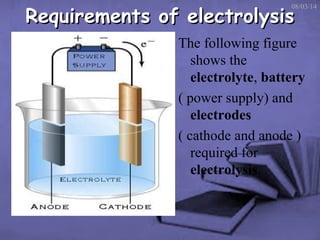
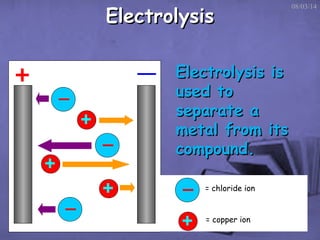
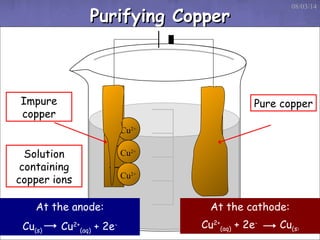
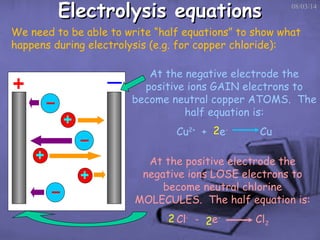
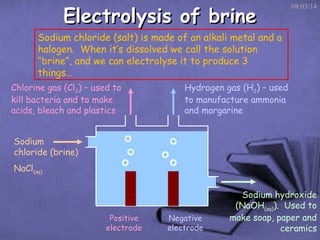
This document discusses electrolysis, which is the process of using direct current to cause non-spontaneous chemical reactions. Electrolysis requires an electrolyte containing free ions, a direct current power supply, and two electrodes. During electrolysis, ions are oxidized or reduced at the electrodes through electron transfer. As an example, electrolysis can be used to purify copper by dissolving impure copper and conducting electrolysis, depositing pure copper at the cathode. Electrolysis equations describe the half-reactions that occur at each electrode. The document also provides an example of electrolyzing brine to produce chlorine gas, hydrogen gas, and sodium hydroxide.