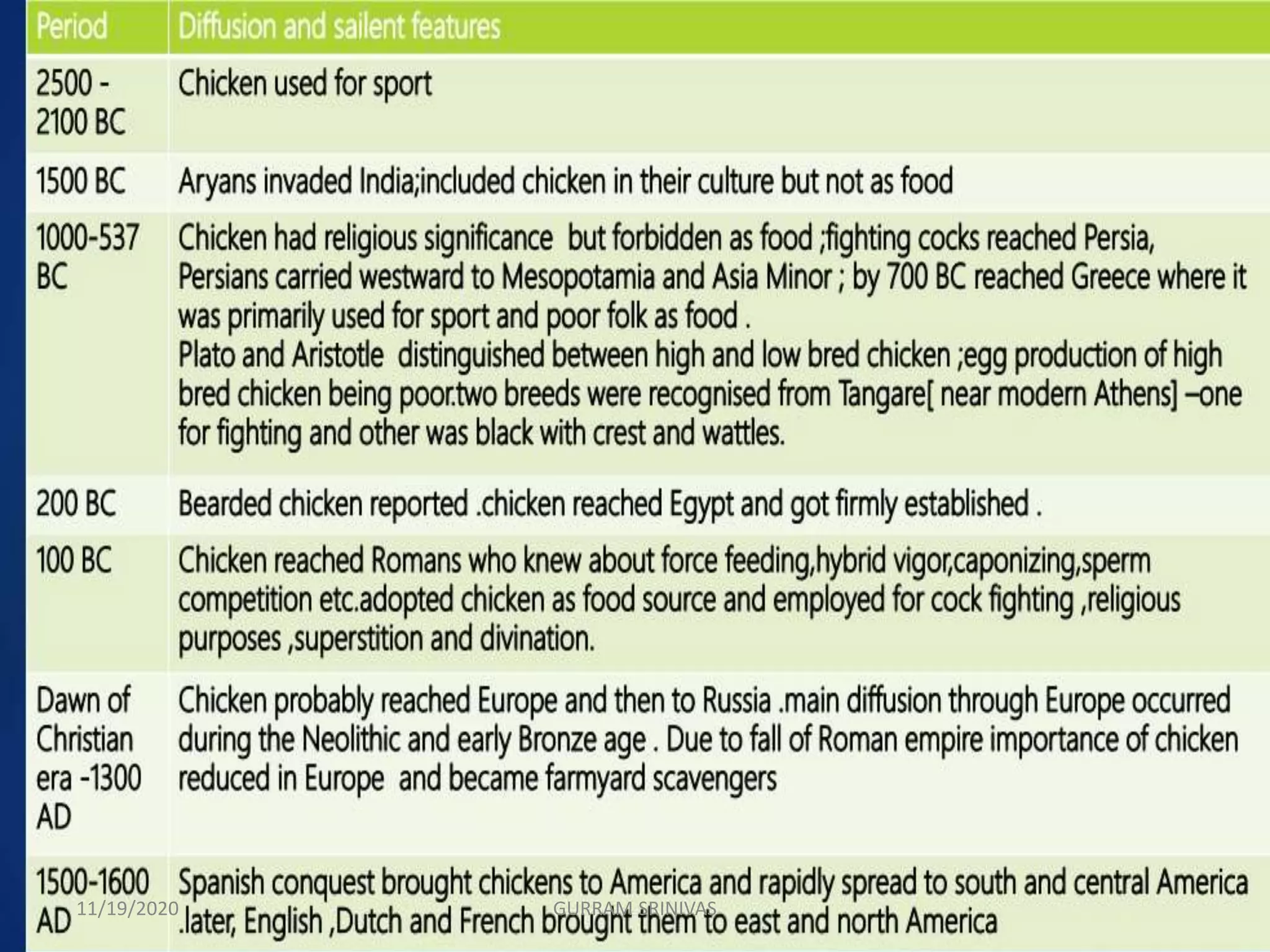
(1) The document discusses the origin and genetic classification of various poultry species. It notes that chickens were first domesticated around 5400 BC in China, while other species like geese and ducks were domesticated in China and Egypt around 2500 BC.
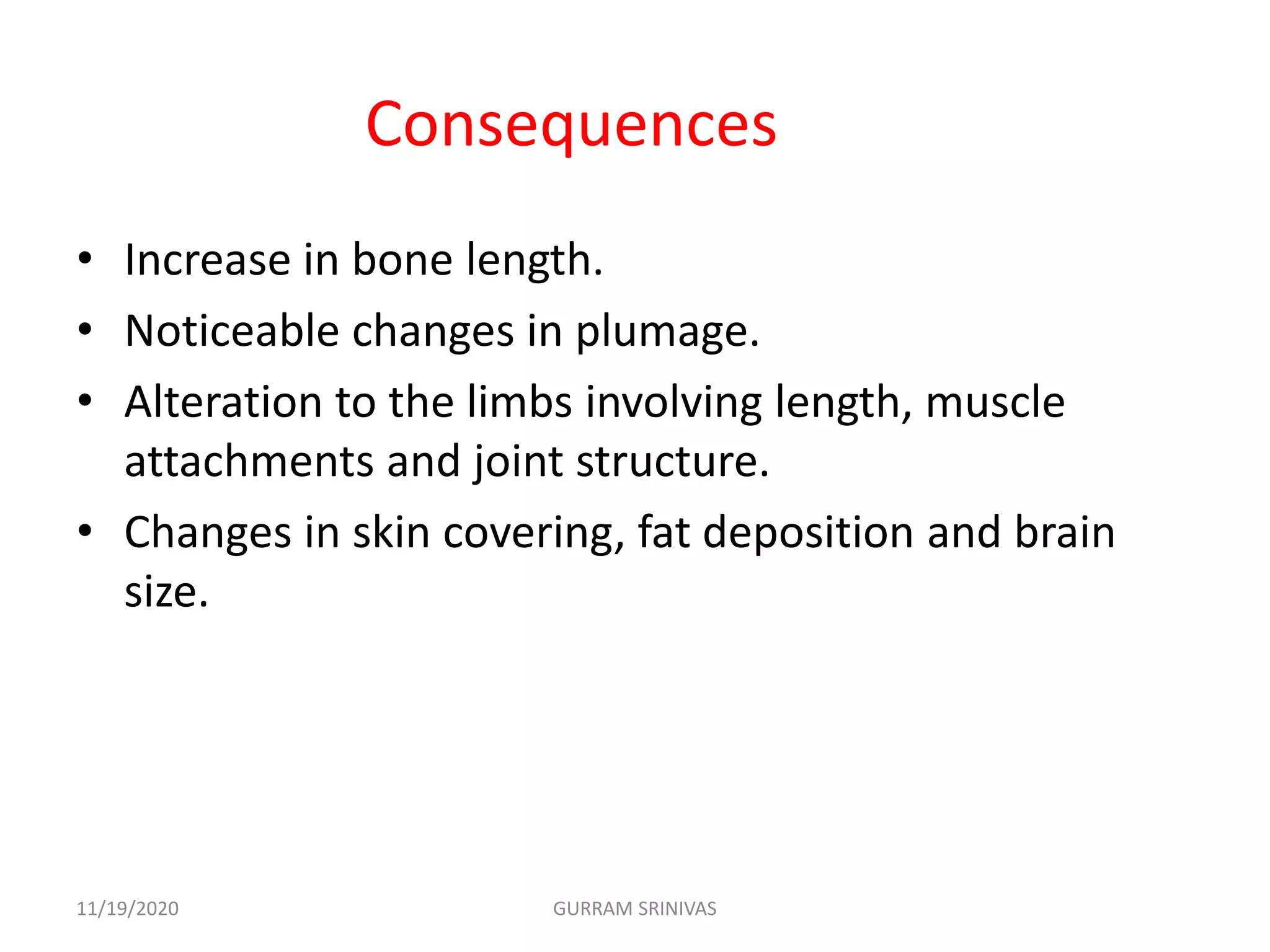
(2) Over time, domestication led to changes in poultry like increased reproduction in captivity and alterations to physical traits. Initially, birds were primarily used for cultural purposes and entertainment, but later became an important human food source.
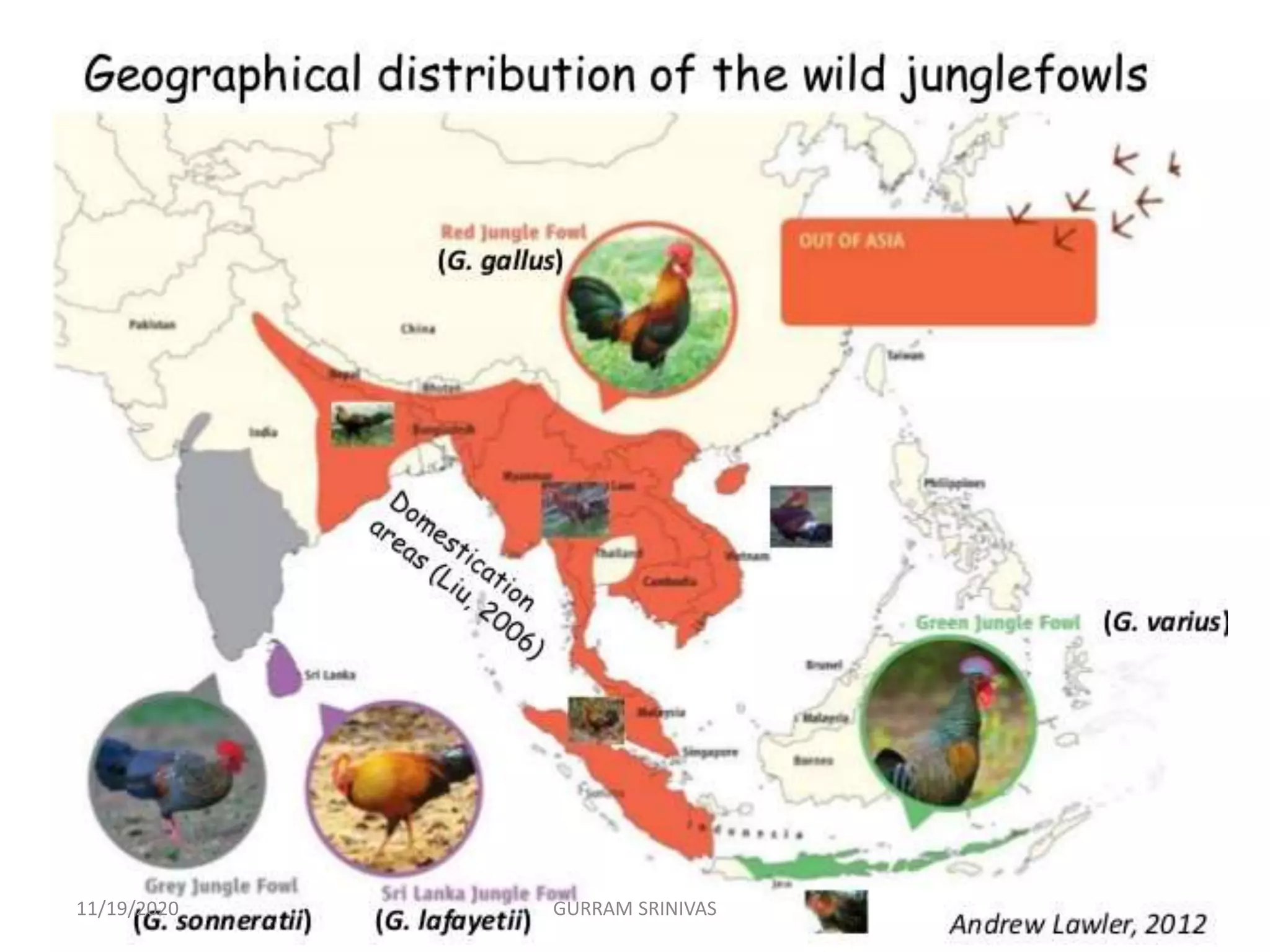
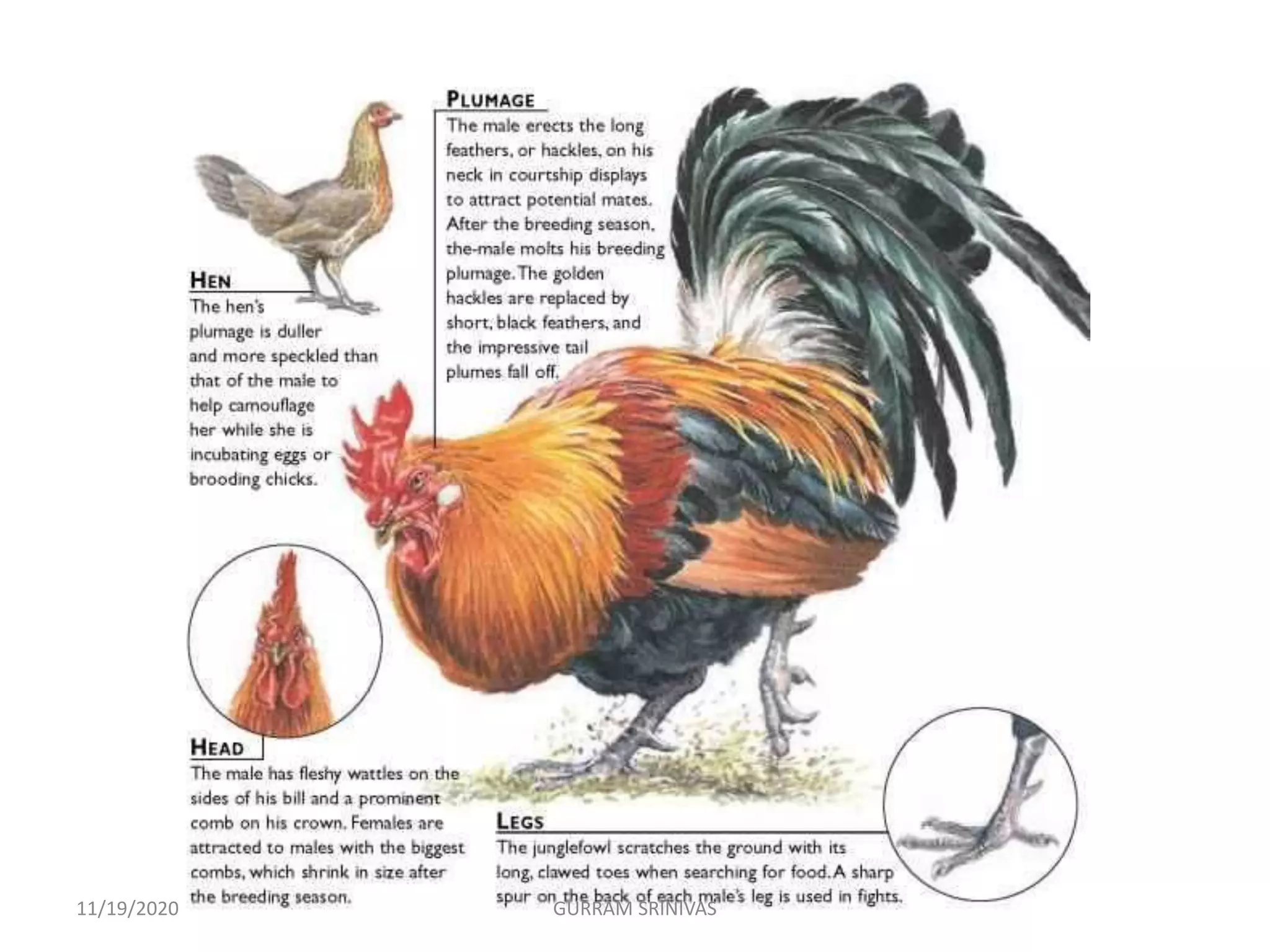
(3) The genetic classification of poultry places them in the animal kingdom down to the genus level. Four wild species of junglefowl in the Gallus genus are discussed, along with their distinguishing physical











![Gallus lafayetti [Ceylon jungle fowl]
• Male plumage is similar to RJF except that breast
feathers are pointed and fringed .males have a
peculiar patch of bluish purple feathers on the upper
breast.
• Plumage of the females is similar to those of RJF
11/19/2020 GURRAM SRINIVAS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/originanddomestcationofpoultry-201119064916/75/Origin-and-domestcation-of-poultry-15-2048.jpg)


![Gallus sonneratti [grey jungle fowl]
• Male plumage is different from other species
• “sealing wax” spots on rachis ;those that are
i.sub-terminal being white
ii.terminal spots being shredded and yellow.
• Occurs in neck hackle ,saddle, and wing coverts.
• Body feathers are black with a white shaft and a grey
border.
• Wing and tail feathers are black ; bird appears grey.
• Female plumage differs from RJF
i.In breast feathers which are white with broad
black/brown borders.
11/19/2020 GURRAM SRINIVAS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/originanddomestcationofpoultry-201119064916/75/Origin-and-domestcation-of-poultry-18-2048.jpg)


![Gallus varius[green jungle fowl]
• Most primitive of four species
• Plumage consists of 16 tail feathers rather than 14 in other
species.
• Short truncate neck hackle feathers in males.
• Male plumage is glossy black , but hackle and saddle
feathers are edged with bronze and yellow imparting a
distinctly green coloration to the bird.
• In females feathers of the back and rump are
penciled(similar to dark Cornish),
i.upper breast feathers have dark edging ,
ii. lower breast feathers are pale and
iii.rest of the plumage has irregular barring.
11/19/2020 GURRAM SRINIVAS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/originanddomestcationofpoultry-201119064916/75/Origin-and-domestcation-of-poultry-21-2048.jpg)