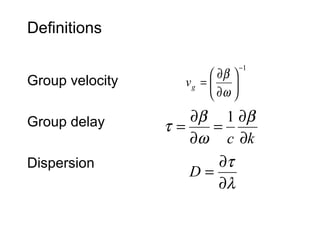
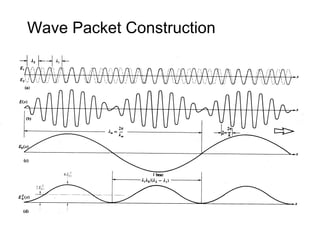
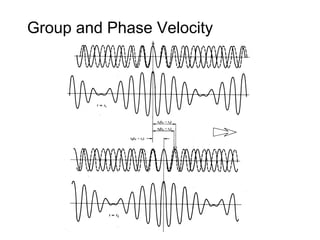
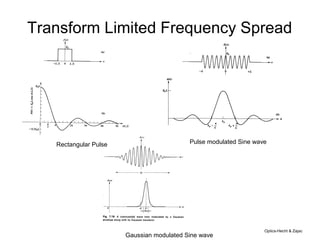
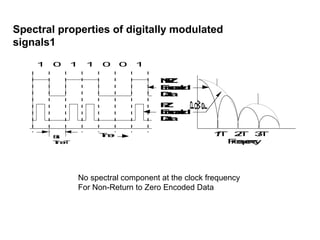
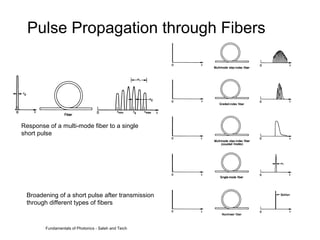
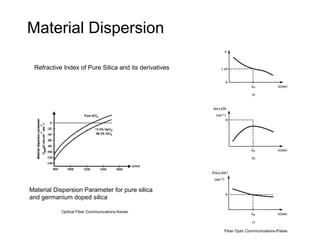
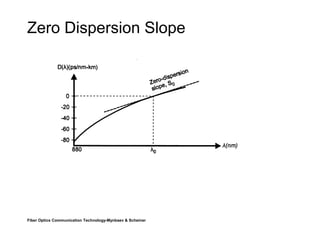
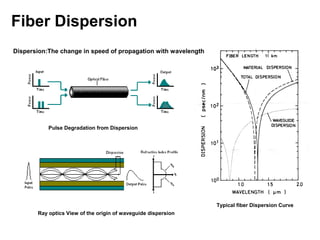
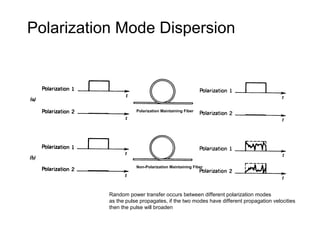
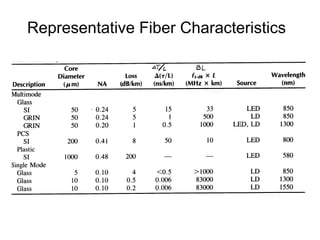
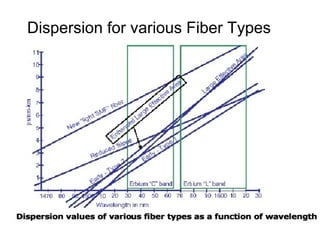
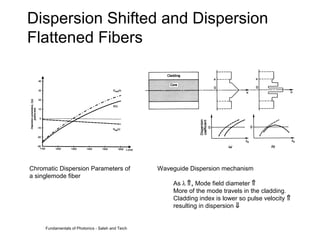
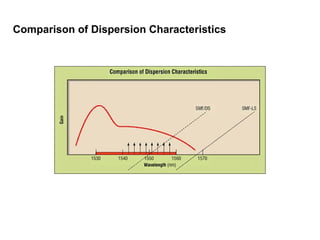
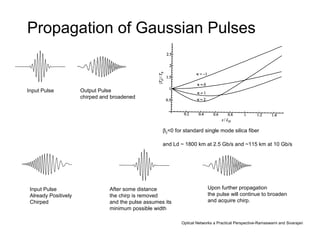
This document discusses different types of dispersion in optical fibers, including modal dispersion, material dispersion, waveguide dispersion, and polarization mode dispersion. It defines important terms related to dispersion like group velocity and group delay. It also examines how dispersion causes pulse broadening over distance as different wavelengths within a pulse propagate at different speeds through the fiber. Finally, it compares the dispersion characteristics of different fiber types like dispersion shifted and flattened fibers which are designed to reduce dispersion effects.