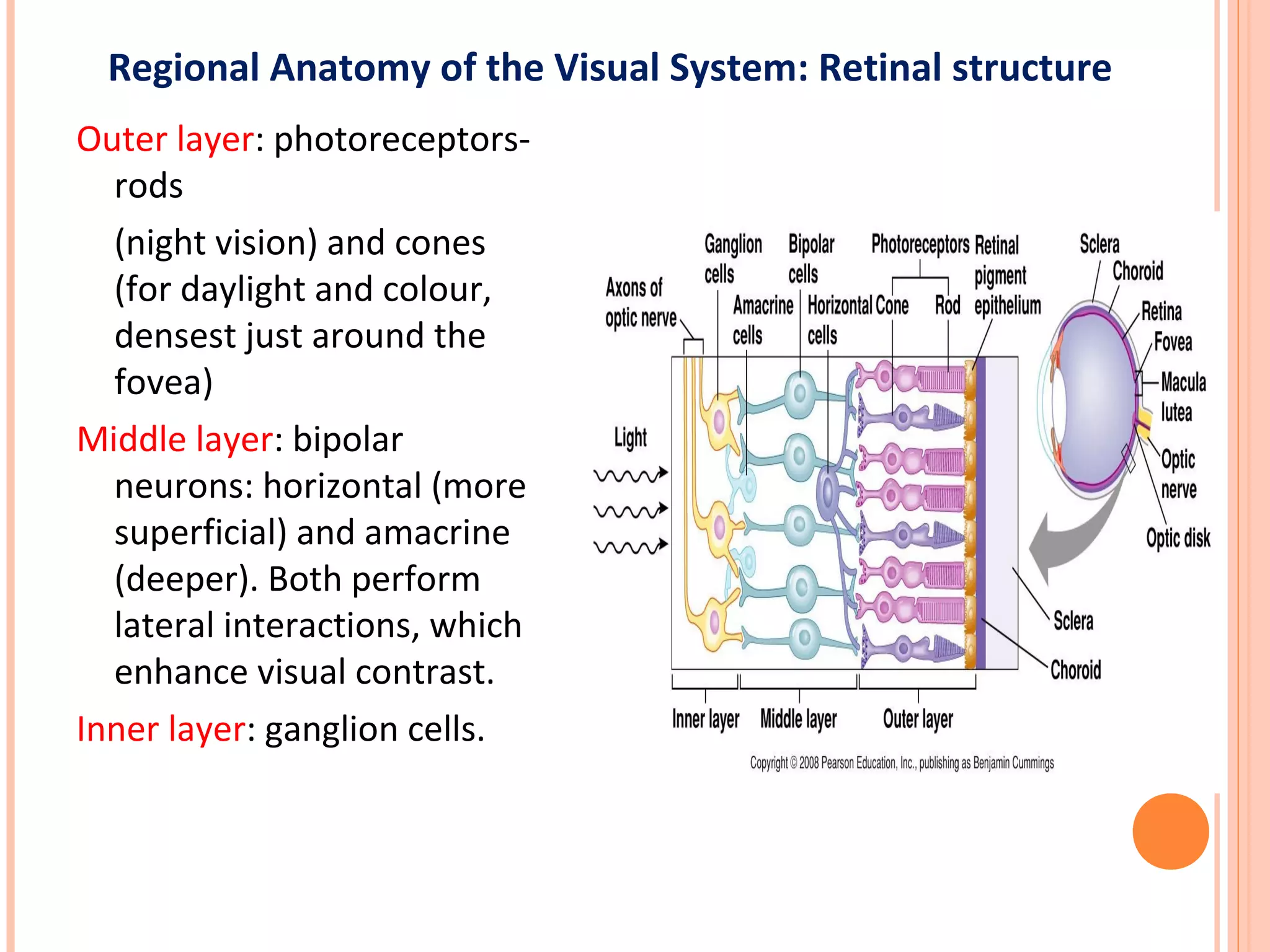
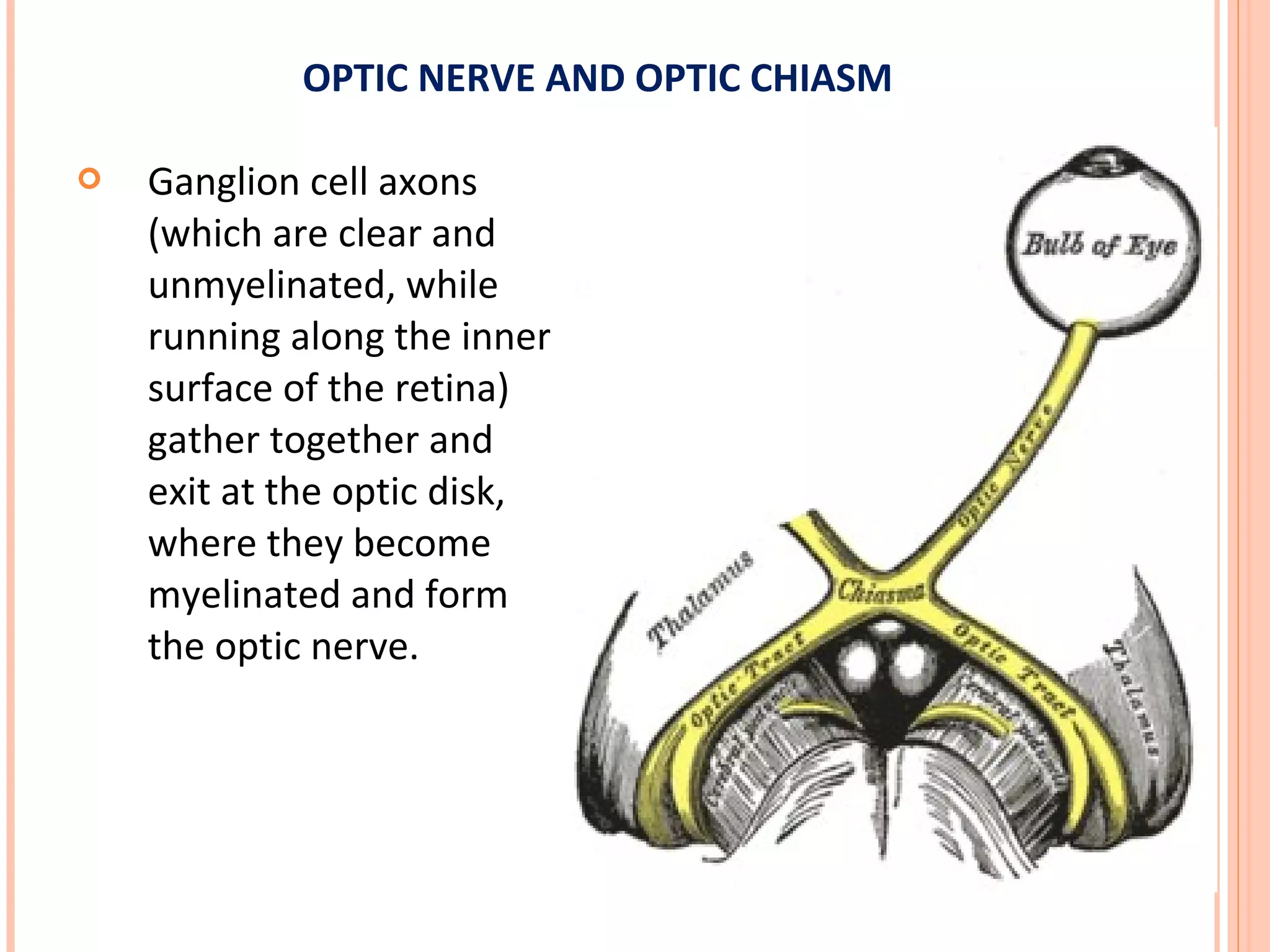
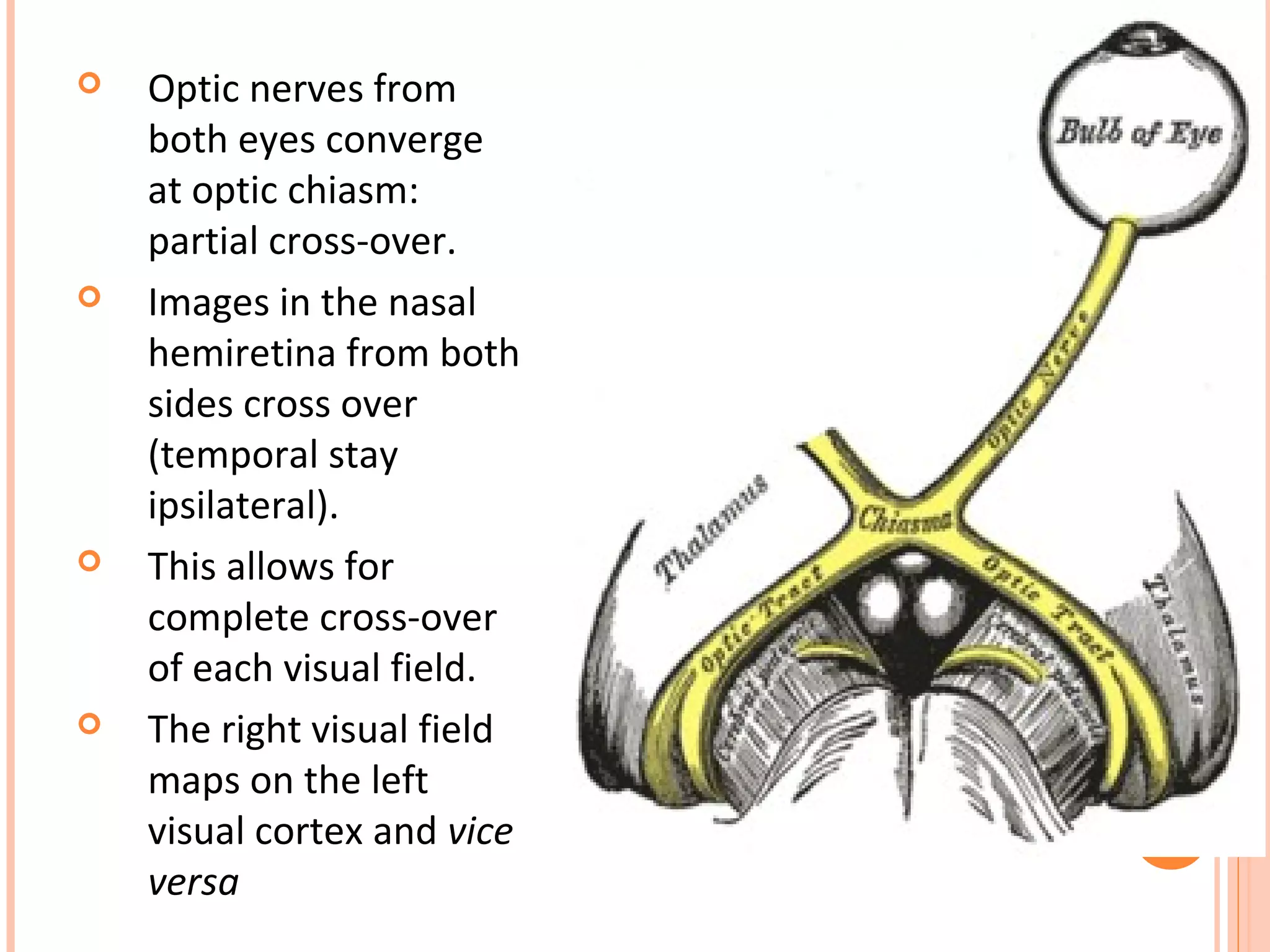
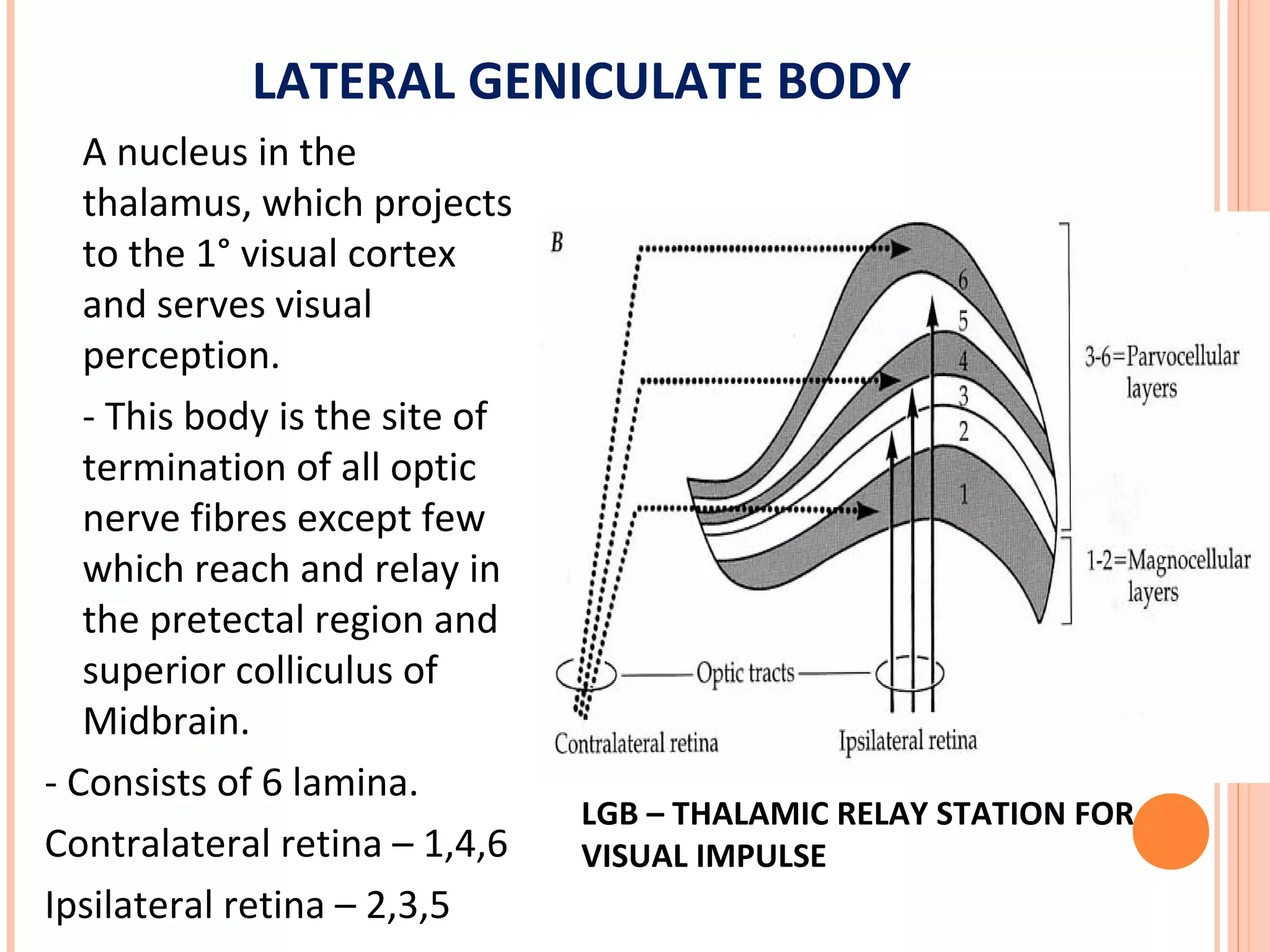
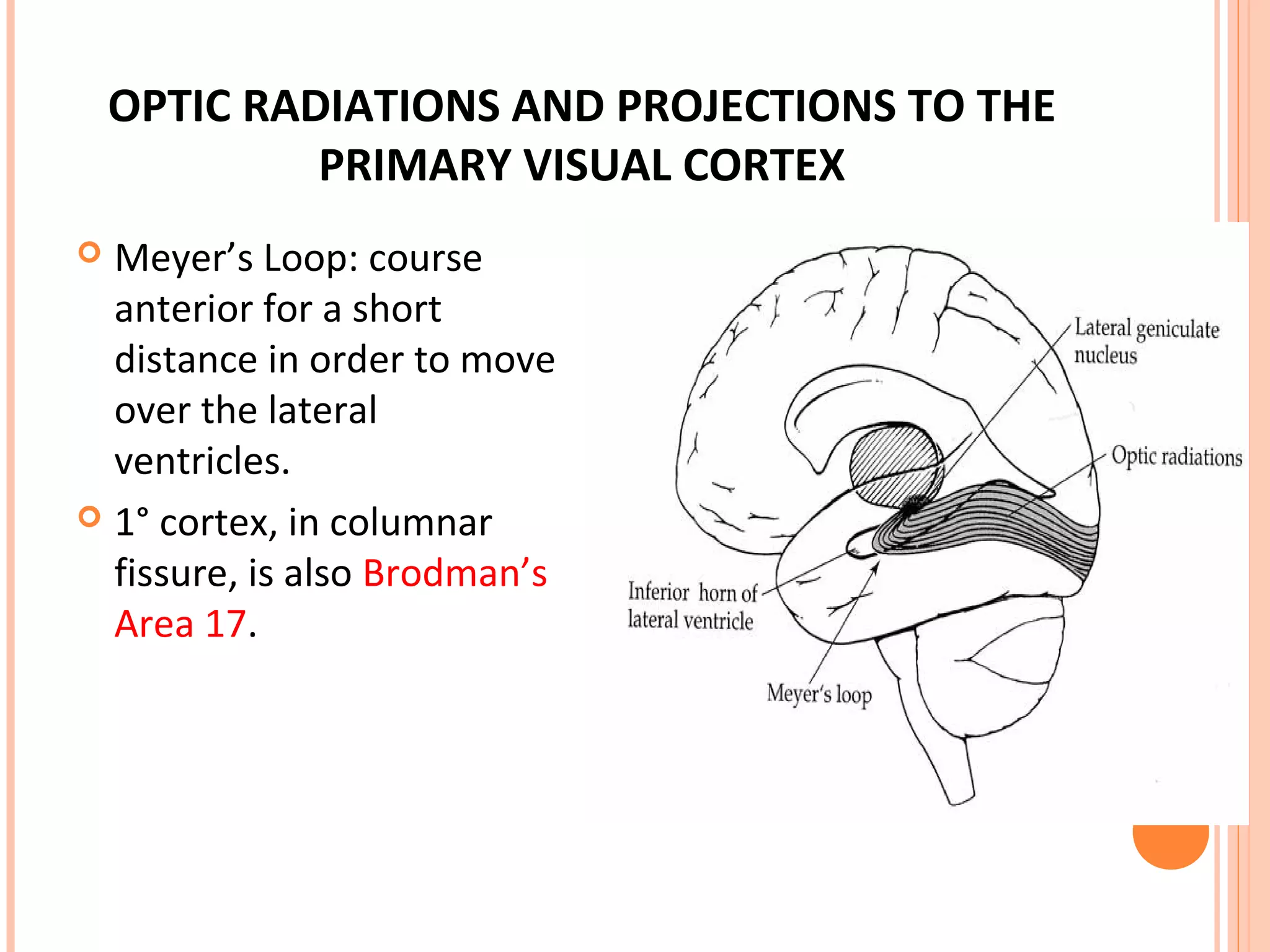
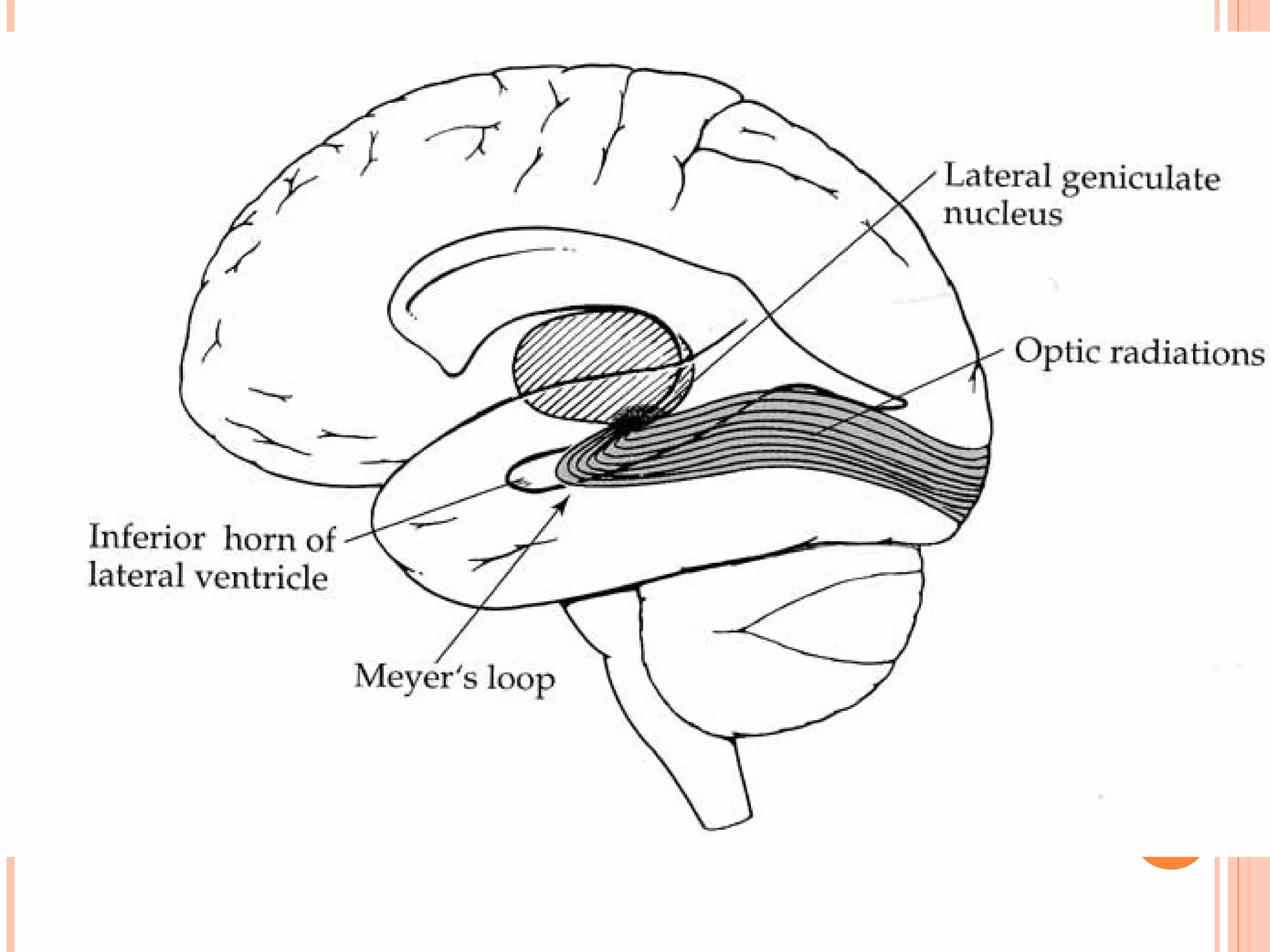
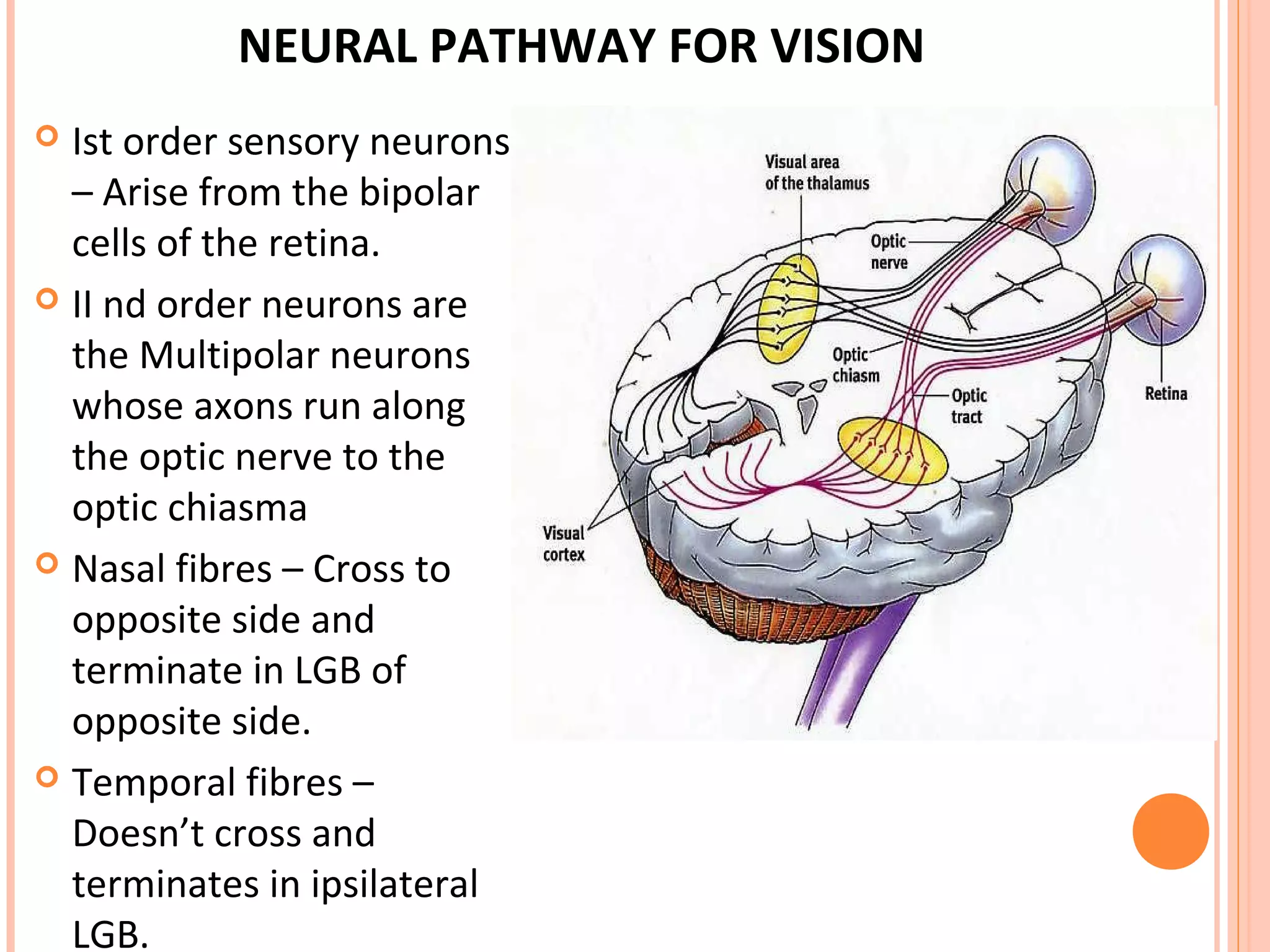
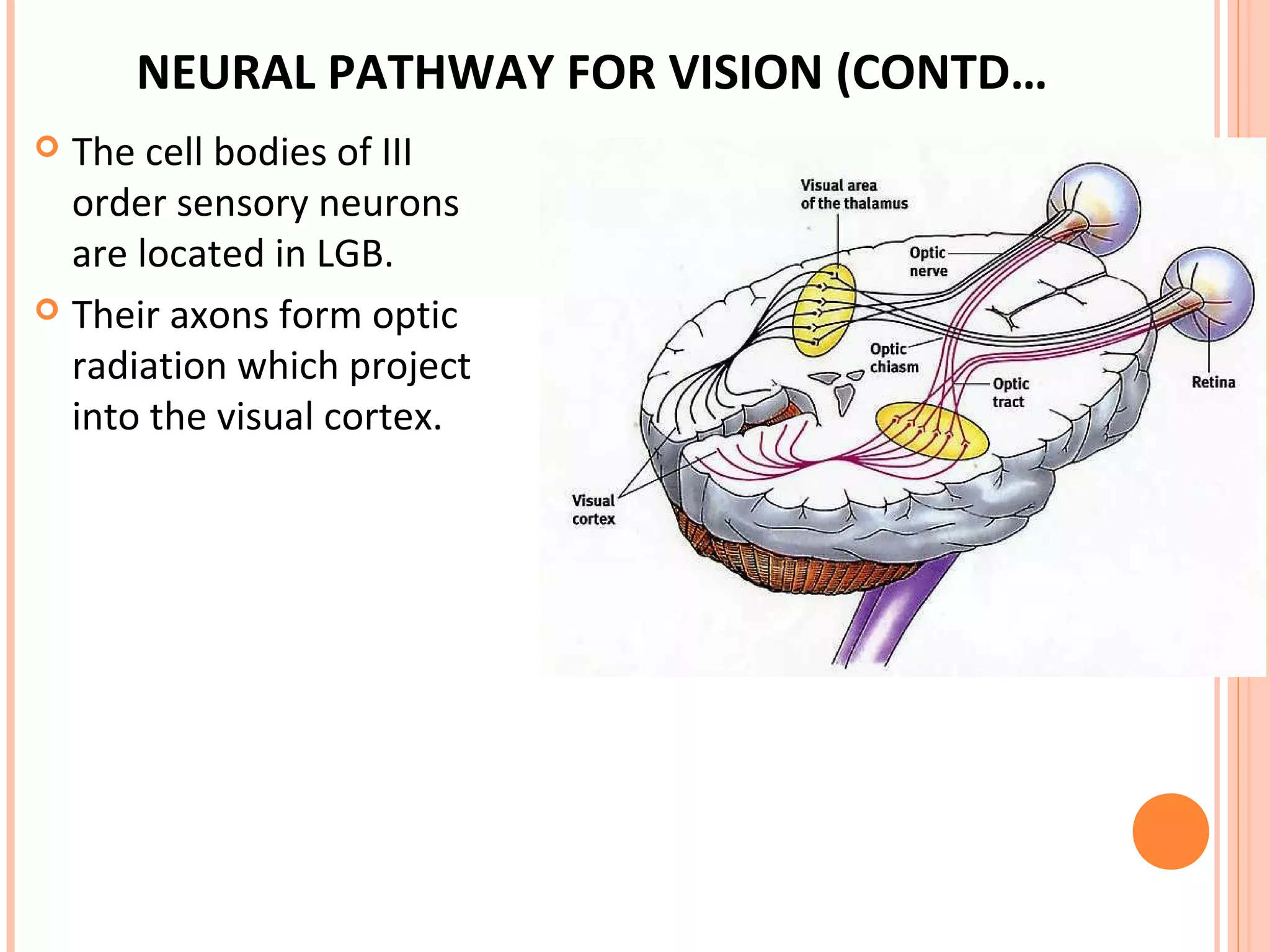
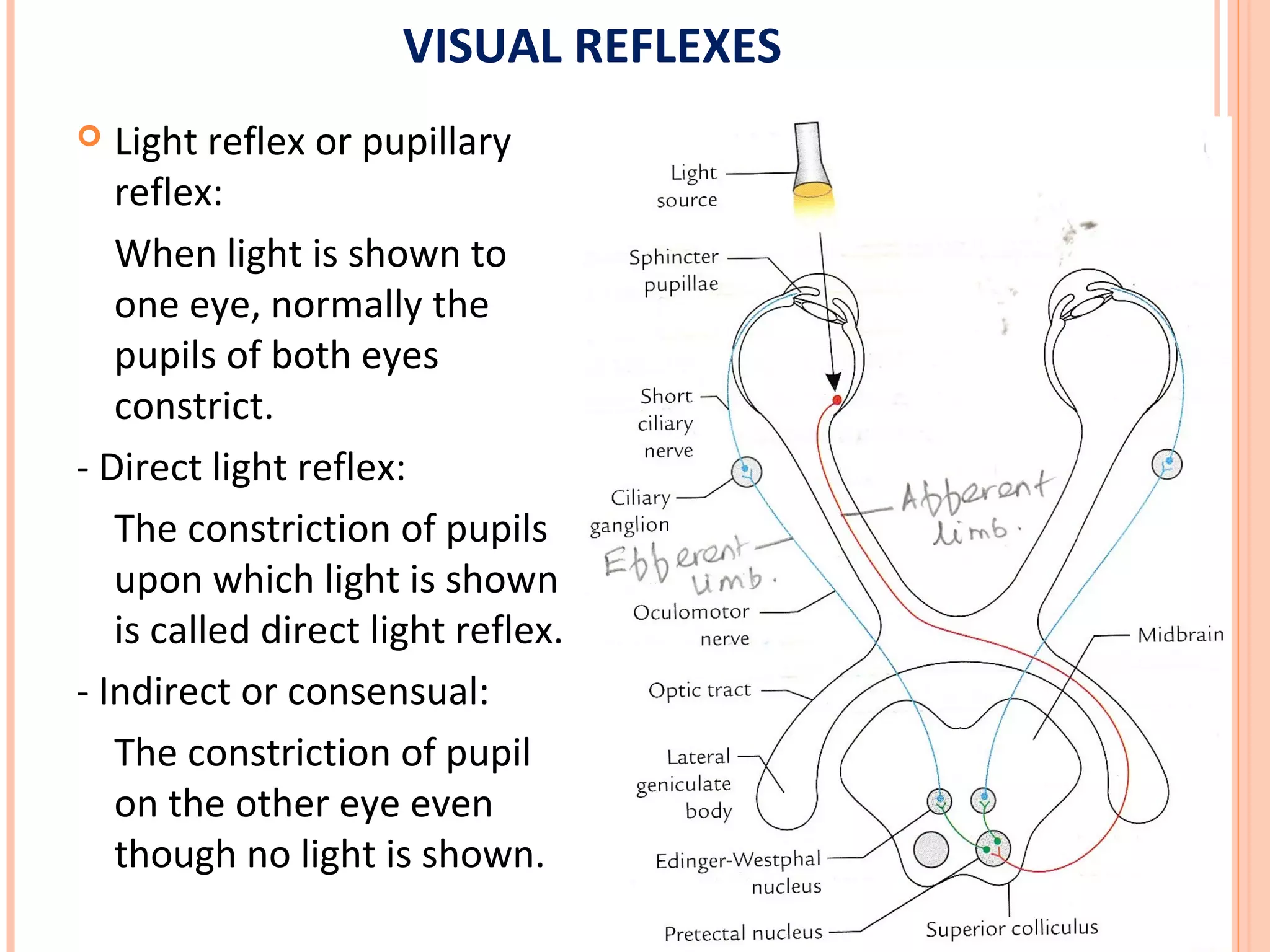
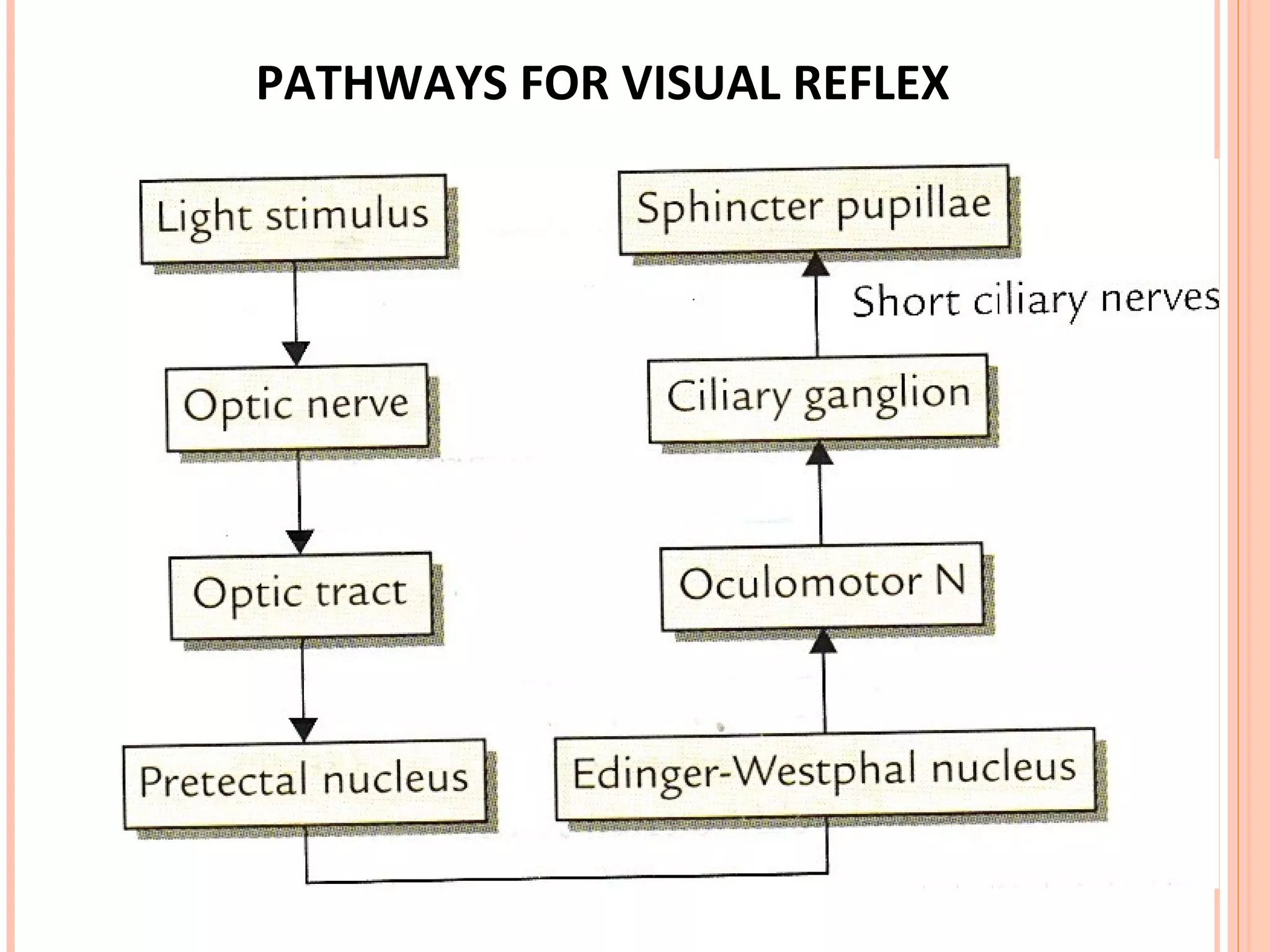
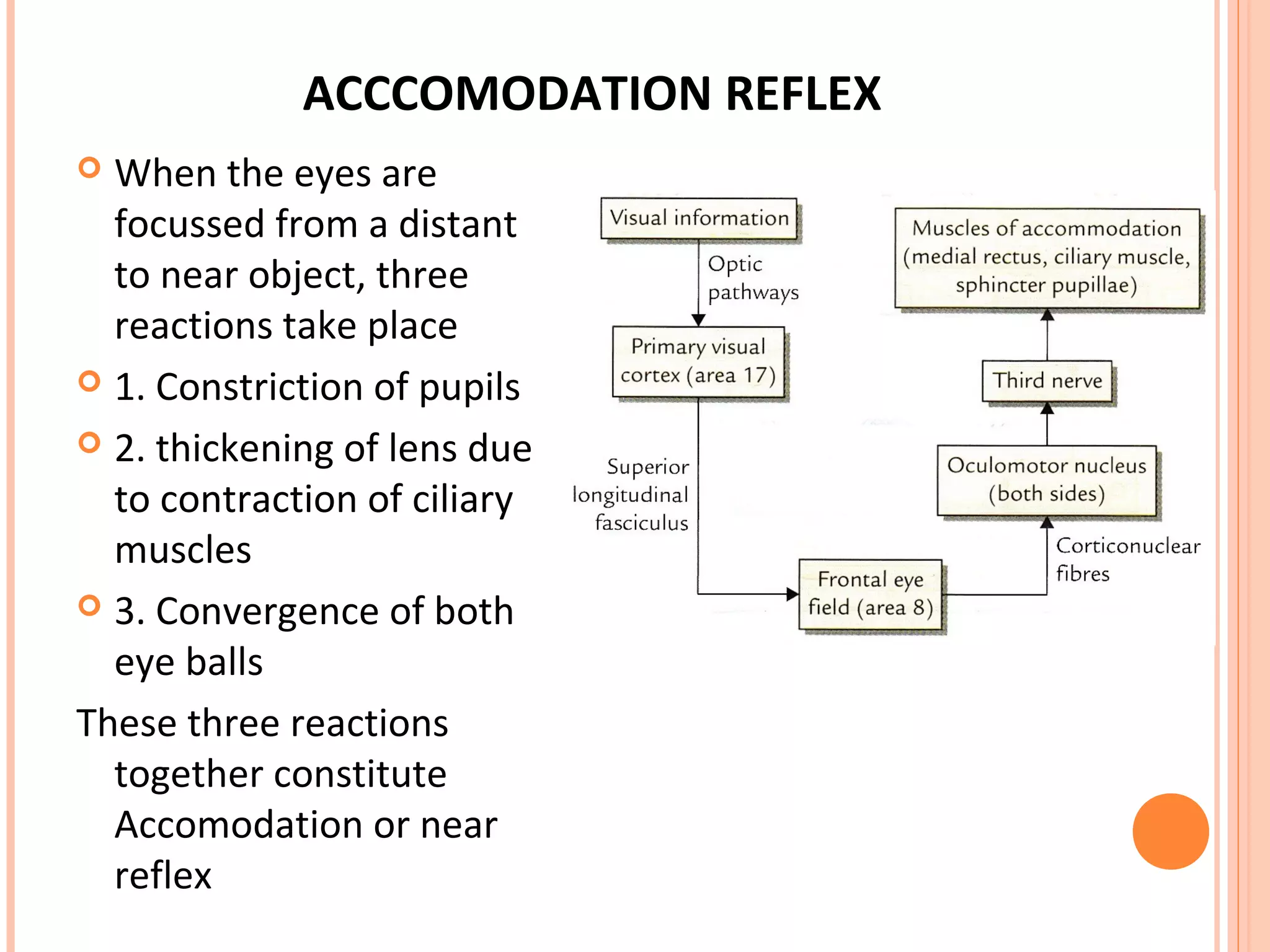
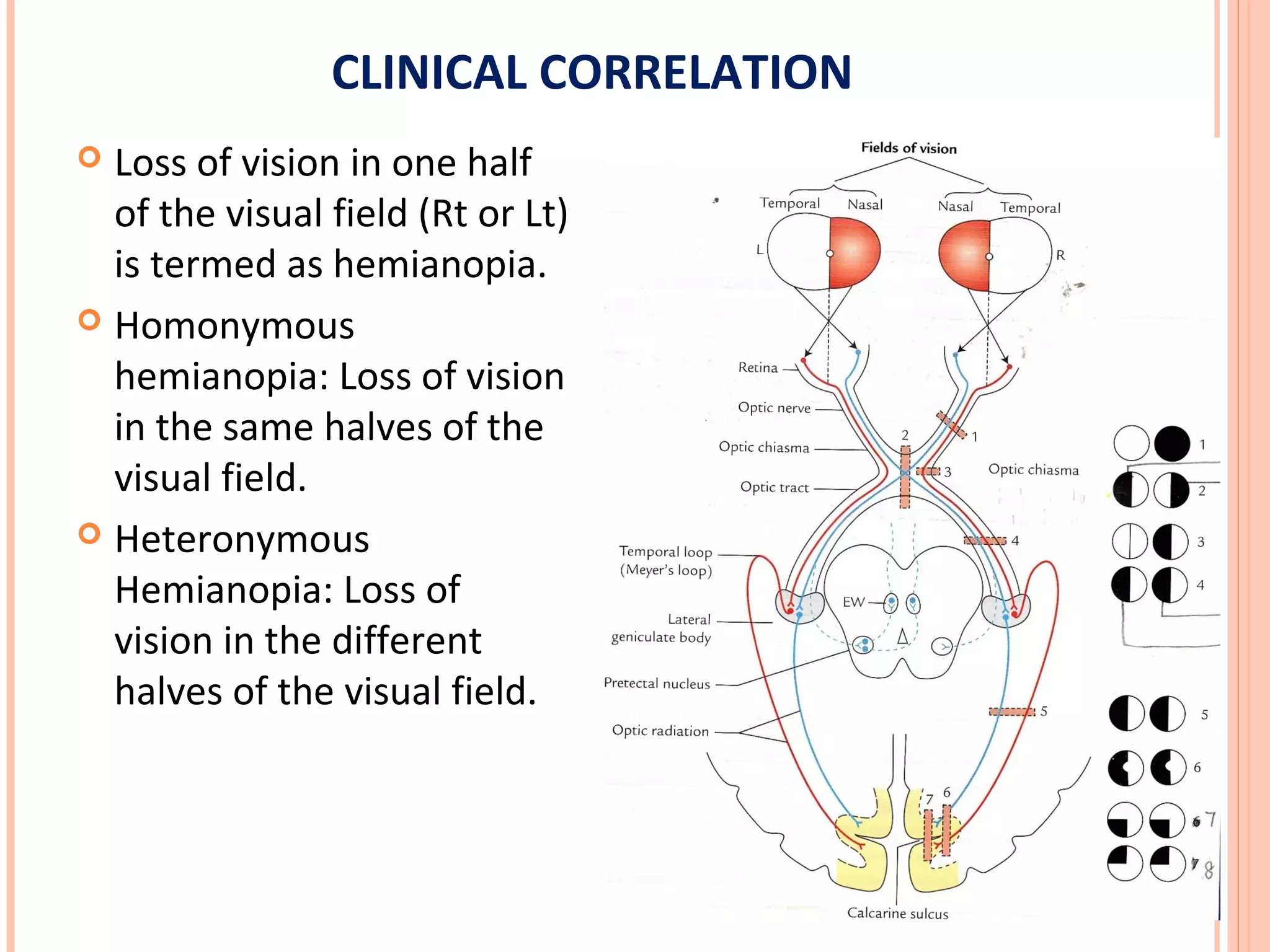
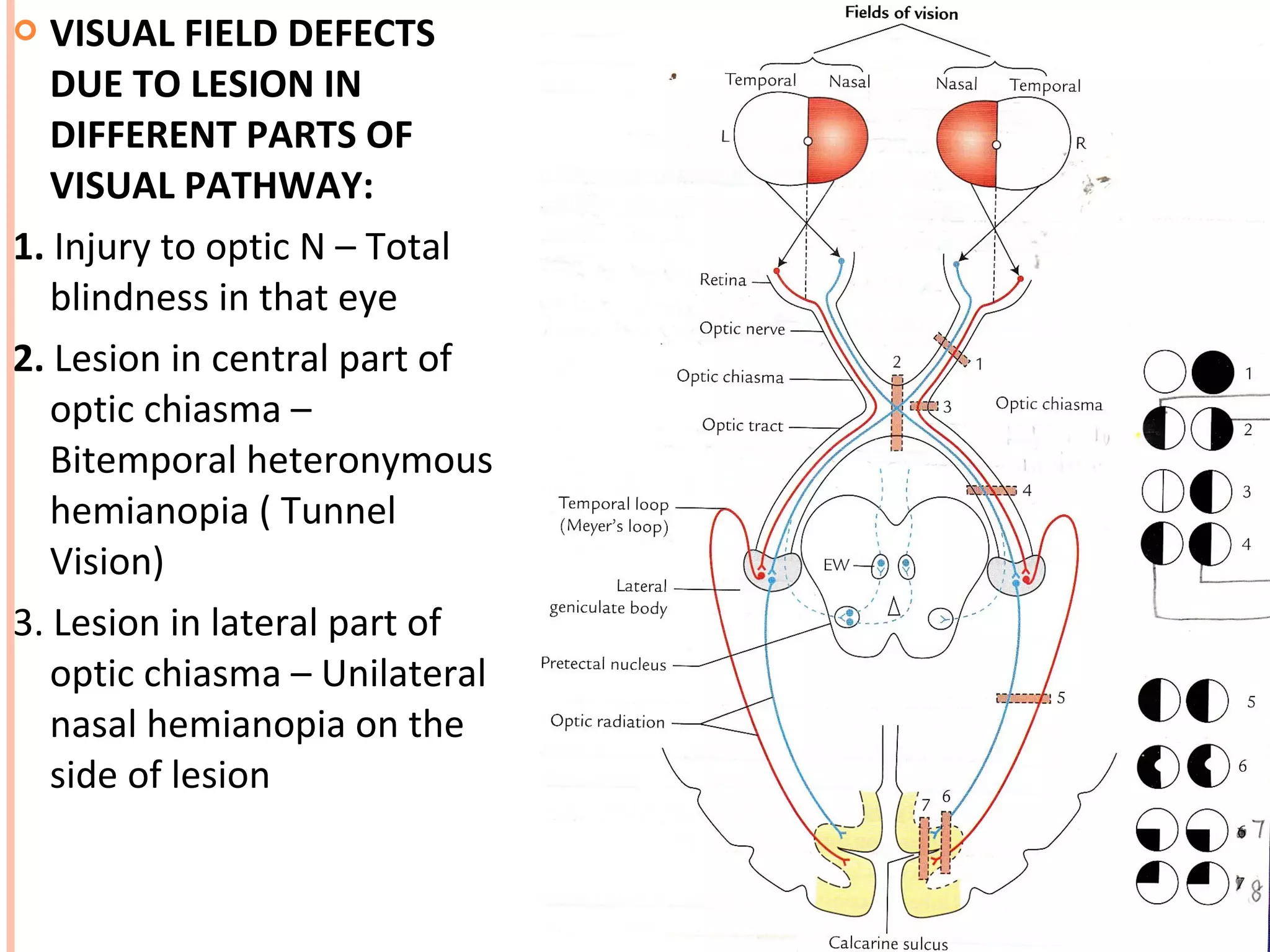
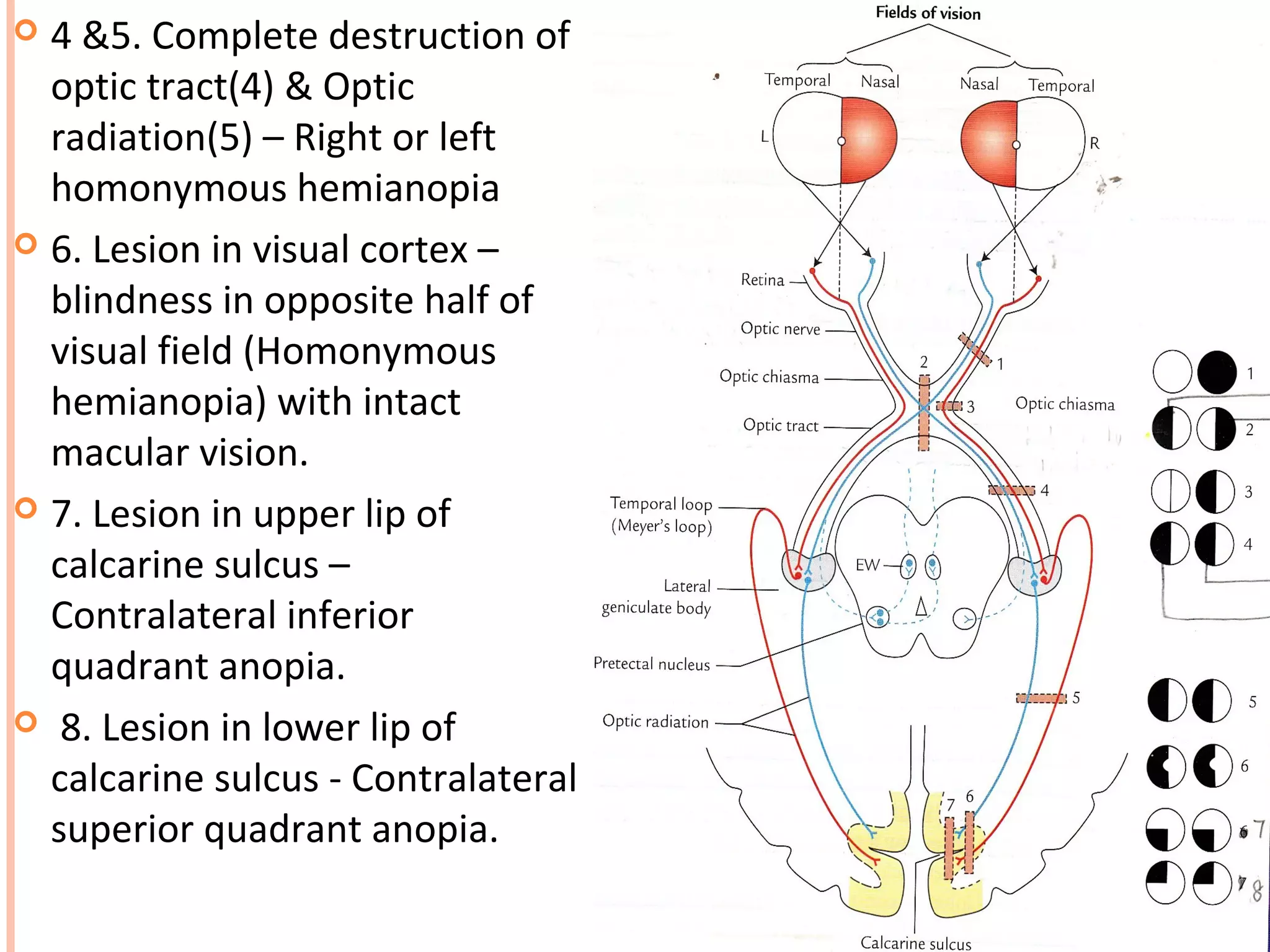
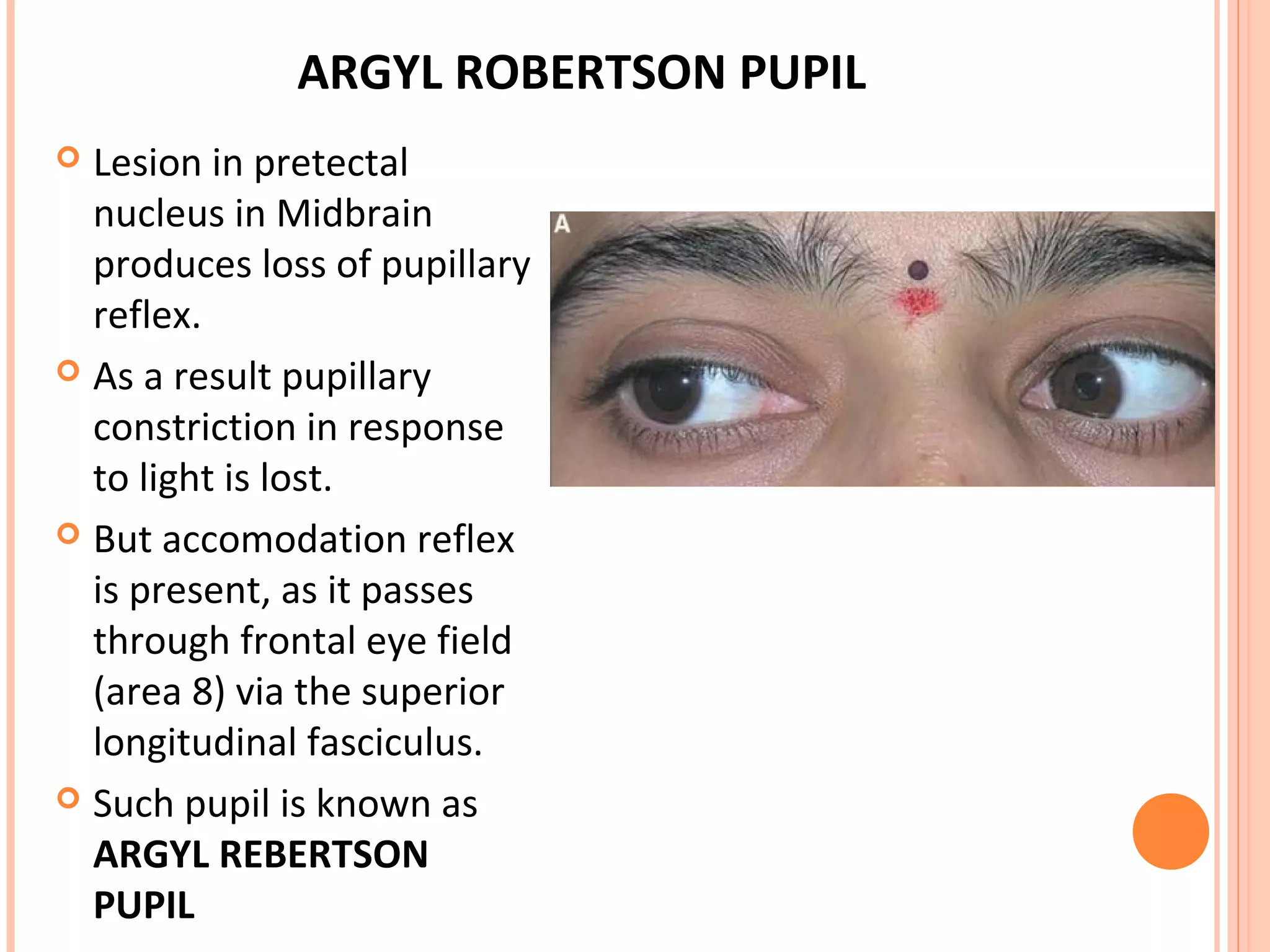
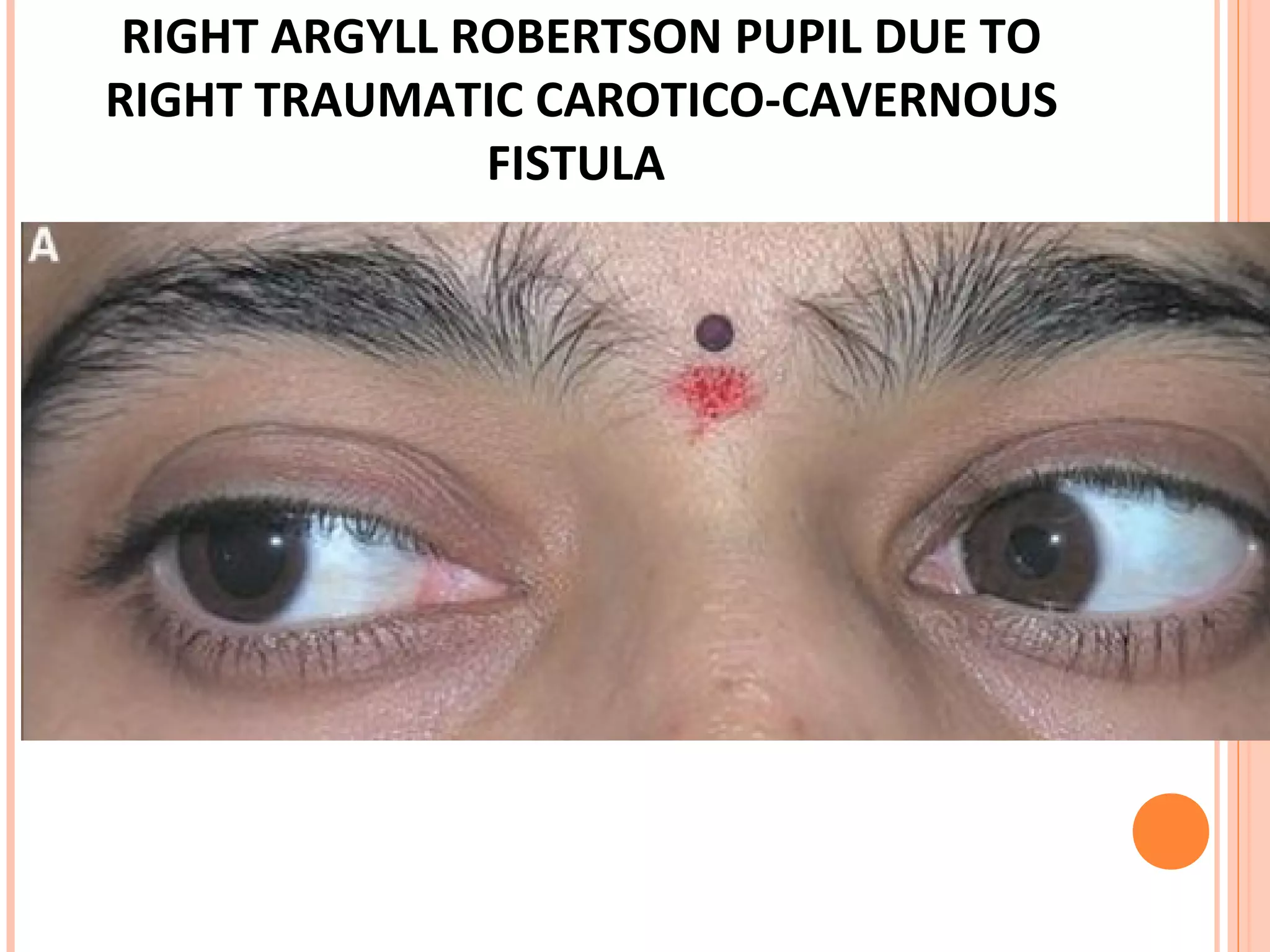
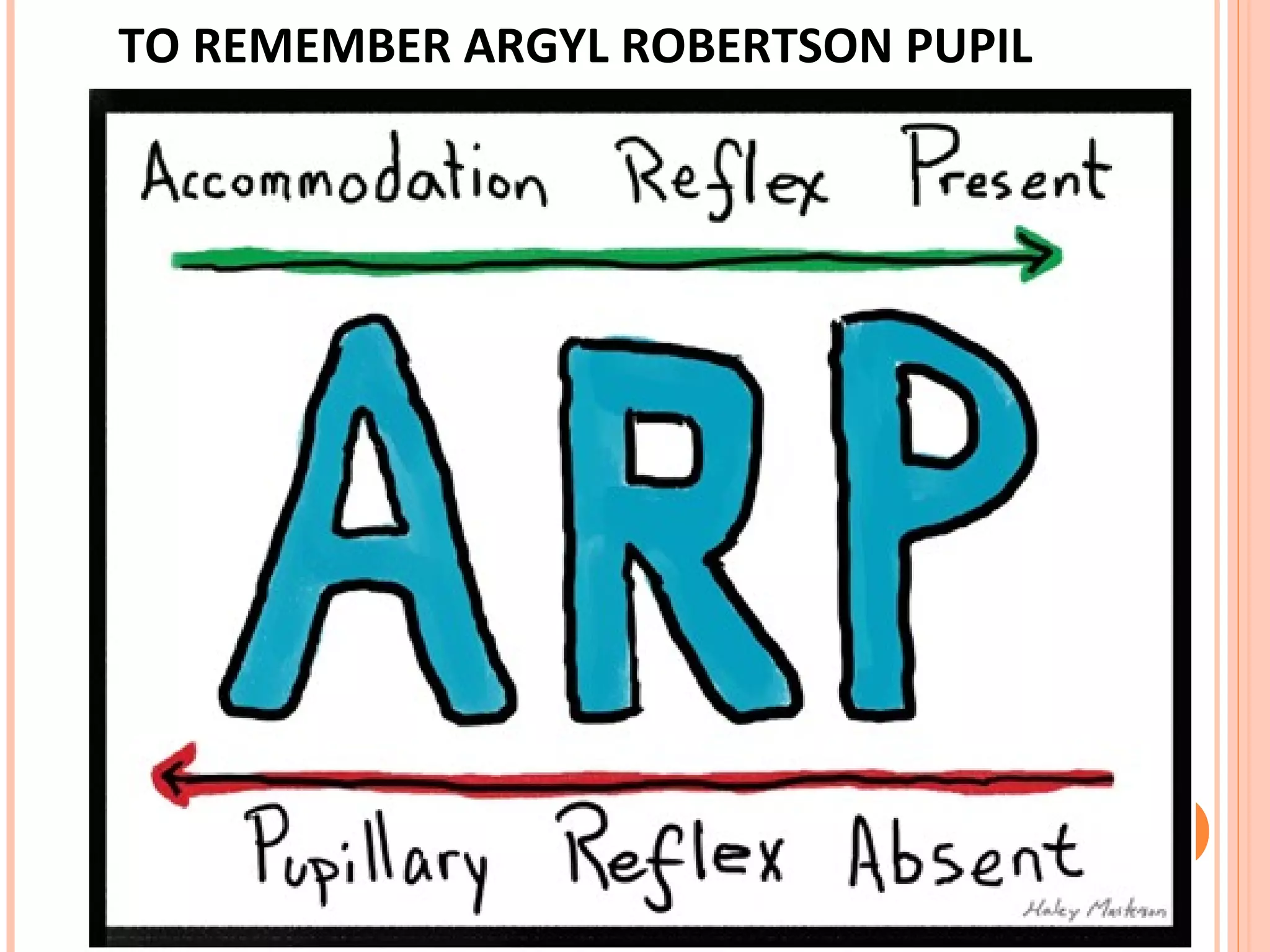
The visual pathway consists of the retina, optic nerve, optic chiasm, optic tract, lateral geniculate body, optic radiations, and visual cortex. The retina contains photoreceptors and bipolar and ganglion cells. Ganglion cell axons form the optic nerve, which crosses at the optic chiasm. The optic tract relays signals to the lateral geniculate body before projecting to the primary visual cortex via the optic radiations. Lesions in different parts of the pathway cause specific visual field defects, such as homonymous hemianopia from damage to the optic radiation. The pupillary light reflex and accommodation reflex are mediated by subcortical structures.