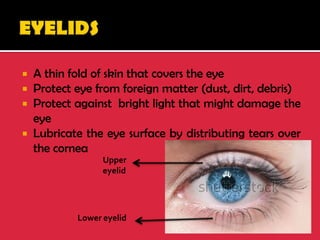
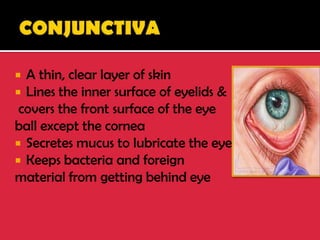
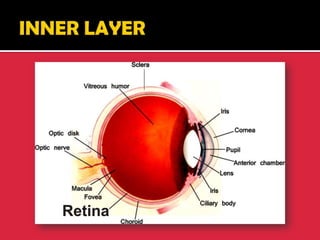
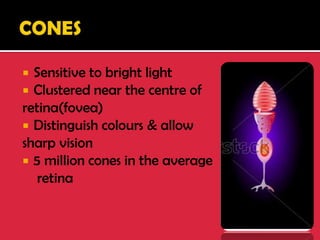
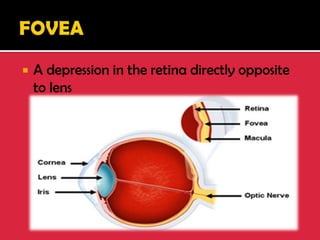
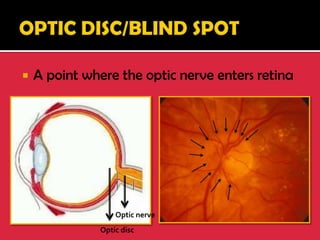
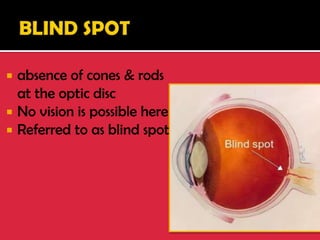
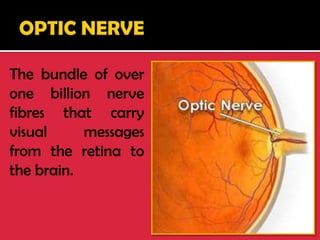
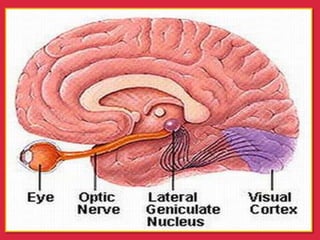
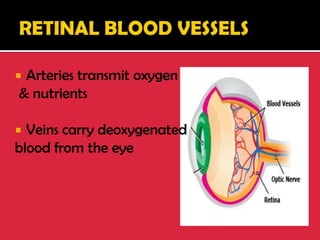
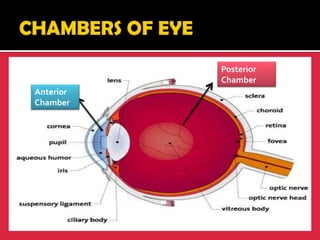
The eye is a spheroid structure around the size of a ping pong ball that functions to distinguish light, dark, shape, color, brightness and distance. It includes structures like the eyelids, conjunctiva, cornea, iris, pupil, lens, vitreous humor, retina, blood vessels and optic nerve. The retina contains light-sensitive photoreceptor cells called rods and cones that convert light into electrical signals to the brain where they are interpreted as vision.