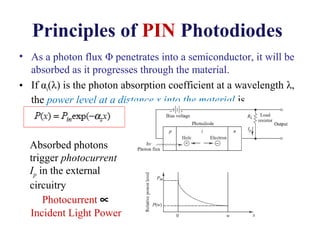
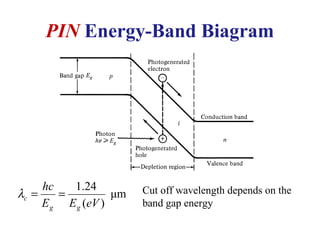
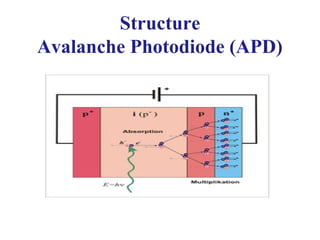
Photodetectors convert optical signals to electrical signals and are the fundamental component of optical receivers. The most common photodetectors are photodiodes, which come in PIN and avalanche photodiode (APD) varieties. PIN photodiodes simply convert light to current, while APDs provide internal gain through impact ionization but introduce excess noise. Key requirements for photodetectors include sensitivity at desired wavelengths, fast response time, low noise, and insensitivity to temperature.