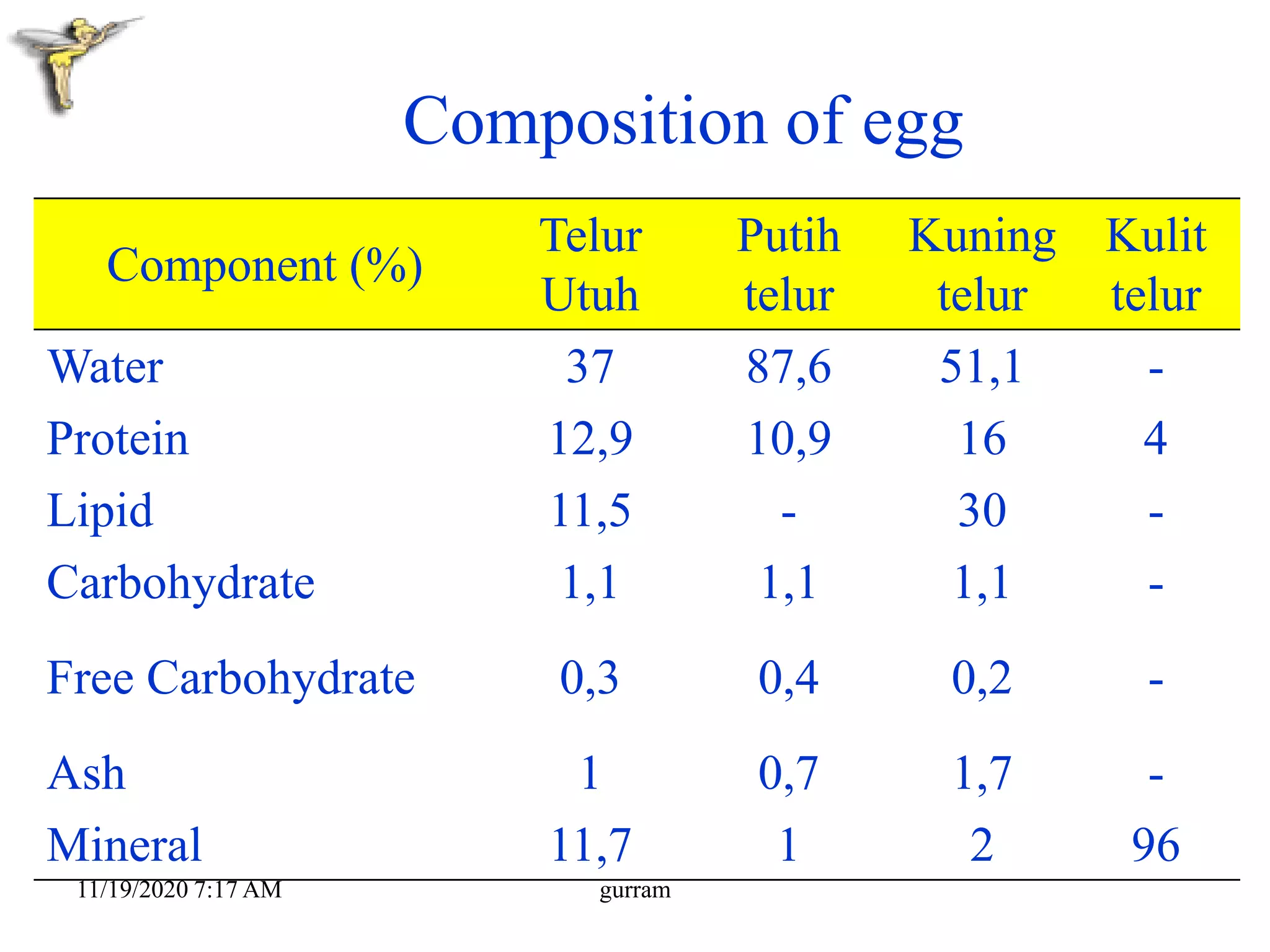
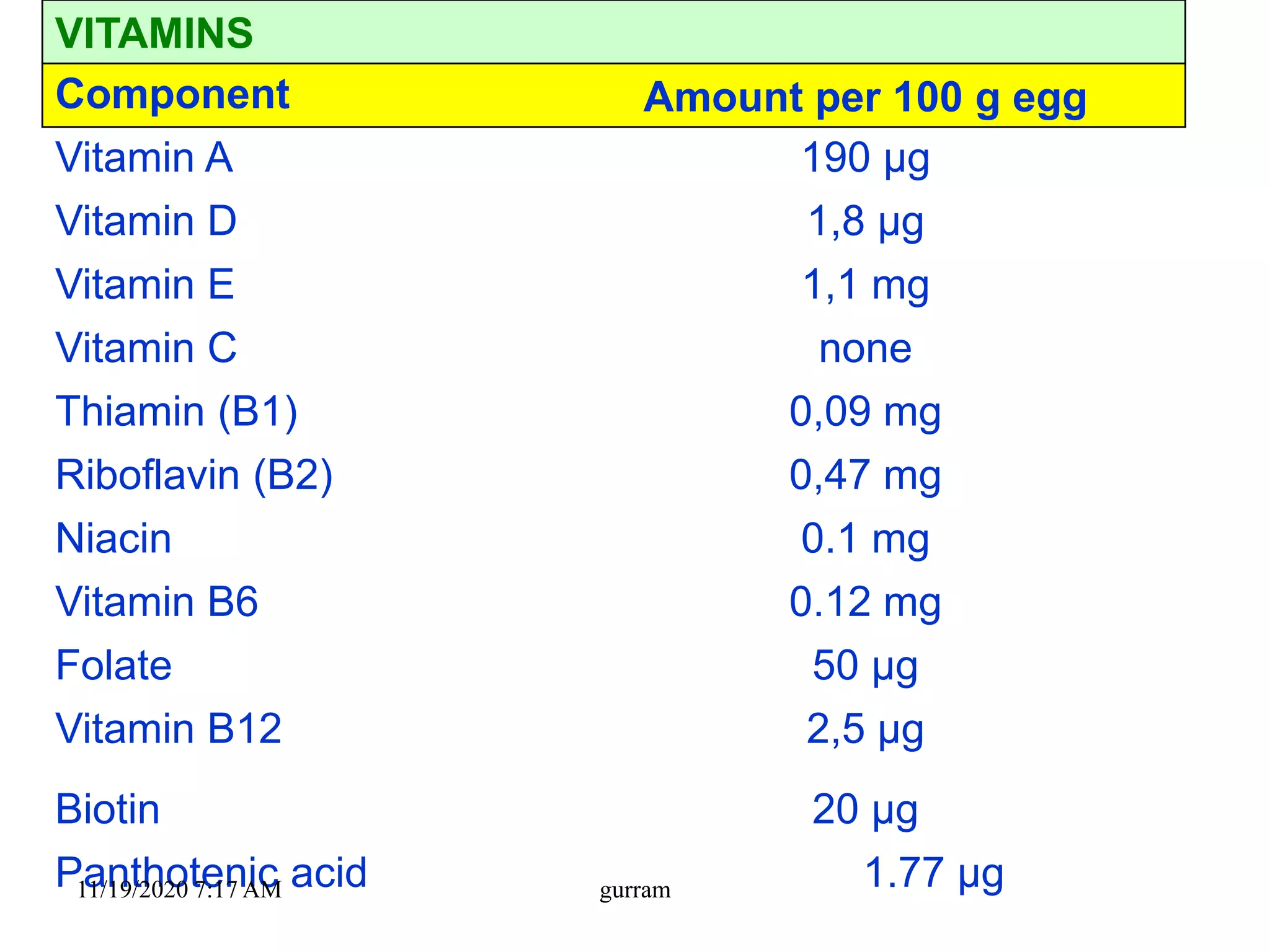
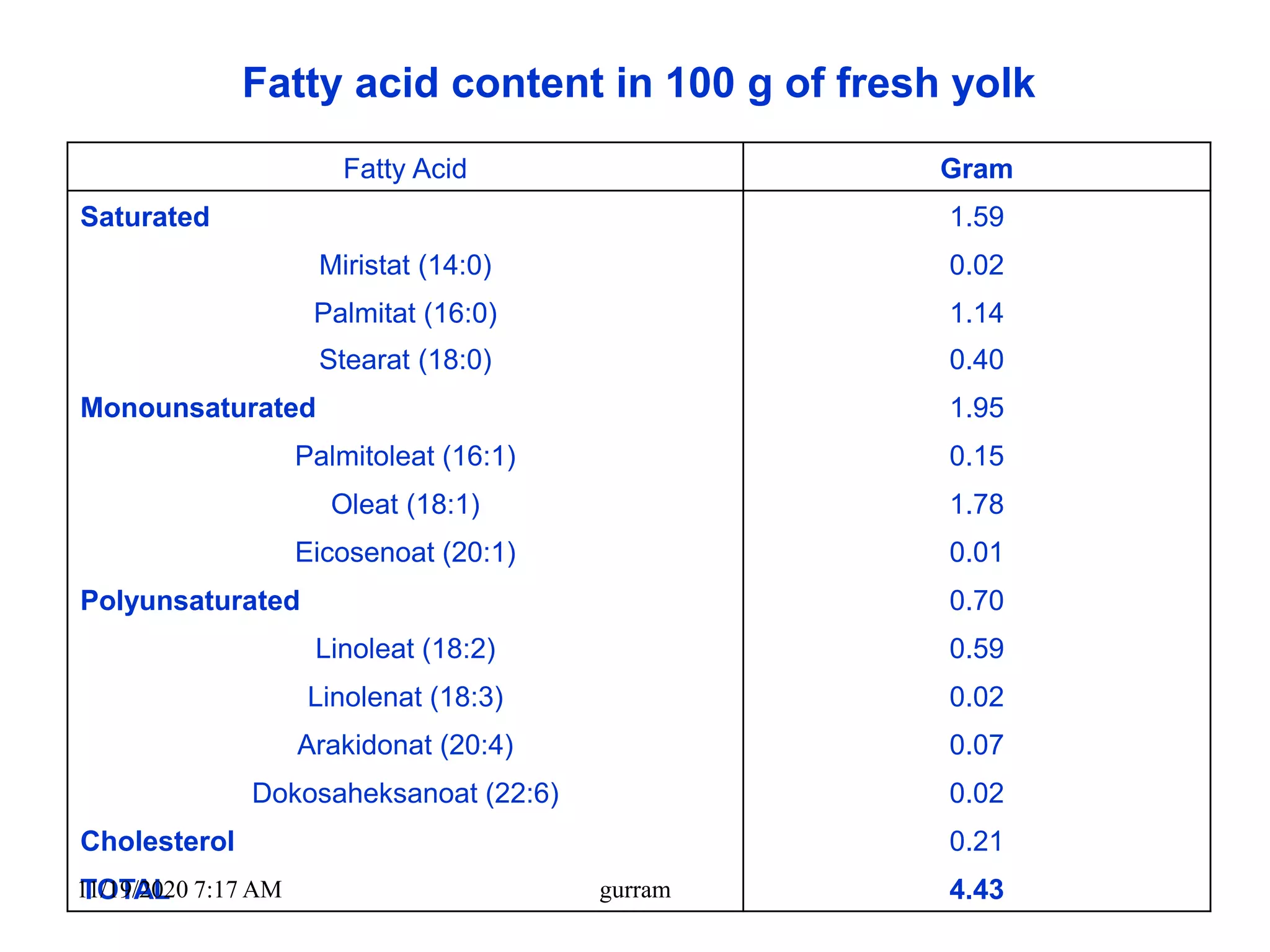
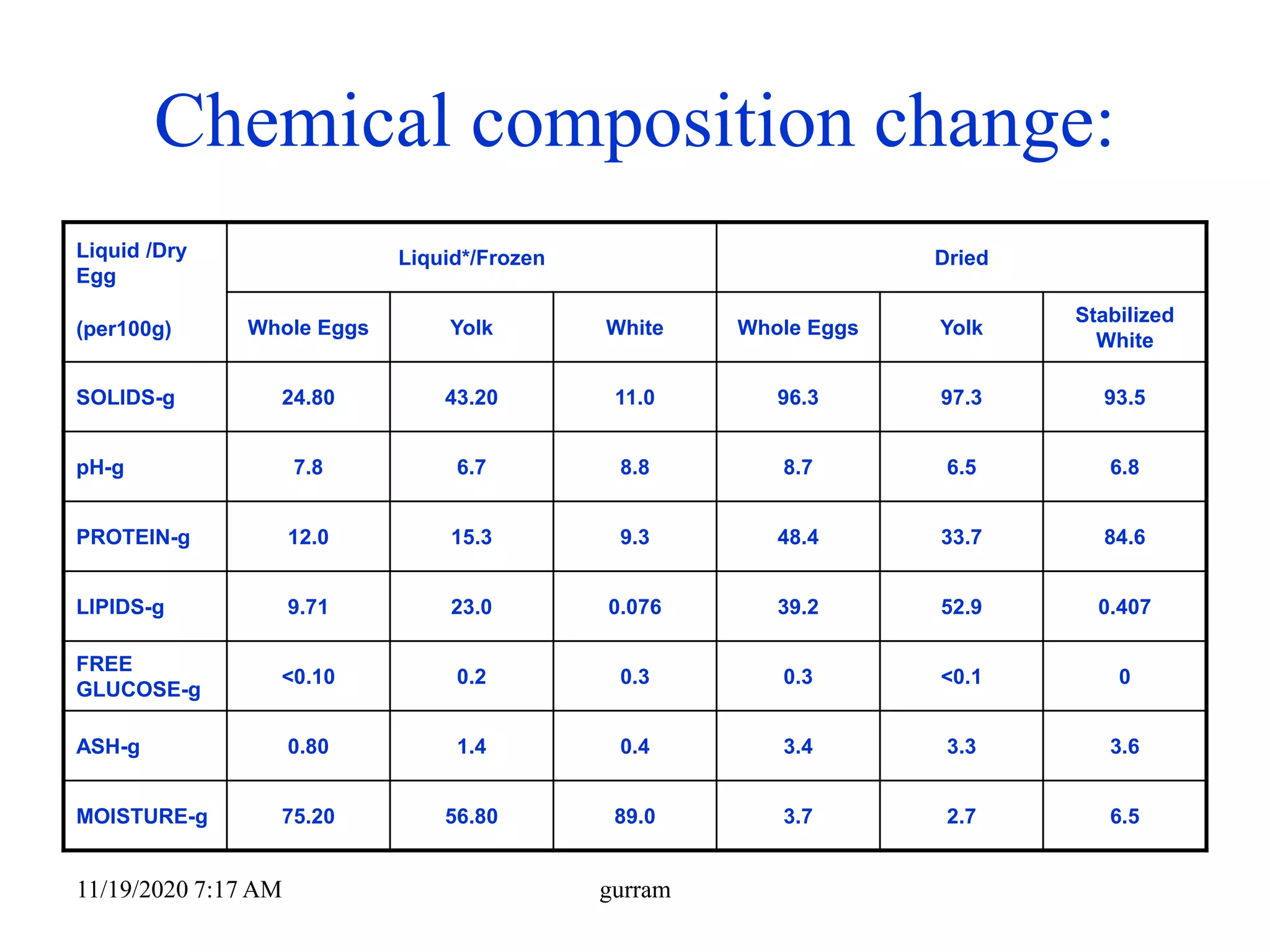
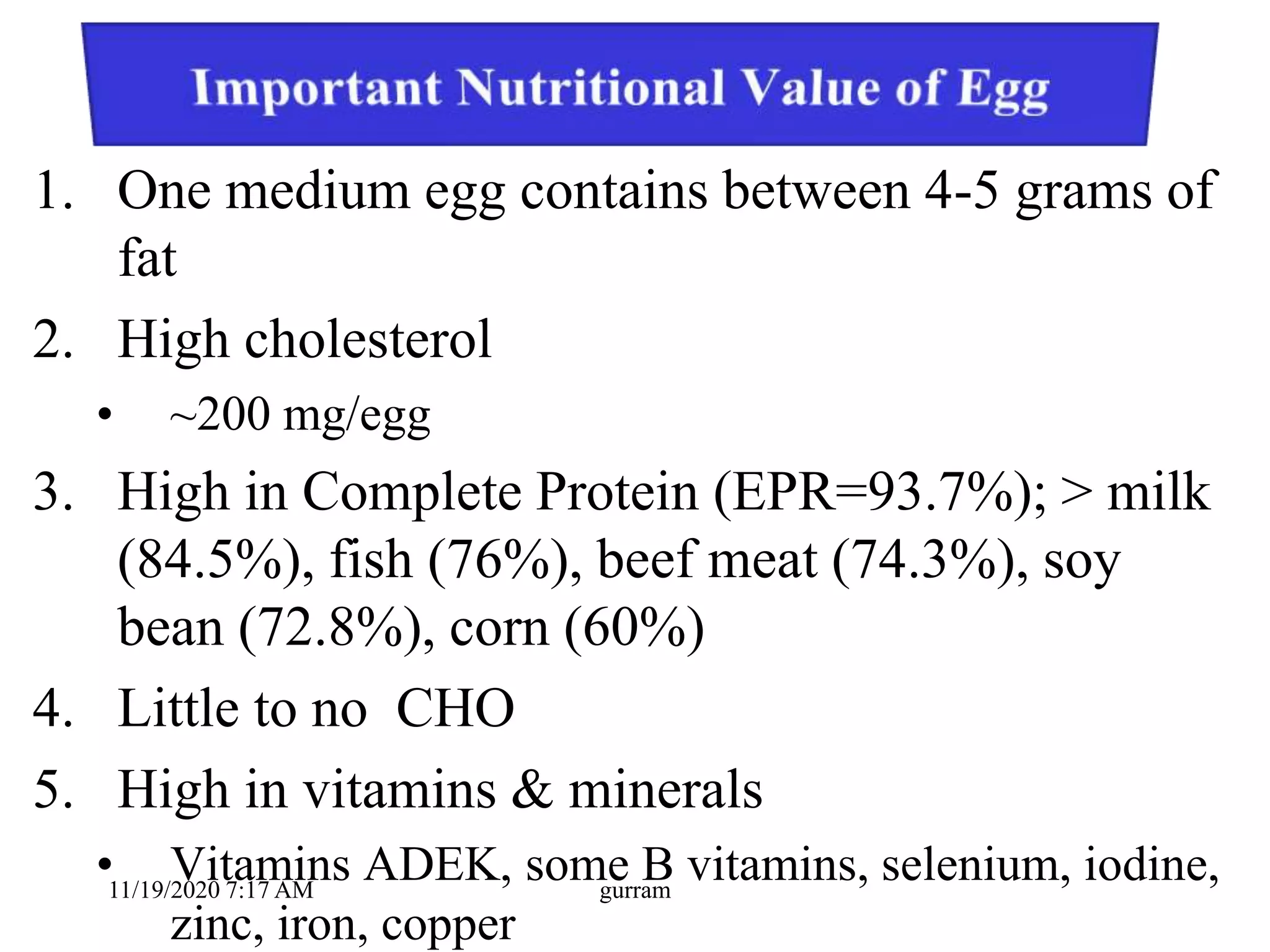
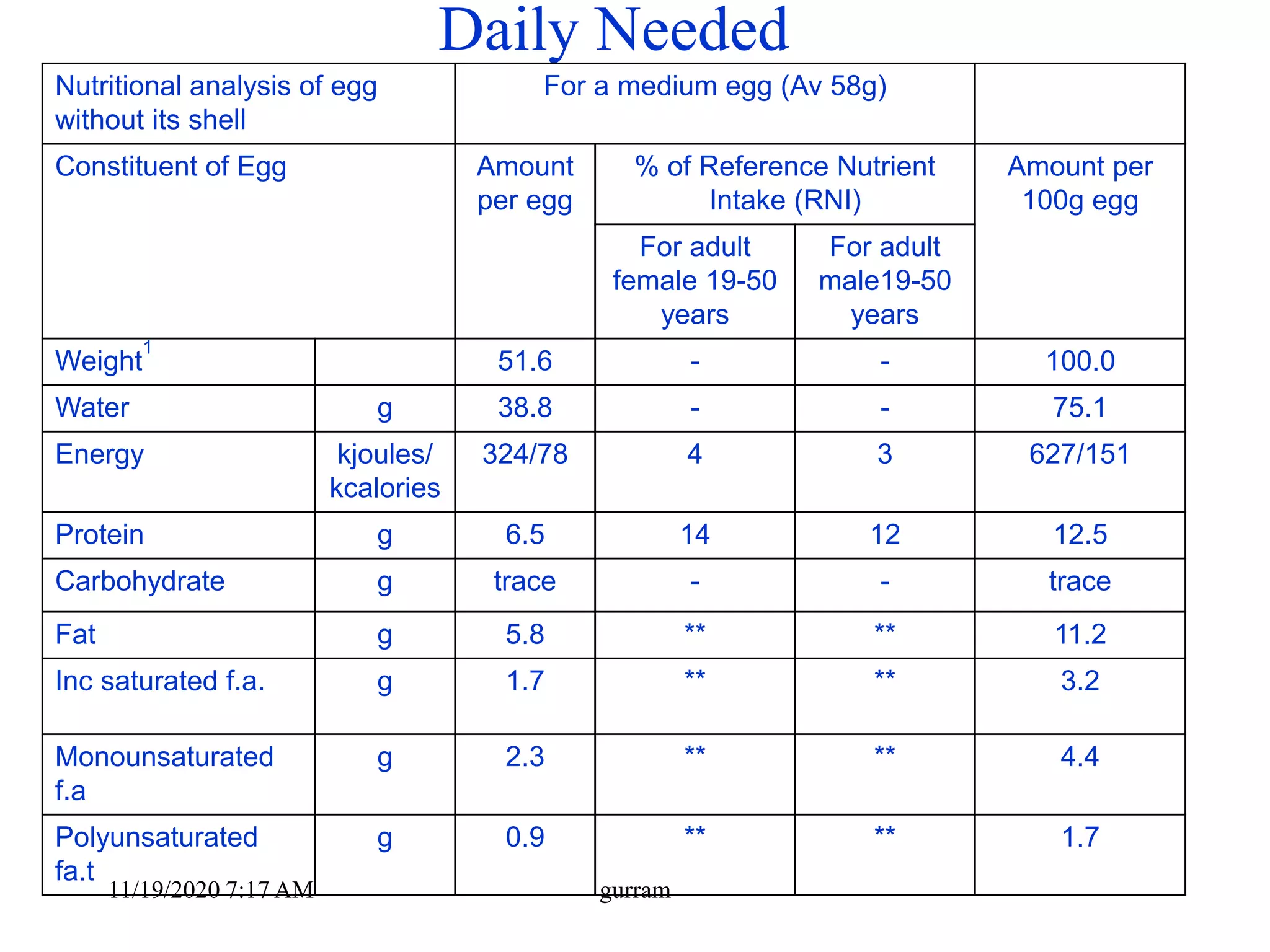
3. Eggs are a highly nutritious food, providing high-quality protein along with vitamins, minerals, and fats. One medium egg contains around 6 grams of protein and 78 kilocalories.






































































![Haugh Unit
• Haugh unit (HU)
HU= 100 log [h-(√G(3w0.37-100)+1,9]
100
HU= Haugh unit
h = heigh of thick albumen (mm)
G= 32,2
w= whole egg weight (g)
Fresh egg: HU=100
Good quality: HU = 75; acceptable until 50
Bad quality (Spoiled egg): HU < 50
11/19/2020 7:17 AM gurram](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/importanceofeggandmeat-201119071740/75/Importance-of-egg-and-meat-egg-quality-value-addition-and-egg-products-98-2048.jpg)