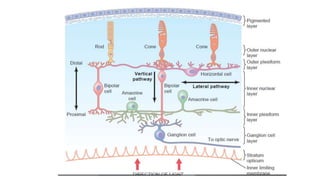
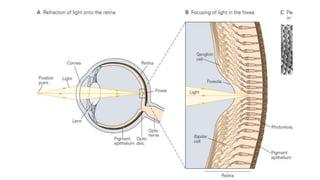
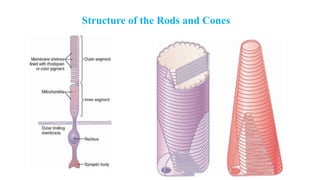
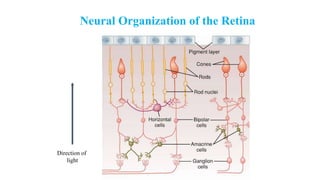
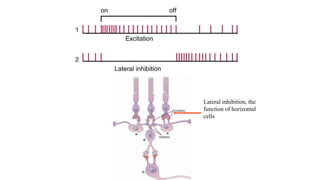
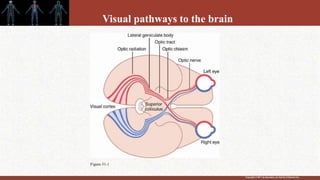
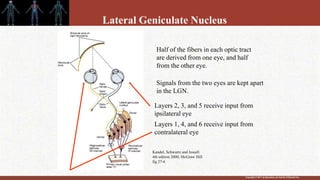
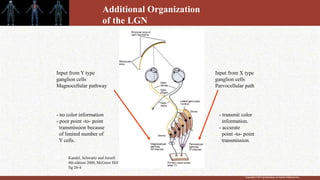
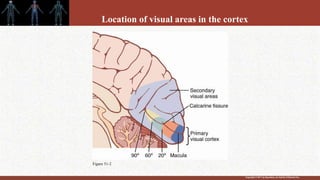
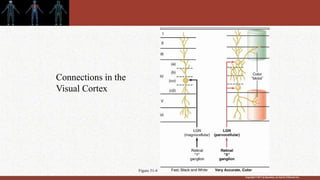
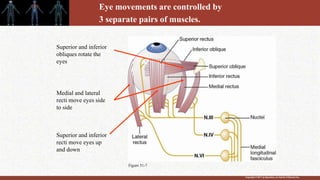
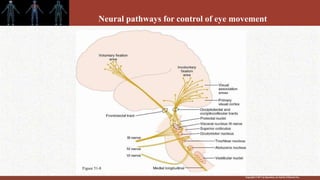
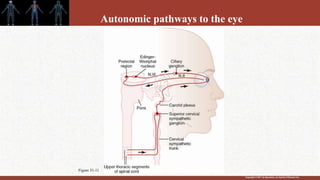
1. The retina contains light-sensitive rods and cones that detect light and transmit signals through neurons to the brain.
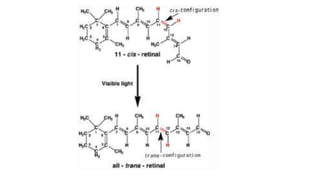
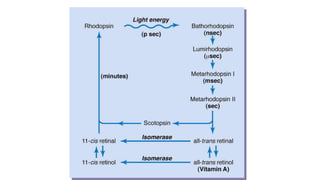
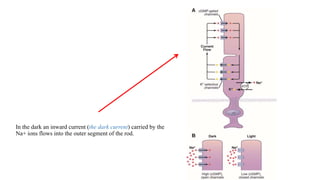
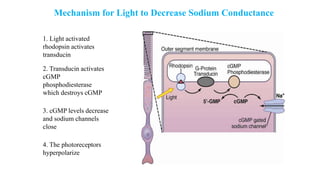
2. Light exposure causes the photopigment rhodopsin in rods to decompose, hyperpolarizing the rods and decreasing the "dark current" of sodium ions flowing into them.
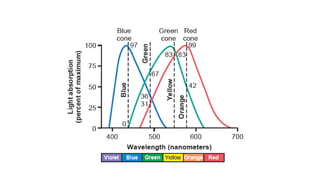
3. The fovea contains only cones, maximizing visual acuity, while the peripheral retina contains more rods for low-light vision.