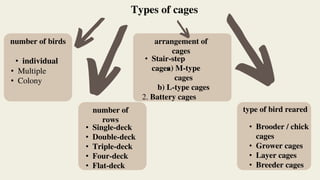
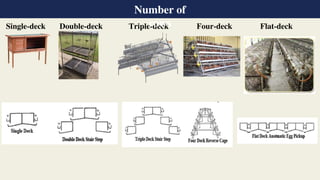
The document discusses various cage systems used in poultry farming, including types of cages and their specifications for different bird rearing stages. It highlights the negative impact of battery cages on chickens' welfare and natural behaviors, leading to psychological and physical health issues. It also mentions regulations and advantages and disadvantages of using cage systems in poultry production.