Embed presentation
Downloaded 275 times







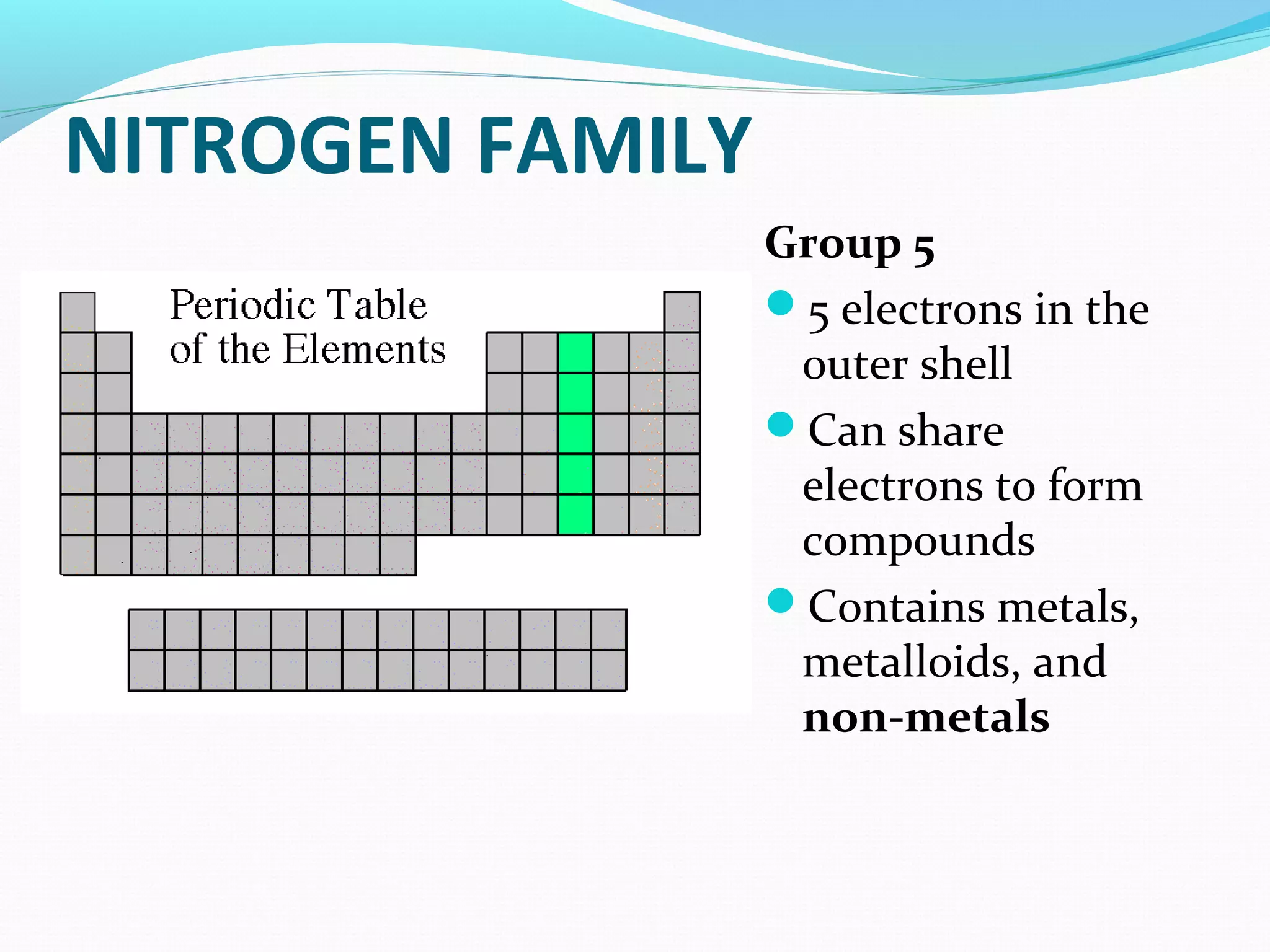
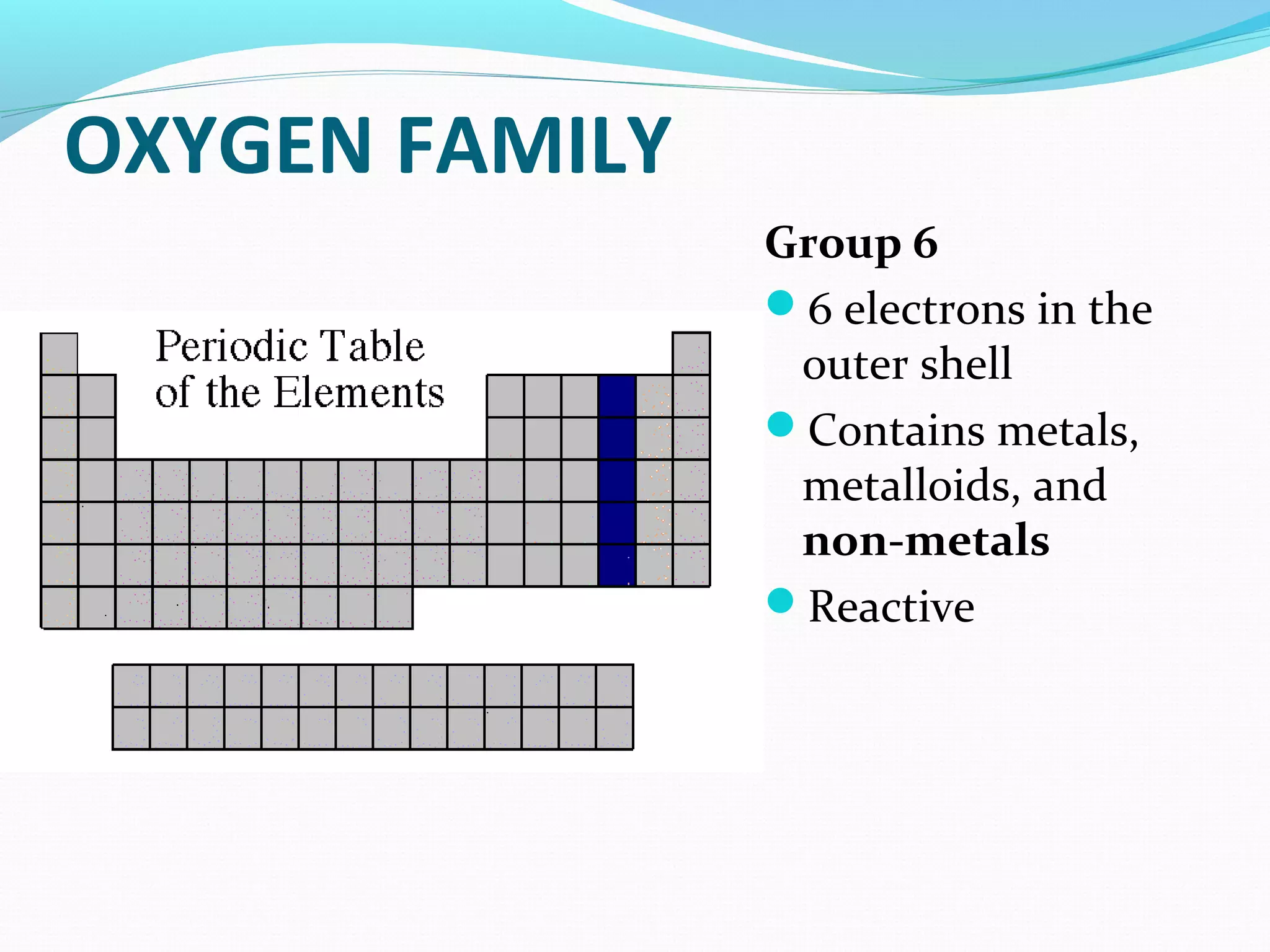
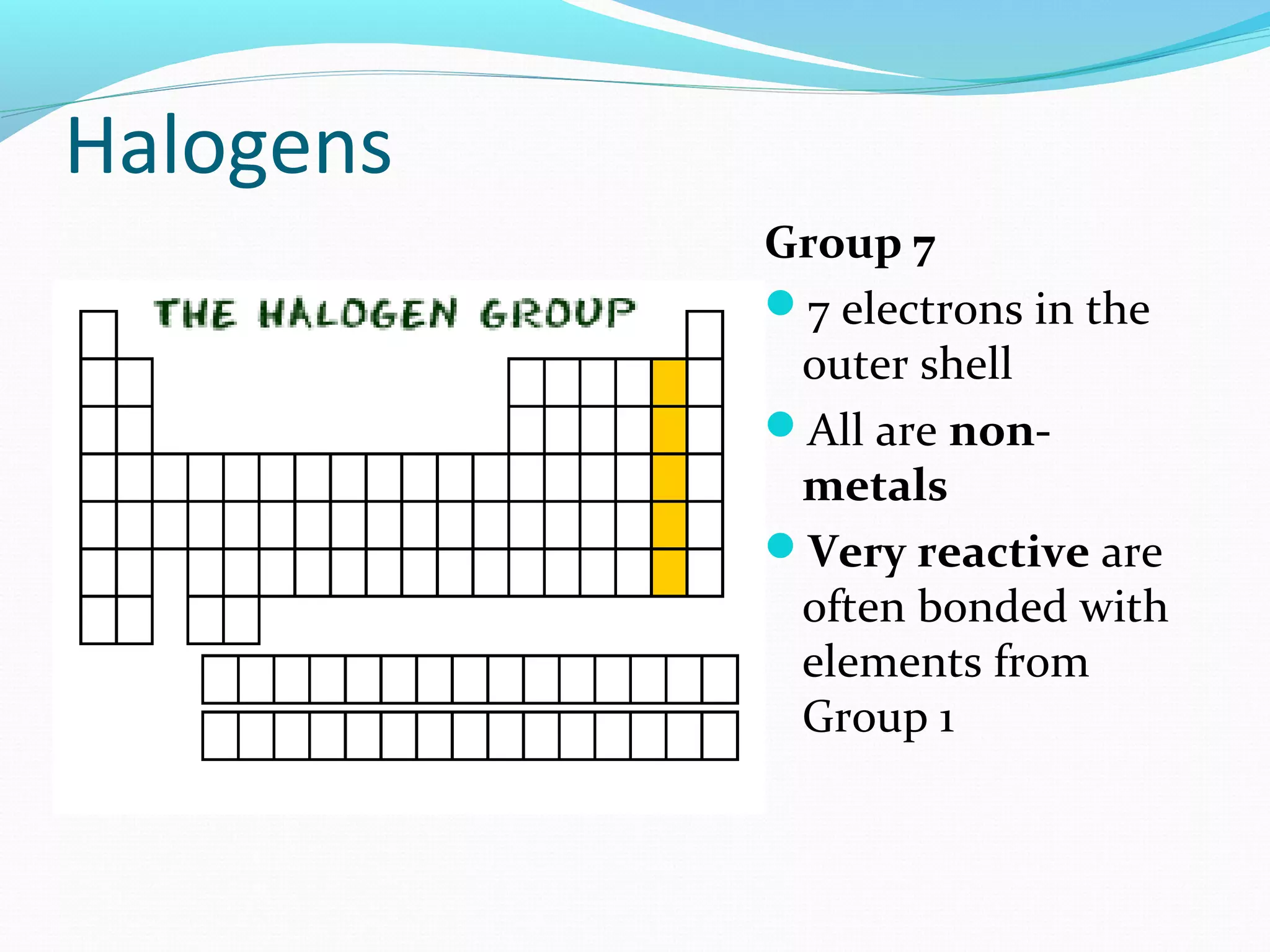
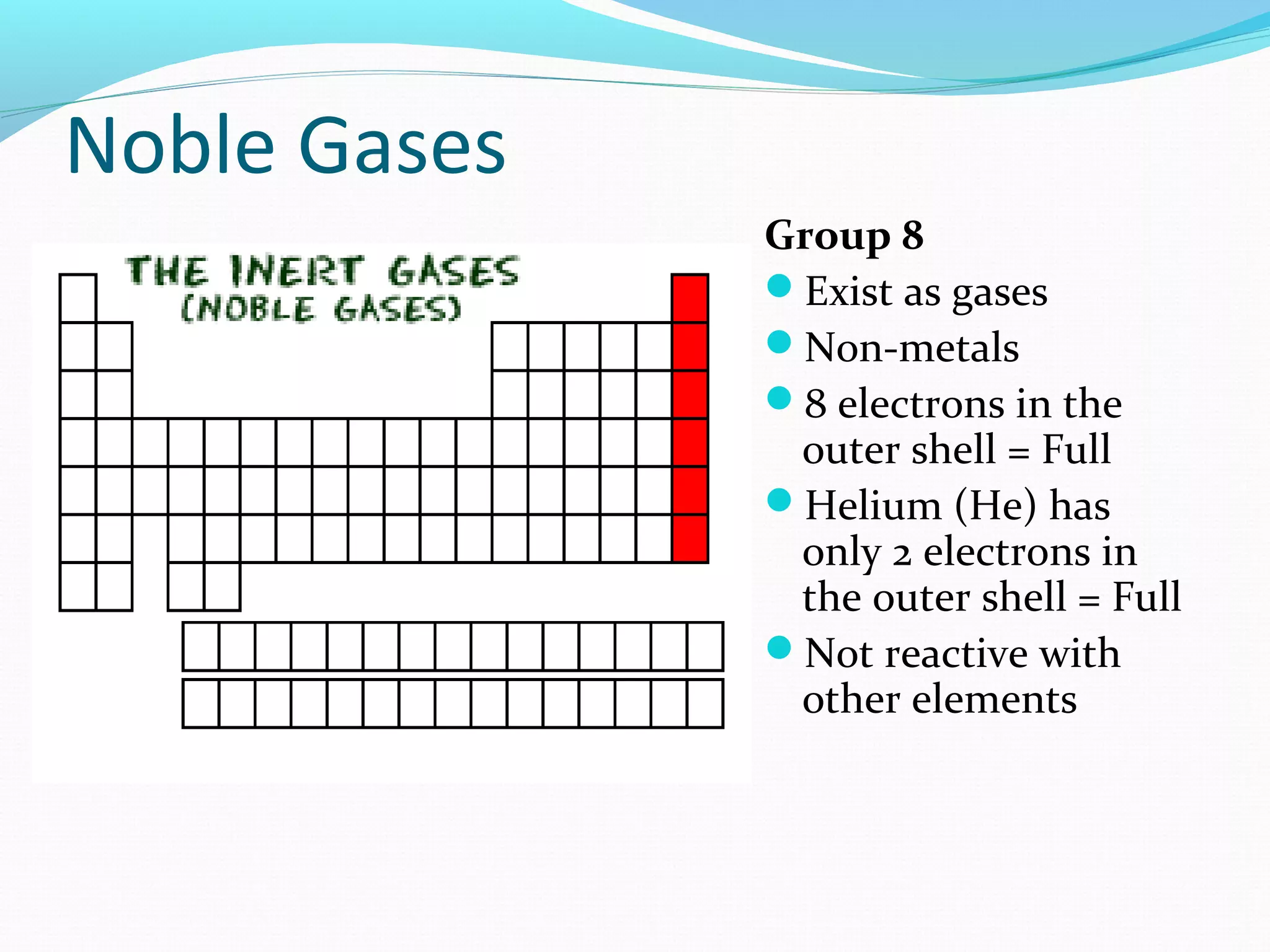



The document discusses the different families of the periodic table. Elements are grouped into families based on their chemical properties. Each family has a specific name and elements within the same family react similarly with other elements. The families include alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, transition metals, boron family, carbon family, nitrogen family, oxygen family, halogens, noble gases, and rare earth metals. Each family is characterized by the number of electrons in the outer shell and whether the elements are metals, non-metals, or metalloids.












