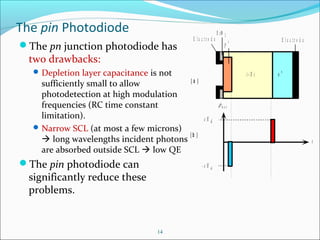
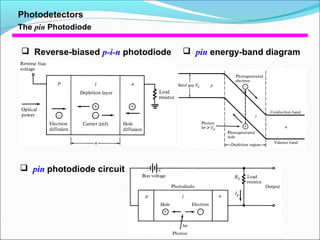
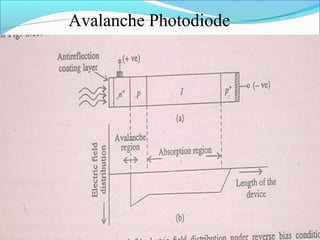
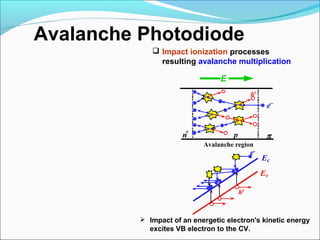
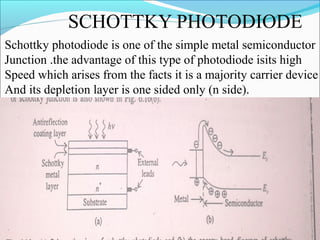
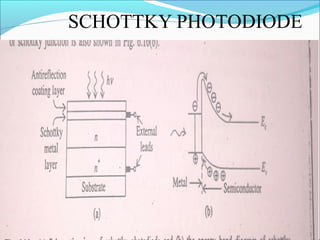
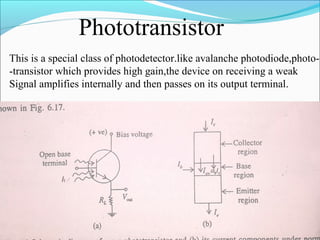
This document discusses different types of photodetectors. It describes photoconductive detectors like light dependent resistors (LDRs) and junction photodetectors including p-n photodiodes, PIN photodiodes, avalanche photodiodes, and Schottky photodiodes. PIN photodiodes are presented as an improvement over p-n photodiodes by having a larger depletion region for higher quantum efficiency. Avalanche photodiodes provide internal gain through impact ionization. Schottky photodiodes have a high speed due to being majority carrier devices. Phototransistors are also discussed as providing gain. Applications mentioned include fiber optics, cameras, medical devices, barcodes, and security systems



![Photodetectors
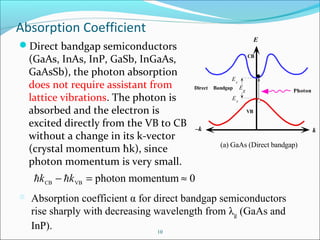
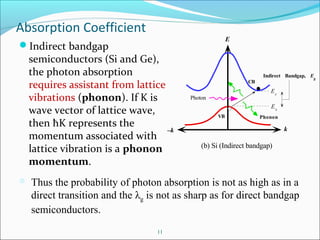
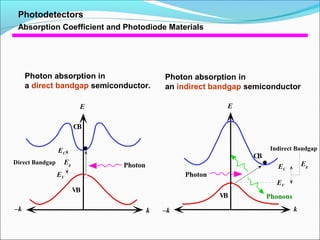
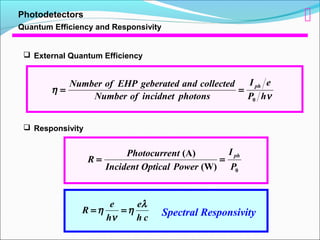
Absorption Coefficient and Photodiode Materials
][
24.1
][
eVE
m
g
g =µλ
Absorbed Photon create Electron-Hole Pair.
Cut-off wavelength
vs. Energy bandgap
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hemlataharmukh-160828082124/85/Photo-detector-by-GIRISH-HARMUKH-9-320.jpg)