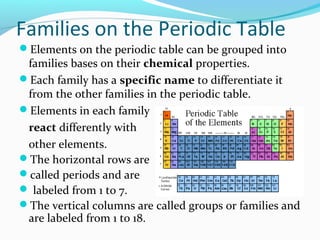
The document summarizes the different families of elements on the periodic table. It explains that elements are grouped into families based on their chemical properties and each family has a specific name. It then proceeds to describe the key properties and representative elements of each family, including alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, transition metals, boron family, carbon family, nitrogen family, oxygen family, halogens, noble gases, and rare earth metals. Each family is assigned a different color for visualization purposes.