This document provides an overview of Kalyan Acharjya's proposed work on face recognition for his M.Tech dissertation. It discusses conducting literature research on existing face recognition techniques, identifying challenges in real-time applications, and exploring standard face image databases. The presentation covers topics such as how face recognition works, applications, and concludes with plans to modify existing algorithms and compare results to related work to enhance recognition rates.


![CONTENTS
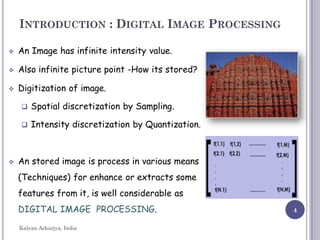
Introduction to Digital Image Processing.
Face Recognition.
Why Face Recognition.
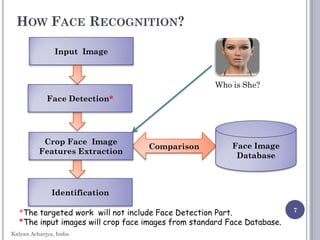
How Face Recognition.
Literature Survey [Going On].
Problem Statement.
Challenges for Real Time Applications.
Standard Face Images Database.
Conclusions and Future Work.
References.
3
Kalyan Acharjya, India](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/facerecognisition-150823114114-lva1-app6892/85/Face-recognition-Face-Identification-3-320.jpg)
![WHY FACE RECOGNITION ?
The world is urged for more and accurate face recognition rate.
How COMPUTER VISITON is possible, as human being are?
Automatic person identification.
FACE RECOGNISITION have lots of real world applications.
Automatic Attendance System.
Security Purposes.
Computer Interaction etc.
Crowd Surveillance. [US (MIT) invested $ 100 million for perfect recognition
system-Times of India, Oct 2013 ].
In 2011, London riots many suspects of partial face images were not
recognized by COTS FR system[15].
6
Kalyan Acharjya, India](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/facerecognisition-150823114114-lva1-app6892/85/Face-recognition-Face-Identification-6-320.jpg)
![LITERATURE SURVEY [1]
Title : Li, Liao and Jain, “Partial Face Recognition,
Alignment free Approach”, IEEE, May, 2013.
Technique Used: Authors proposed an alignment free
face recognition method based on multi-key point
descriptors. (MKD).
Conclusion: Authors concluded that MKD method is
superior than leading commercial FR systems like
Pitpatt and faceVACS SDK.
8
Kalyan Acharjya, India](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/facerecognisition-150823114114-lva1-app6892/85/Face-recognition-Face-Identification-8-320.jpg)
![9
LITERATURE SURVEY CONTD..[2]
Title : Mersico, Nappi and Wechsler, “Robust Face
Recognition fro Uncontrolled Pose and Illumination ”,
IEEE, January, 2013.
Technique Used: Authors proposed a novel frame work
based on normalization strategies and Face Analysis
for Commercial Entities (FACE).
Conclusion: The result showed the significant increase
in recognition rate [95% in FERET fa Database] in
accuracy, whether comparison with other available
algorithms.
Kalyan Acharjya, India](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/facerecognisition-150823114114-lva1-app6892/85/Face-recognition-Face-Identification-9-320.jpg)
![10
LITERATURE SURVEY CONTD.. [3]
Title : Park and Savvides , “Individual Kernal Tensor
Subspaces for Robust Face Recognition: A Computationally
Efficient Tensor Framework without requiring Mode
Factorization ”, IEEE, Oct, 2007.
Technique Used: The work based on high order tensor to
construct a multi linear structure and model the multiple
factors of face variations.
Conclusion: The paper introduced the new concept that
appearance factor, the factor of person’s identity modeled
by a tensor structure can be used for better face
recognition system specially for difference types of
appearance of same faces.
Kalyan Acharjya, India](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/facerecognisition-150823114114-lva1-app6892/85/Face-recognition-Face-Identification-10-320.jpg)
![11
LITERATURE SURVEY CONTD.. [4]
Title: Karim, Lipu, Rahman and Sultana , “Face Recognition
using PCA based Method”, IEEE, 2010.
Technique Used: The work based on Principle Component
Analysis (PCA).
Conclusion: The paper concluded the Principle Component
Analysis is better then their predecessor, where recognition
rate 84.1 % (Male Face) and 95.45 % (Female Face) in case
of Indian face database.
Also recognition rate 92.5 % (Male Face) and 85 % (Female
Face) in case of University of Essex, UK face database.
Kalyan Acharjya, India](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/facerecognisition-150823114114-lva1-app6892/85/Face-recognition-Face-Identification-11-320.jpg)
![12
LITERATURE SURVEY CONTD..[5] MANY MORE…..!
Title : Meade, Kumar and Phillips, “Comparative
performance of Principle Component Analysis , Gabor
Wavelets and Discrete Gabor Wavelets”, Canadian
Journal of Electronics and Computer Engg., Spring,
2005.
Technique Used: Comparative performance analysis of
PCA with Gabor Wavelets and Discrete Gabor
Wavelets.
Conclusion: Gabor Wavelets showed the best
performance on FERET database, as Gabor Wavelets is
least affected by illumination levels.
Kalyan Acharjya, India](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/facerecognisition-150823114114-lva1-app6892/85/Face-recognition-Face-Identification-12-320.jpg)

![14
AVAILABLE FACE RECOGNITION ALGORITHMS
BASED ON [4]
Principle Component Analysis (PCA).
Normalization of Histogram Analysis (NHA).
Independent Component Analysis (ICA).
Normalized Cross Correlation (NCC).
Sum of Absolute Difference (SAD).
Linear Discernment Analysis (LDA).
Discrete Wavelets Transform (DWT).
Gabor Wavelet Transform(GWT).
Multilayer Appearance-Tensor based (MAT).
Multiple Descriptor Key point (MDK-SDK).(Partial Face Also) etc.
Kalyan Acharjya, India](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/facerecognisition-150823114114-lva1-app6892/85/Face-recognition-Face-Identification-14-320.jpg)
![15
CHALLENGE FOR FACE RECOGNITION [1]
External Occlusion
By other face
Self Occlusion
By non frontal pose
Facial Accessories
By Sunglass
Not Proper
Illumination
Sensor saturation
By under exposure or
over exposure
Limited Field of View
(FOV) By out of camera.
Kalyan Acharjya, India](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/facerecognisition-150823114114-lva1-app6892/85/Face-recognition-Face-Identification-15-320.jpg)
![STANDARD FACE RECOGNITION DATABASE [4]
The Choice of appropriate database to be used based
on targeted work.
Color FERET Database
Yale Face Database.
PIE Database.
FIA Video Database.
CBCL Face Recognition Database.
Expression Image Database.
Mugs hot Identification Database.
Identification Database.
Indian Face Database.
Face Recognition Data, University of Essex, UK 16
Kalyan Acharjya, India](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/facerecognisition-150823114114-lva1-app6892/85/Face-recognition-Face-Identification-16-320.jpg)

![18
REFERENCES
[1] Li, Liao and Jain, “Partial Face Recognition, Alignment free Approach”, IEEE
Transaction on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, VOL 35, No 5, May,
2013.
[2] Mersico, Nappi and Wechsler, “Robust Face Recognition fro Uncontrolled Pose
and Illumination ”, IEEE Transaction on Systems, man and Cybernetics:
systems, VOL. 43, NO. 1, January, 2013.
[3] Park and Savvides , “Individual Kernal Tensor Subspaces for Robust Face
Recognition: A Computationally Efficient Tensor Framework without requiring
Mode Factorization ”, IEEE on Systems, man and Cybernetics: systems, VOL. 37,
NO. 5 , Oct, 2007.
[4] Karim, Lipu, Rahman and Sultana ,“Face Recognition using PCA based
Method”, IEEE, 2010.
[5] Meade, Kumar and Phillips, “Comparative performance of Principle
Component Analysis , Gabor Wavelets and Discrete Gabor Wavelets”, Canadian
Journal of Electronics and Computer Engg., VOL. 30, NO. 2, Spring, 2005.
Kalyan Acharjya, India](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/facerecognisition-150823114114-lva1-app6892/85/Face-recognition-Face-Identification-18-320.jpg)
![REFERENCES CONTD..
[6]Kar, Debbarma, Saha and Pal, "Study of Implementing Automated
Attendance System using Face Recognition Technique” International Journal of
Computer and Communication Engineering, VOL. 1, No. 2, July 2012.
[7] Balcoh, Yousaf, Waqar and Baig,”Algorithm for Efficient Attendance
Management: Face Recognition based Approach”, IJCSI (Online), Vol.9, No.1,
July 2012.
[8] Jiang, Sadka and Crooks, "Technical Correspondence-Multimodal Biometric
Human Recognition for Perceptual Human-Computer Interaction ” IEEE
Transaction on Systems, man and Cybernetics-Part C:Applications and Review,
VOL. 40, NO. 6, November, 2010.
[9]Jyoti, Chadha, Vaidya and Roja,”A robust, low-cost approach to Face
Detection and Face Recognition”, CiiT International Journal of Digital Image
Processing, ISSN 0974-9586(Online), Vol. 15, No 10, October 2011.
[10] Lu and Tan,”Cost-Sensitive Subspace Analysis and Extensions For Face
Recognition”,IEE transactions on Information forensics and Security, Vol. 8, No
3, March 2013.
19
Kalyan Acharjya, India](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/facerecognisition-150823114114-lva1-app6892/85/Face-recognition-Face-Identification-19-320.jpg)
![REFERENCES CONTD..
[11] Toole, Philips, Jiang and Abdi,”Face Recognition Algorithms Surpass
Human Matching Faces over changes in Illumination”, IEEE
Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, VOL. 29, No.
9, September 2007.
[12]Zhang, Shan, Chen and Gao,”Local Gabor Binary Patterns Based on
Kullback-Leibler Divergence for Partially Occluded Face Recognition”,
IEEE Signal Processing Letters, Vol. 14, No.11, November 2007.
[13] Liu and Liu, “A hybrid Color and Frequency Features Method for
Face Recognition”,IEEE transactions on Image Processing, Vol. 17, No.
10. October 2008.
[14] Mohanty, Sarkar, Kasturi and Phillips, "Subspace Approximation of
Face Recognition Algorithms: An Empirical Study”, IEEE Transactions
on Information Forensics and Security”, Vol. 3, No. 4, December 2008.
[15] “Police use Facial recognition Technology to Nab Rioters”,
http://www.msnbc.msn.com/id/44110353/ns
20
Kalyan Acharjya, India](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/facerecognisition-150823114114-lva1-app6892/85/Face-recognition-Face-Identification-20-320.jpg)

