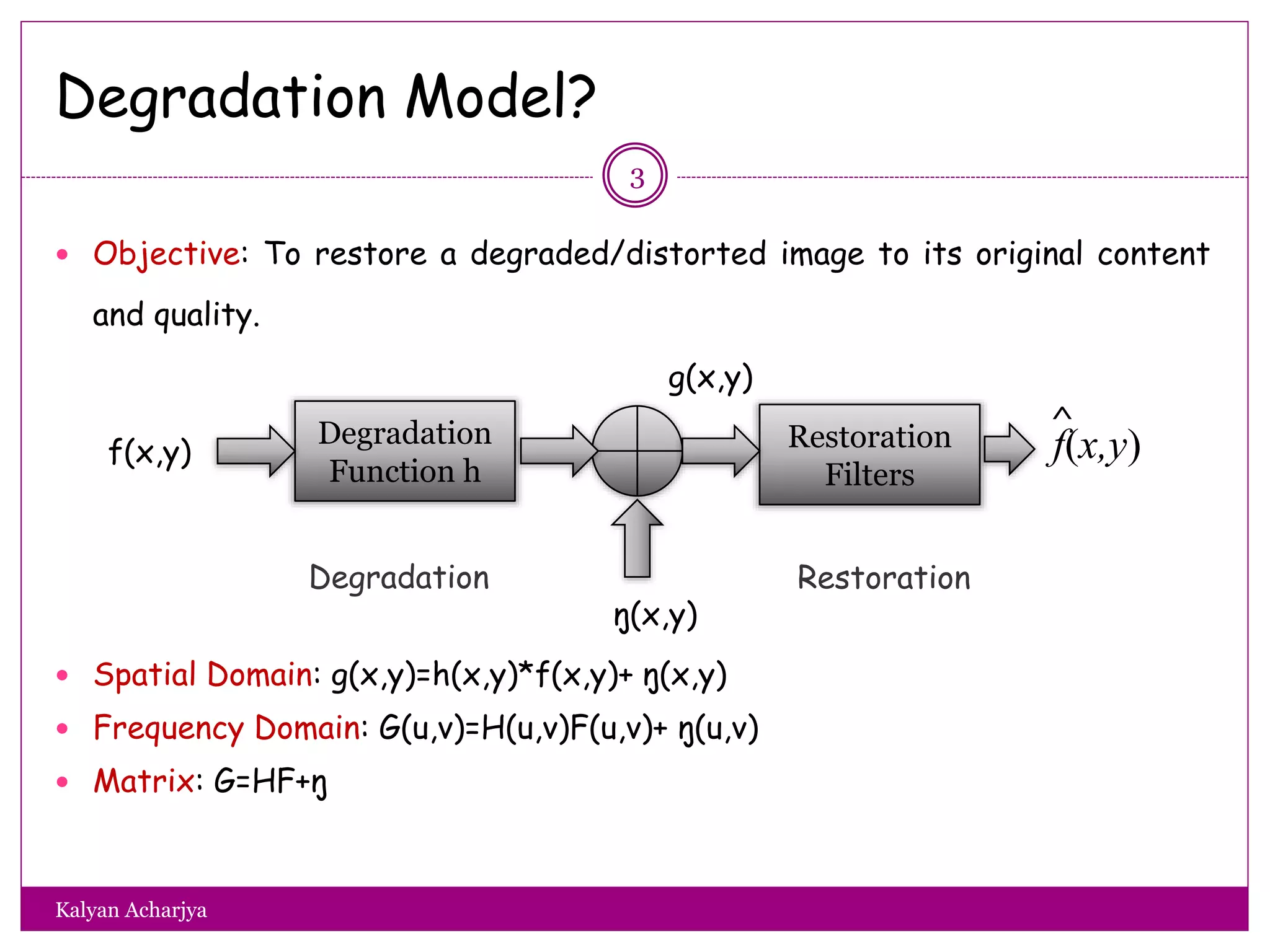
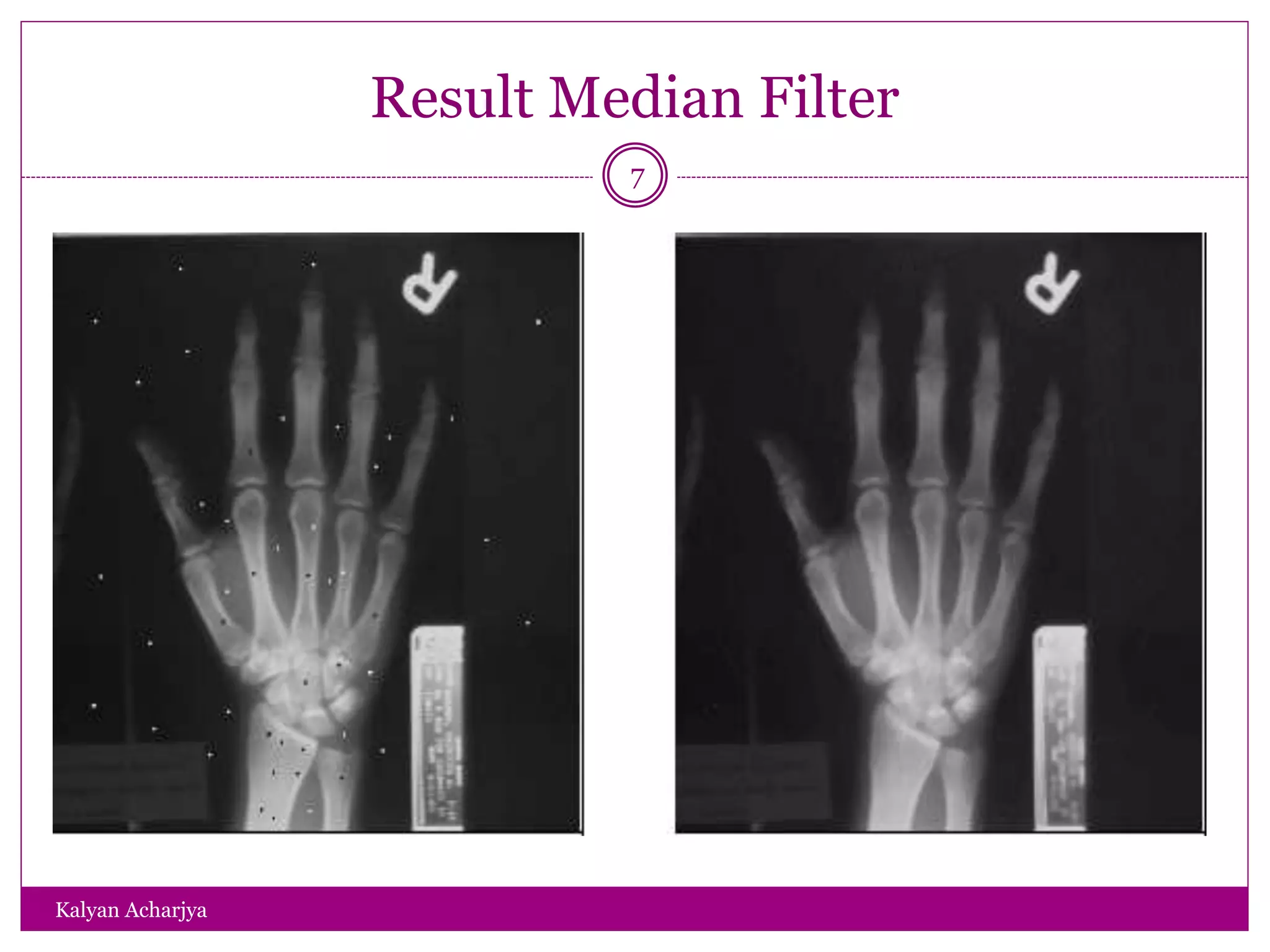
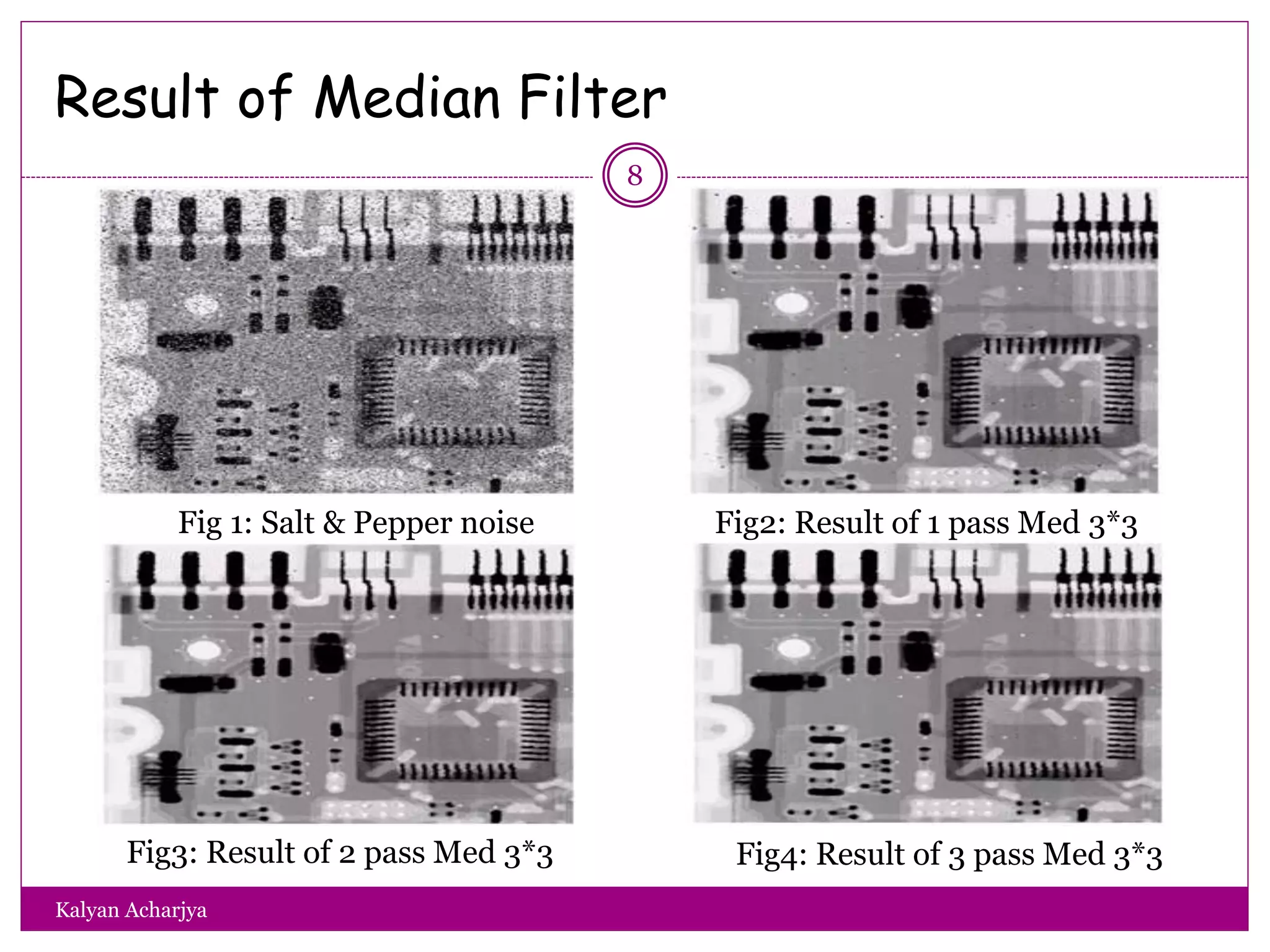
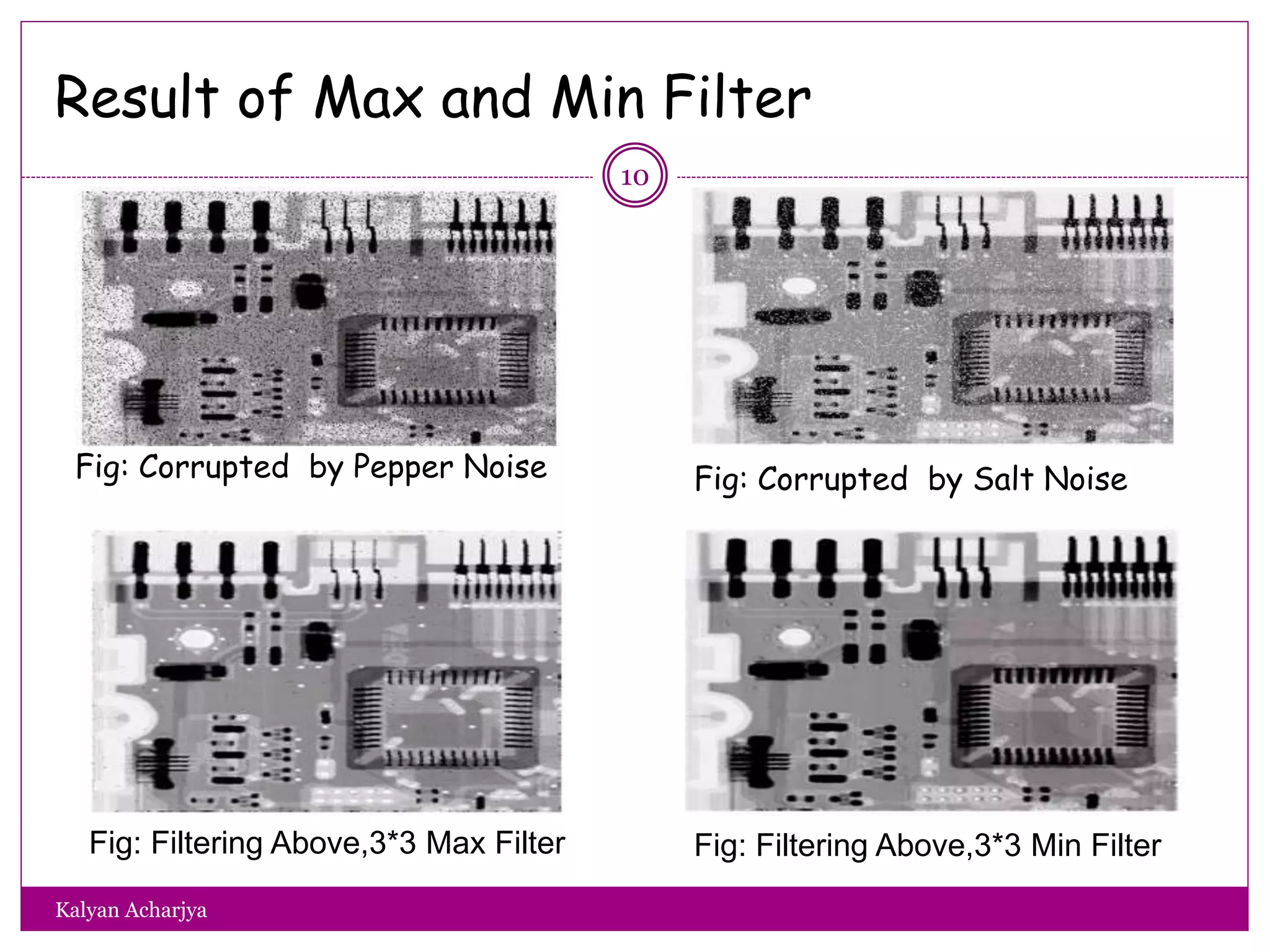
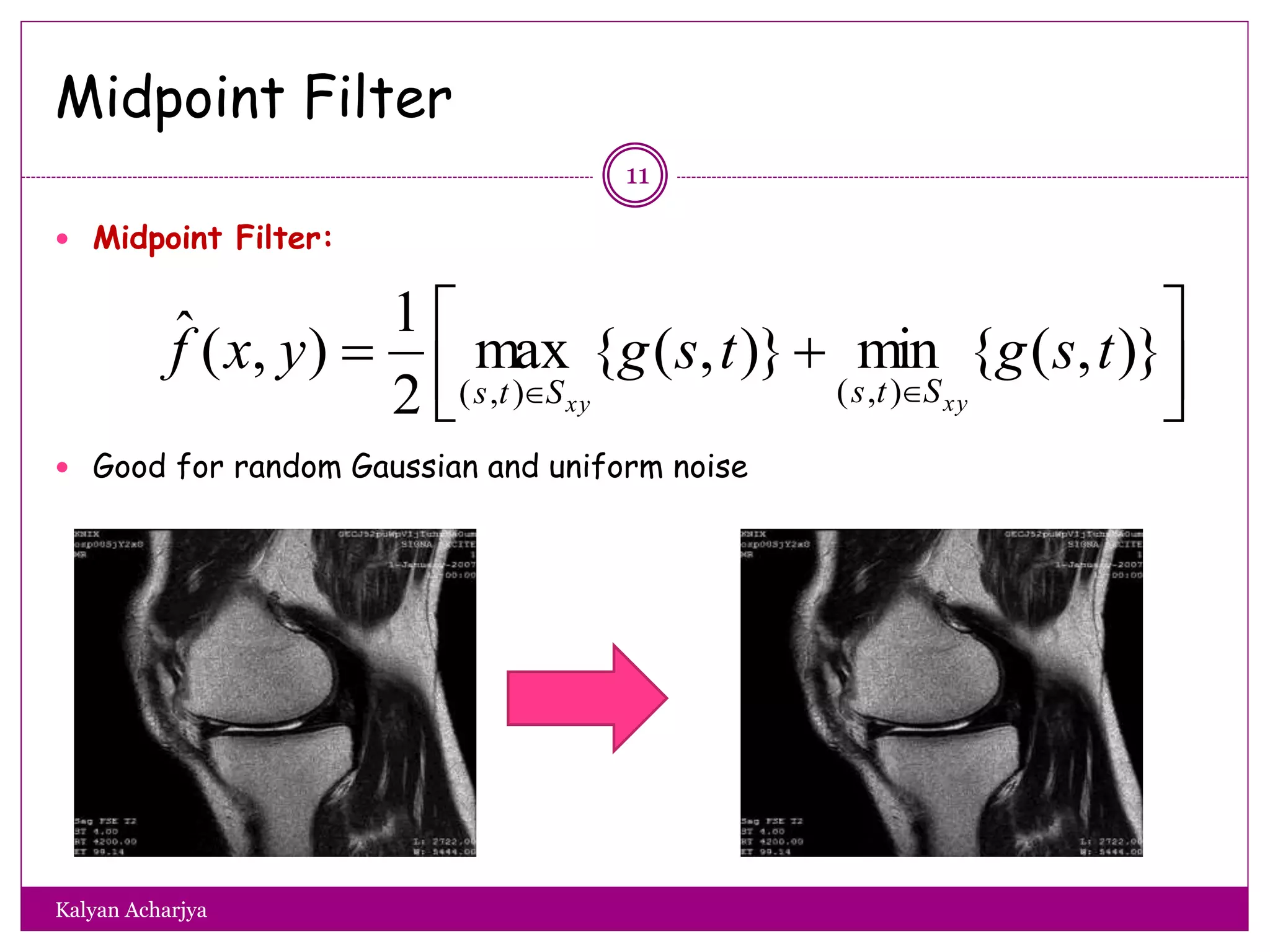
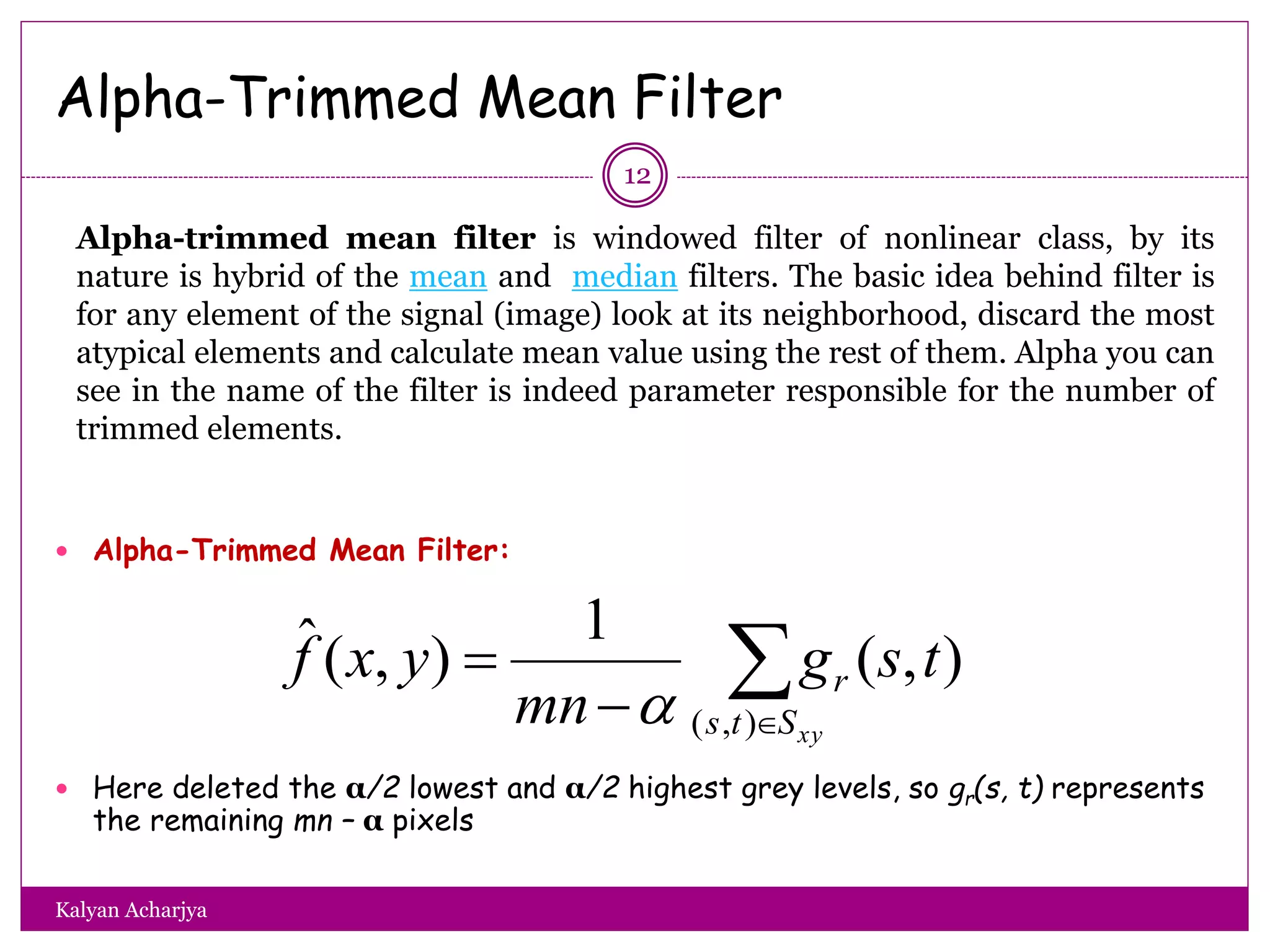
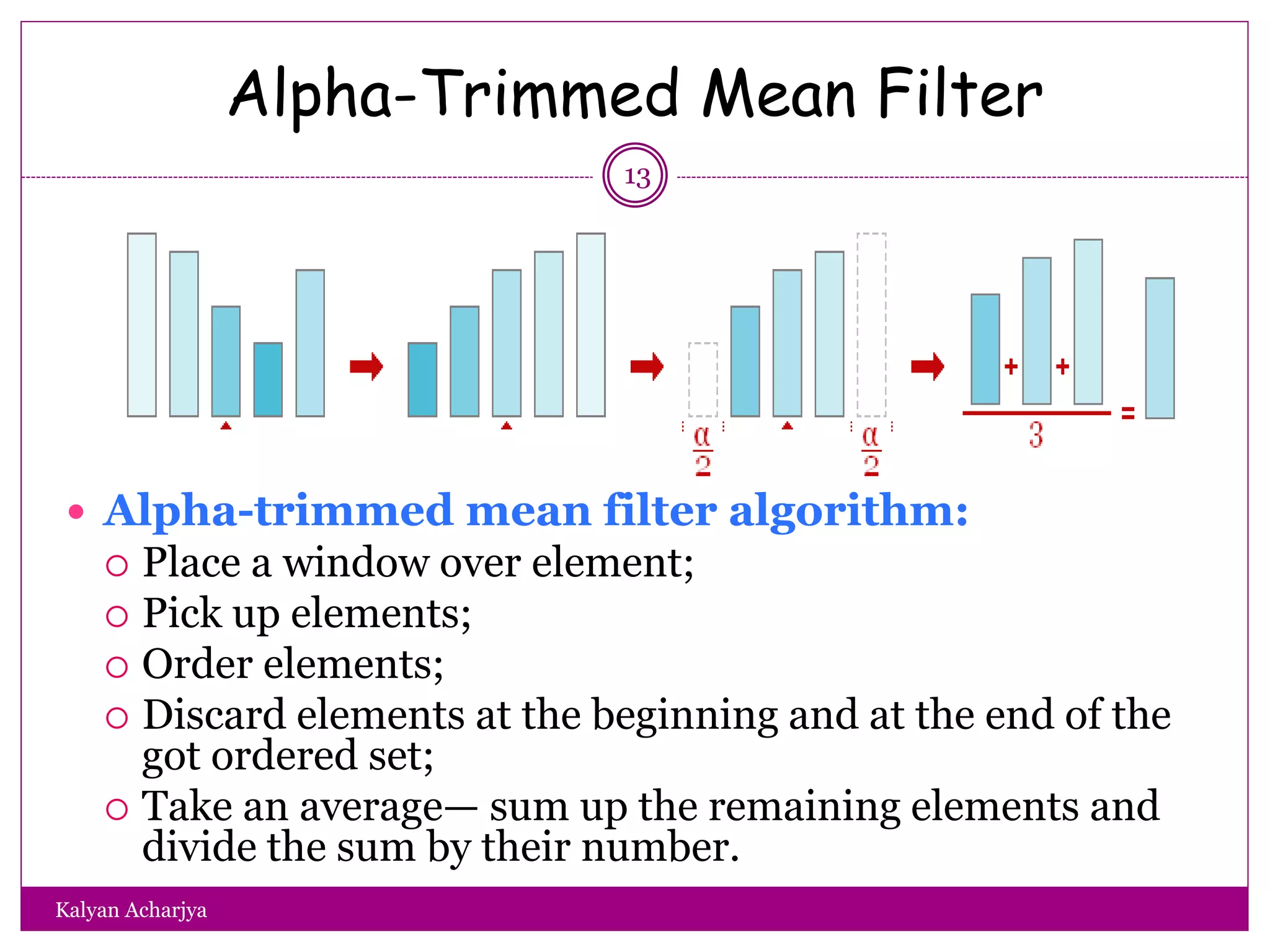
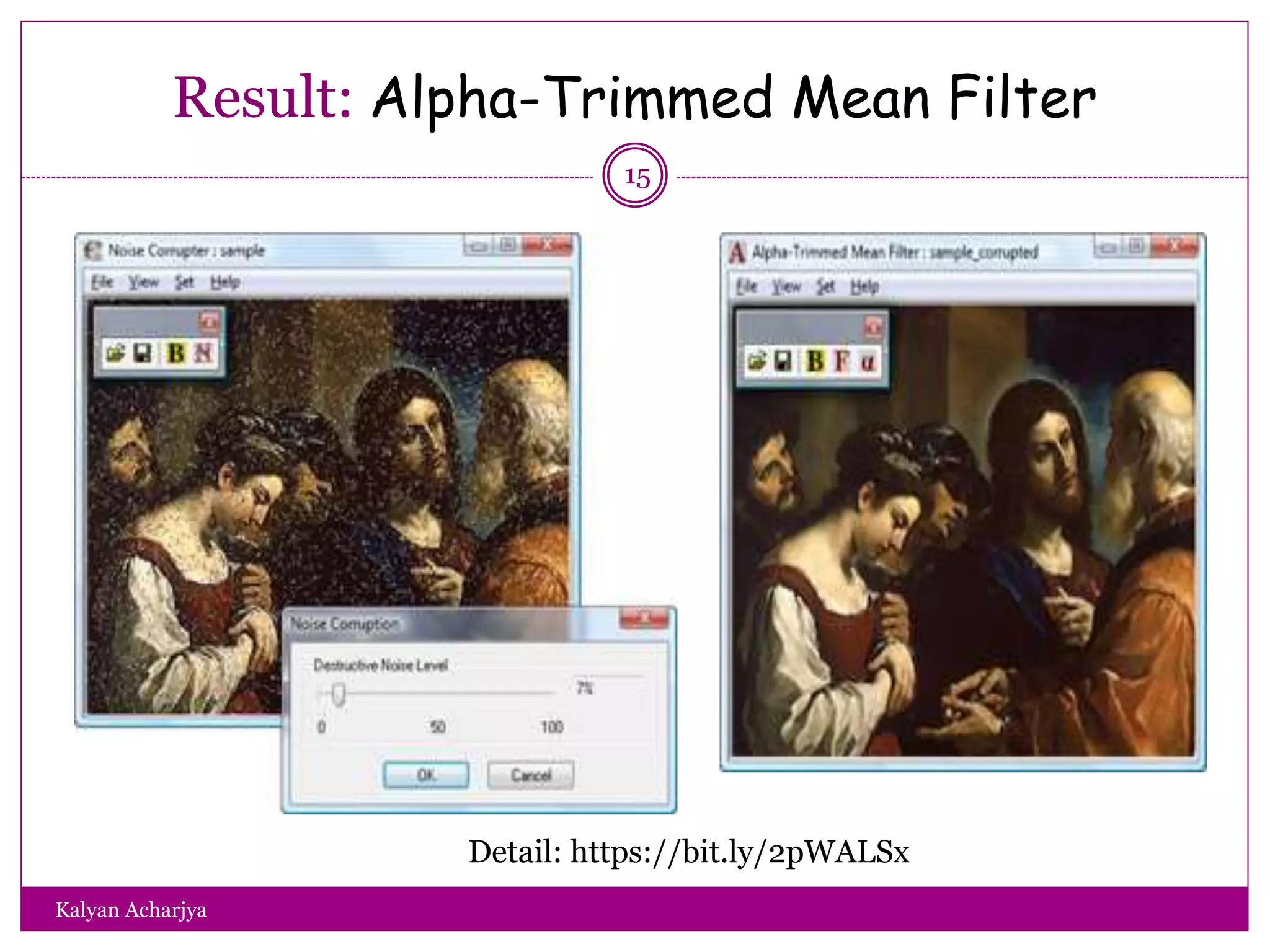
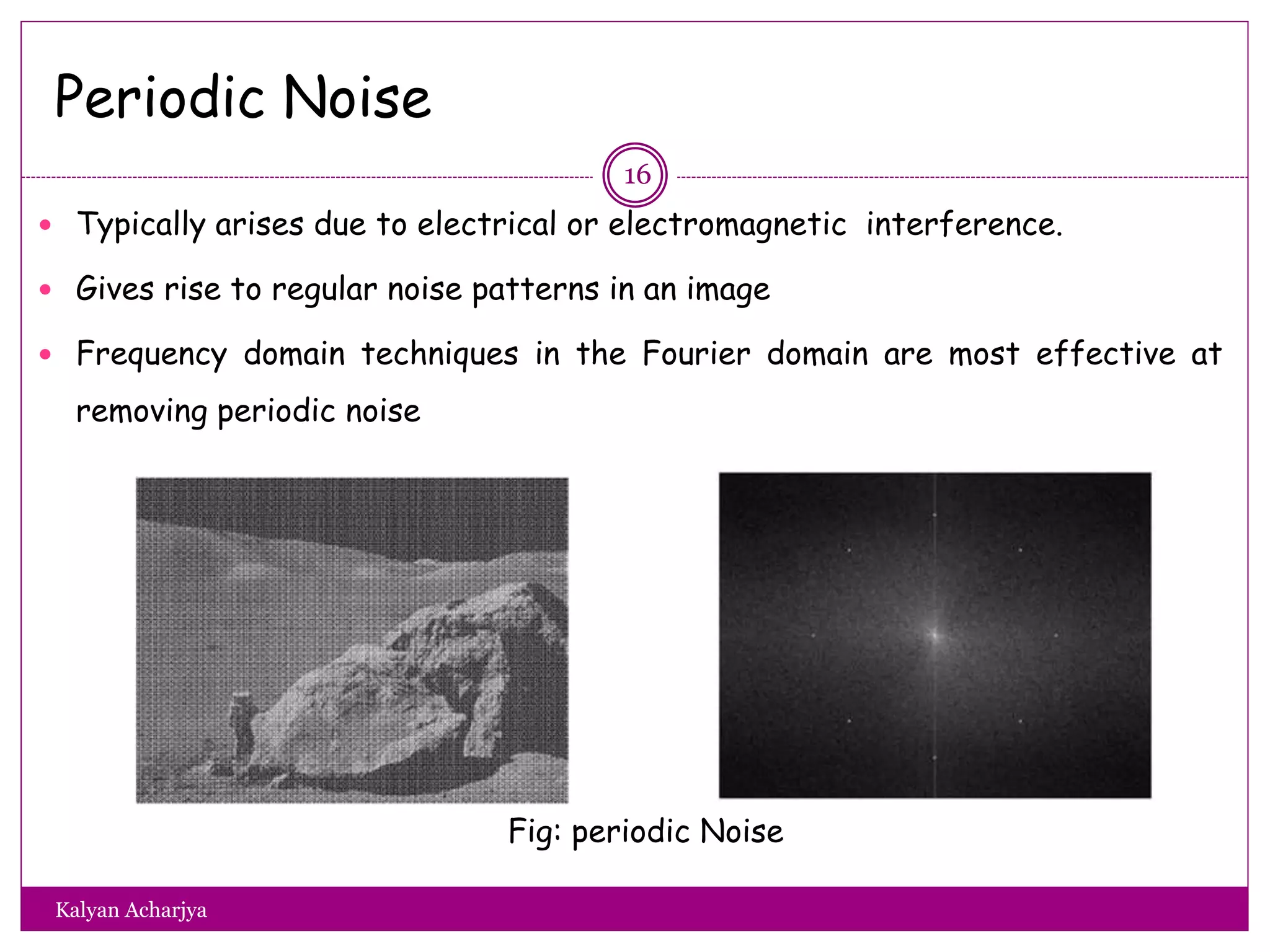
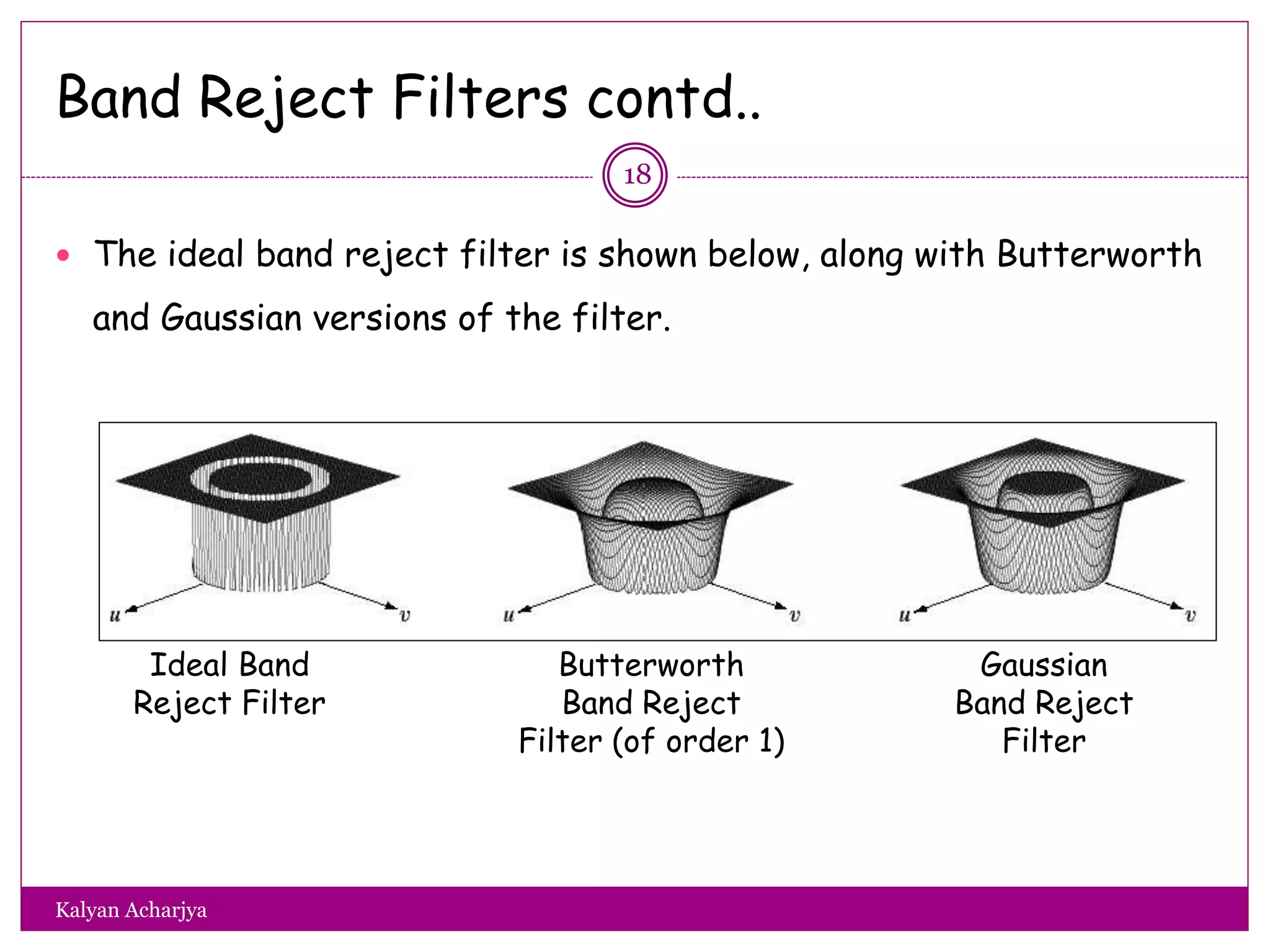
The document discusses image restoration techniques, focusing on methods to restore degraded images to their original quality. It covers various filters, such as median, maximum, minimum, midpoint, and alpha-trimmed mean filters, highlighting their effectiveness against different types of noise. Additionally, it emphasizes frequency domain techniques, particularly band reject filters, for managing periodic noise and concludes with adaptive and nonlinear processing methods.