This document provides an overview of the key concepts in photochemistry of vision including:
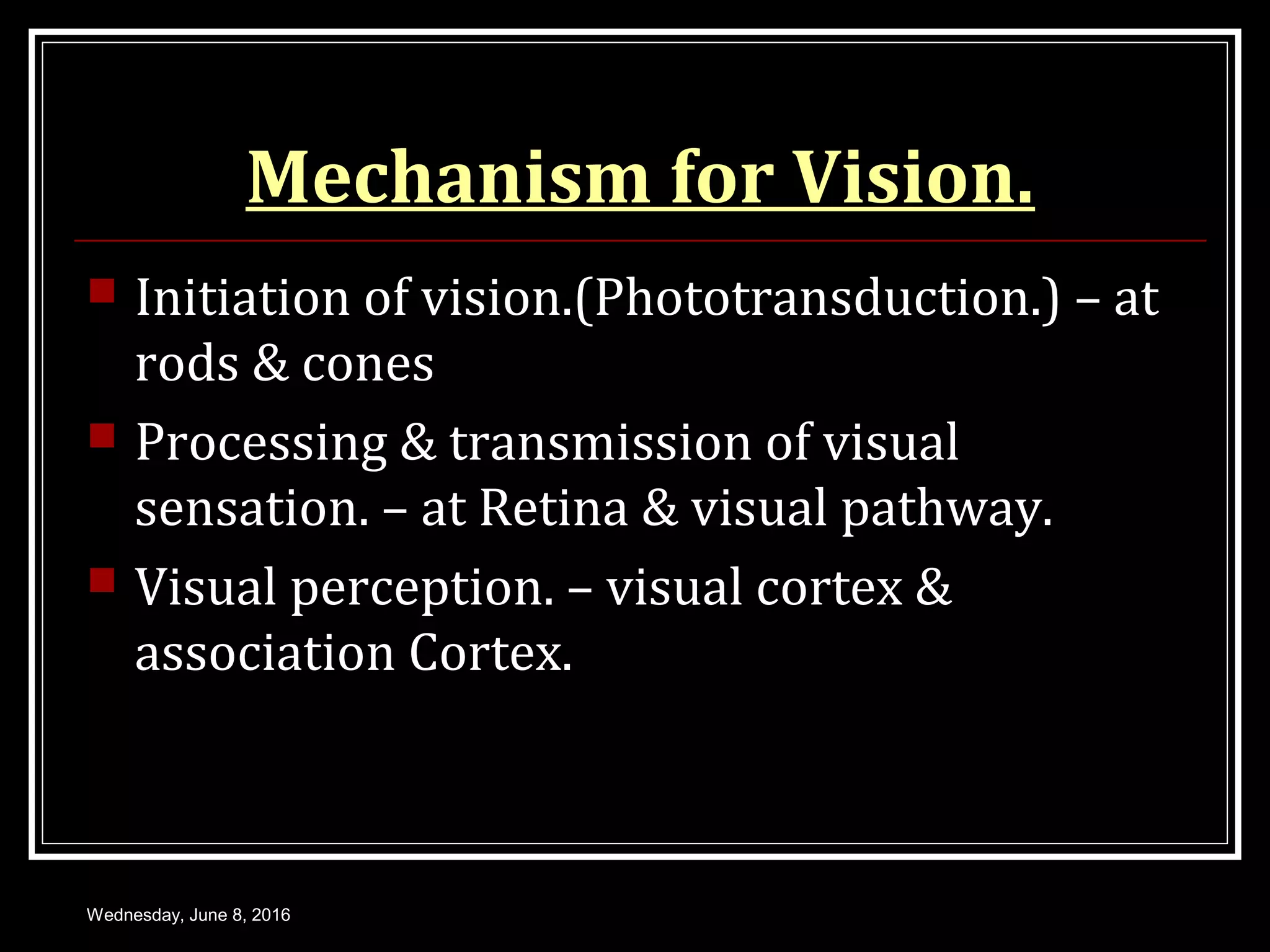
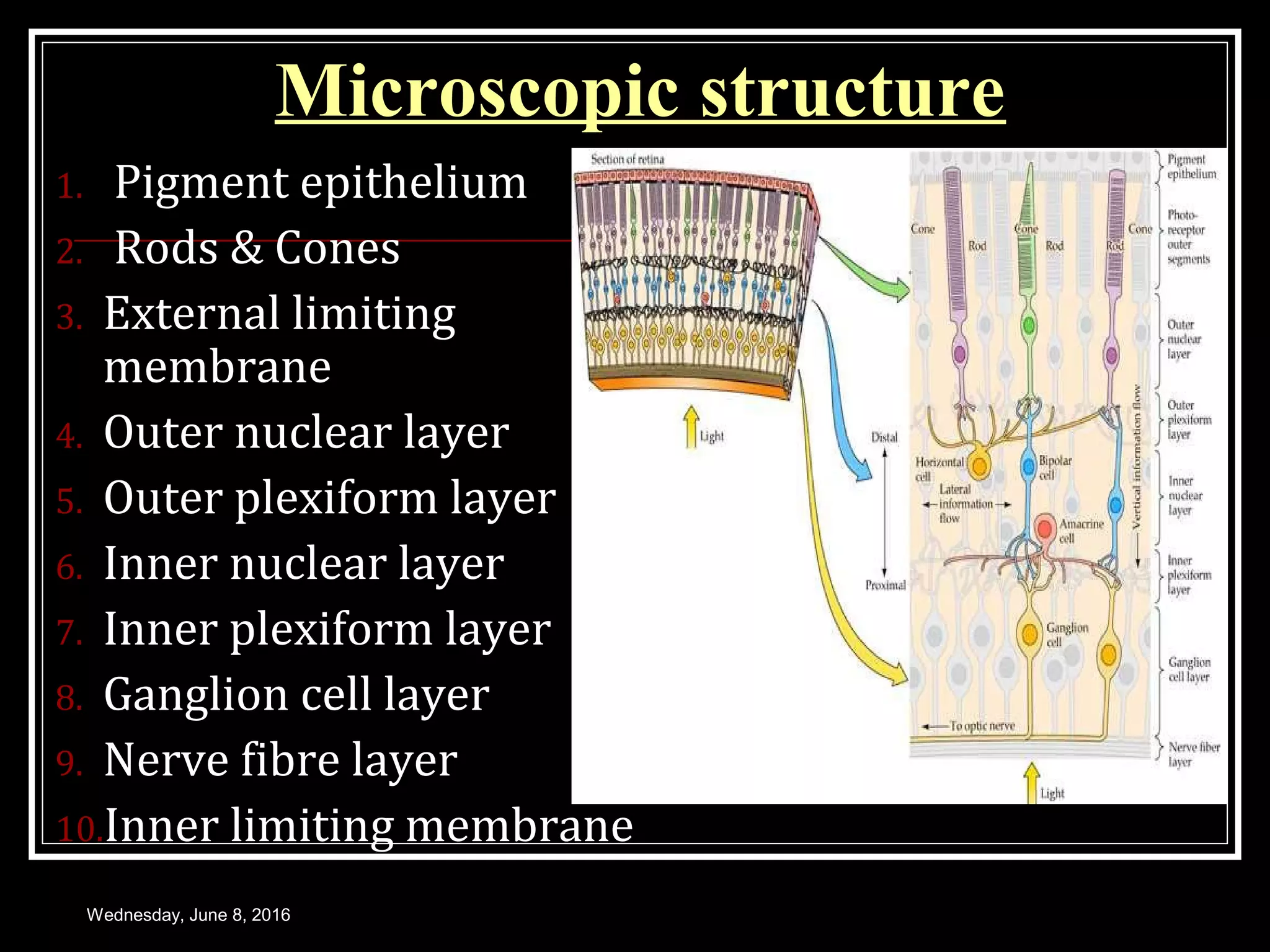
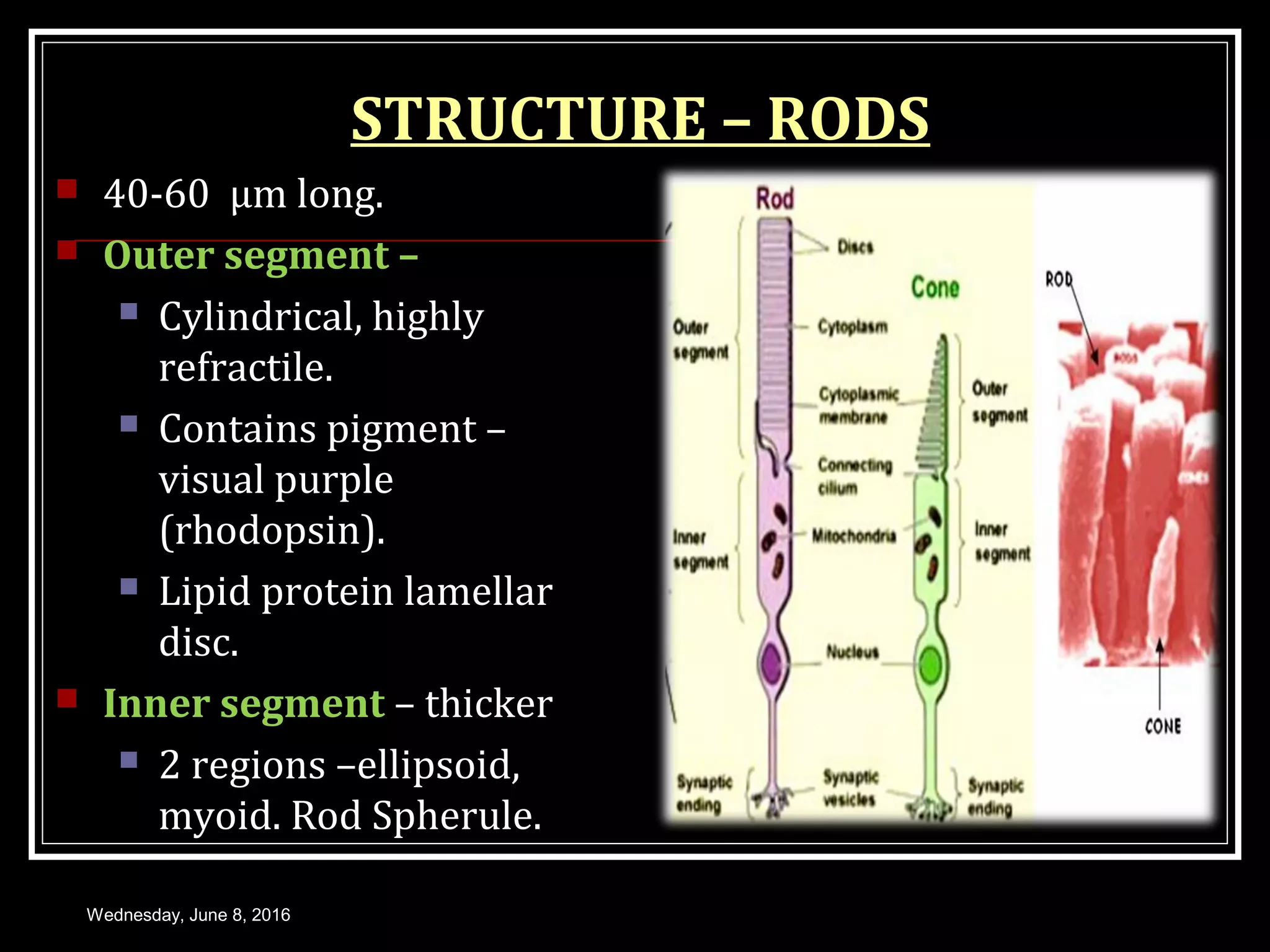
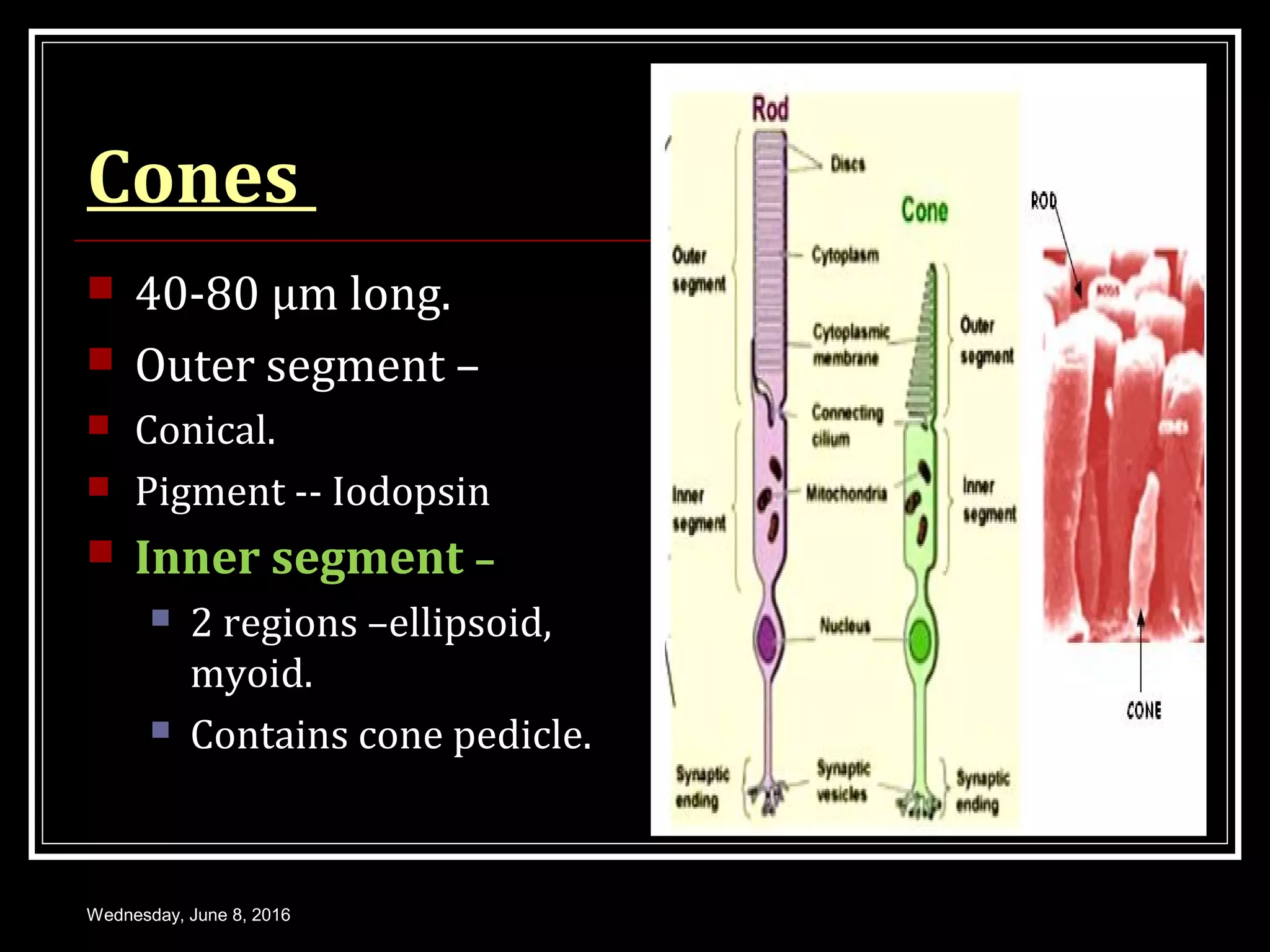
- The structure and function of the retina, photoreceptors, and visual pigments in initiating the visual process.
- The mechanism of phototransduction which converts light energy into nerve impulses through a series of biochemical reactions within the photoreceptors.
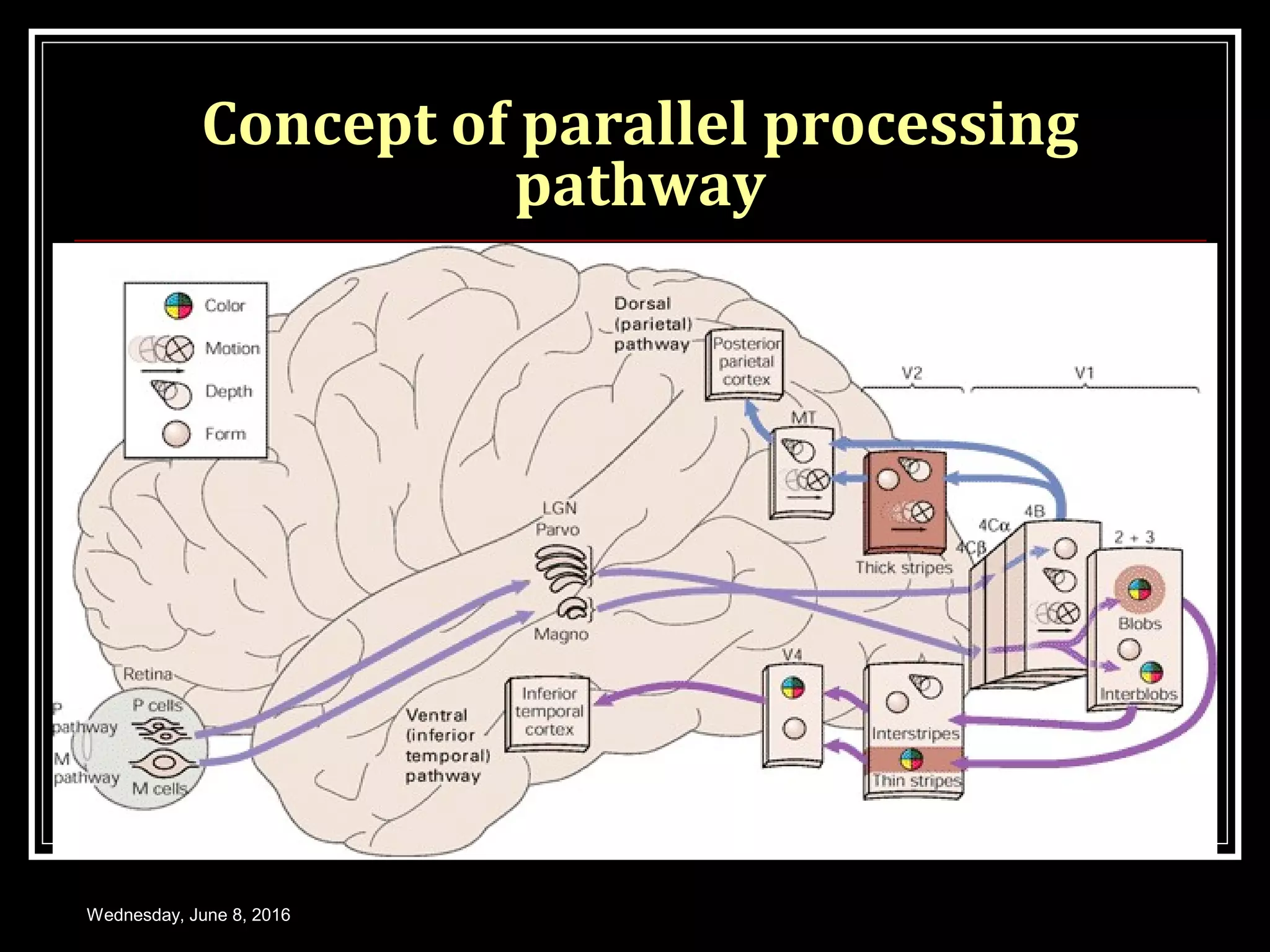
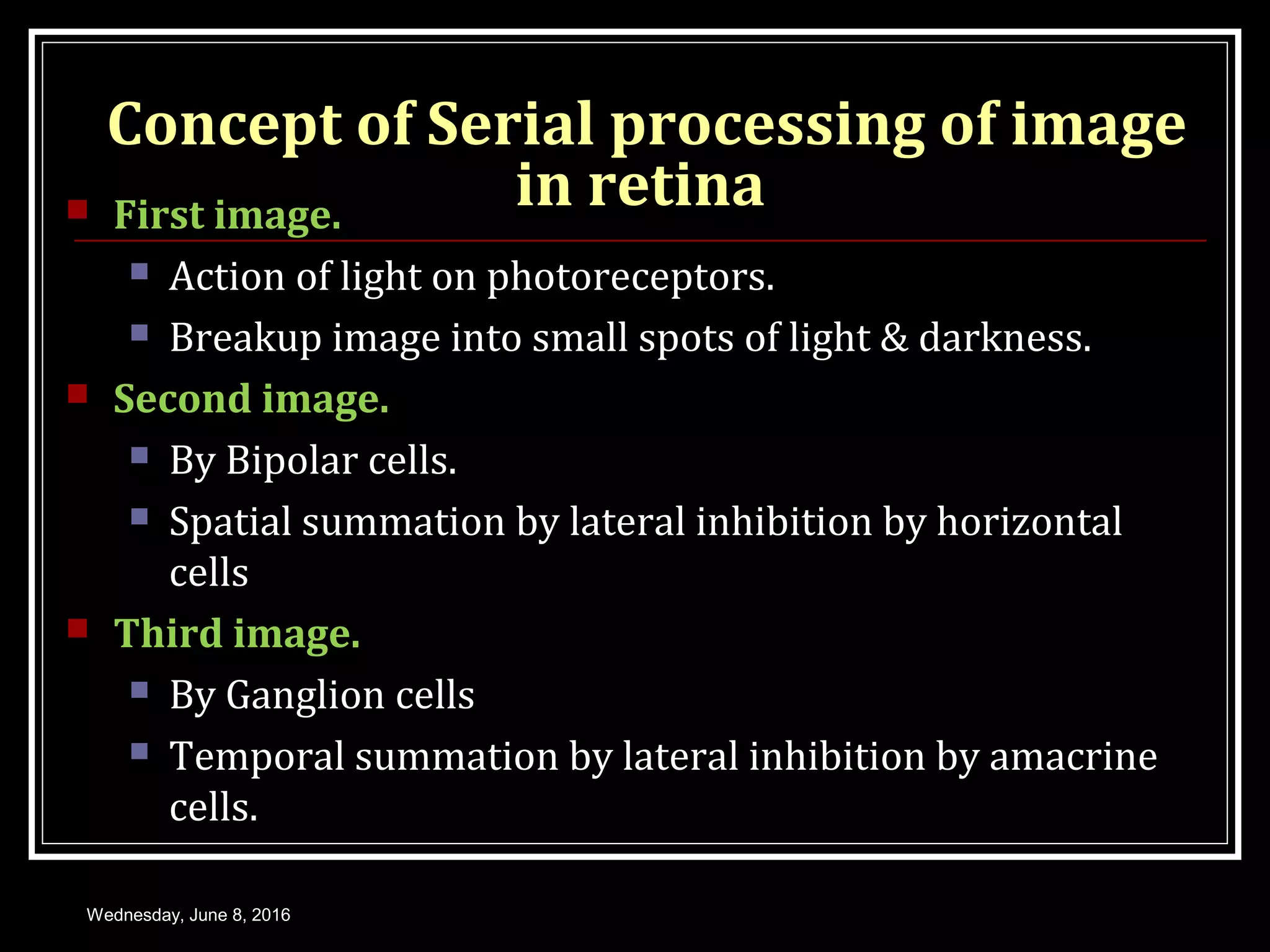
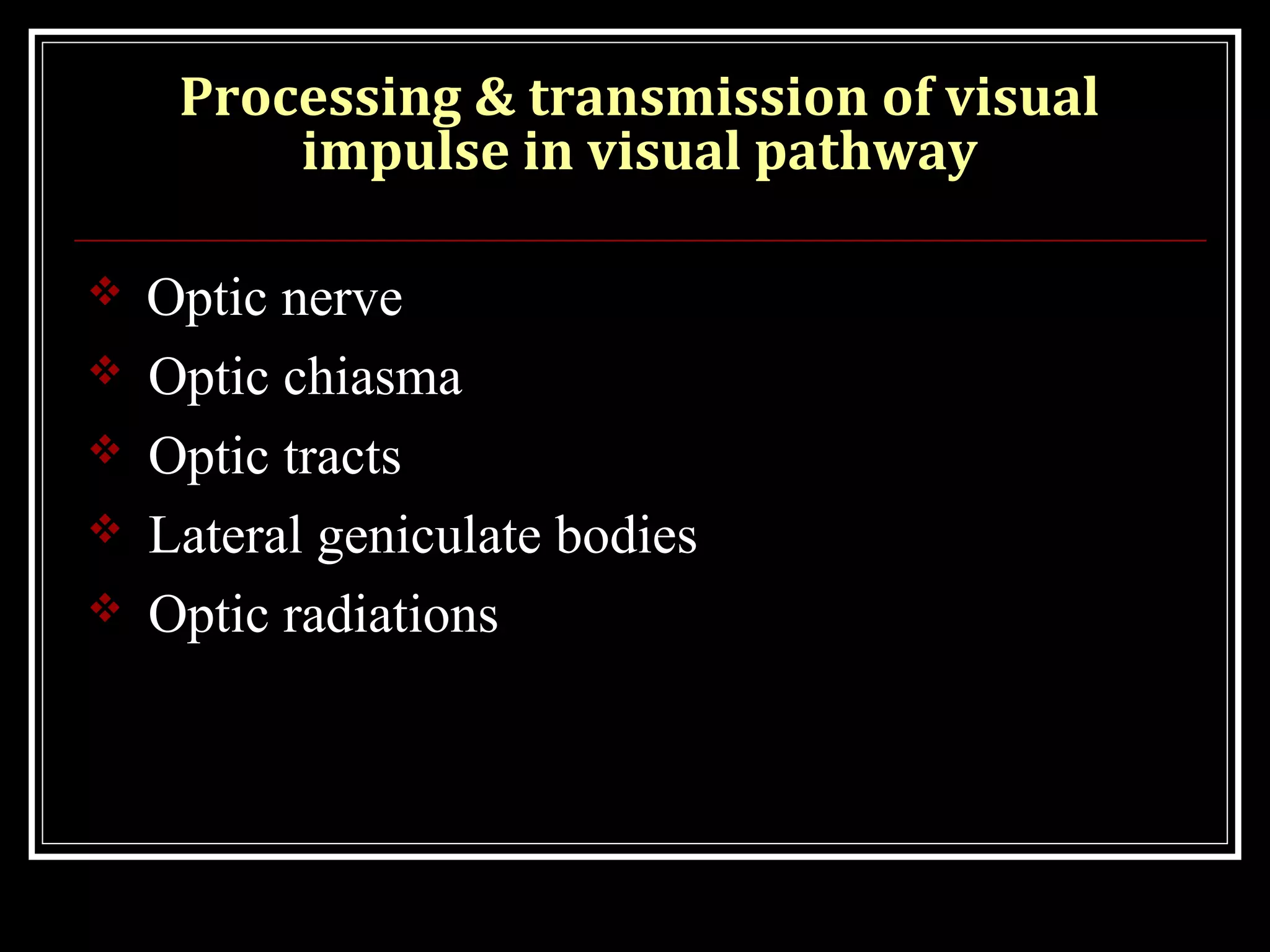
- How the visual impulse is processed and transmitted from the retina through the optic nerve, chiasm, tracts and lateral geniculate bodies to the visual cortex where visual perception occurs. Parallel processing pathways and the serial processing of images within the retina are also discussed.