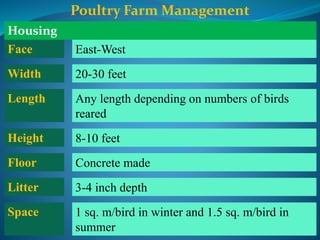
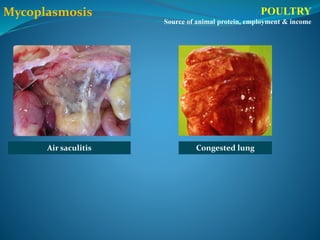
This document provides information on poultry farming and management. It discusses the main species of birds reared for economic benefits, including chickens, ducks, geese, quails and pigeons. It outlines the benefits of poultry farming such as low capital requirements and high returns. It also describes important considerations for poultry housing, drinking/feeding systems, chick quality, and brooding management. Finally, it discusses common poultry diseases caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites, as well as deficiency diseases, and provides treatment recommendations.