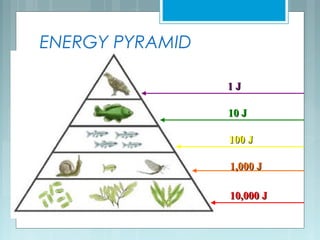
This document discusses trophic levels in food chains and energy transfer through ecosystems. It defines trophic levels as the position organisms occupy in a food chain based on what they consume for energy. Food chains show the transfer of energy from producers like plants at the first trophic level to primary, secondary, and tertiary consumers at higher levels. Food webs represent multiple interconnected food chains and alternative pathways for energy transfer. There is a 90% loss of energy between each trophic level, demonstrating that less energy is available at higher levels. This energy transfer can be represented by an ecological pyramid that shows decreasing numbers of organisms and available energy as one moves up trophic levels in an ecosystem.