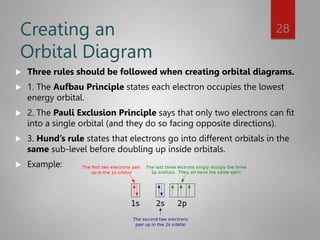
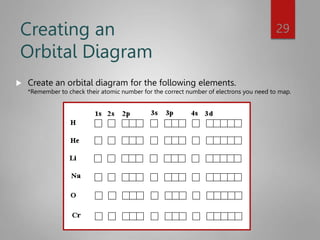
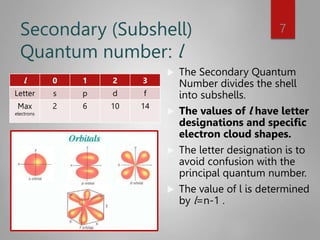
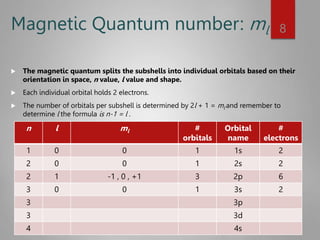
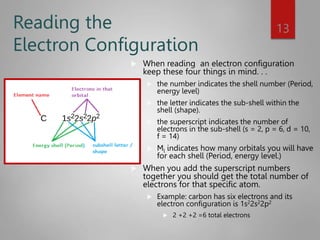
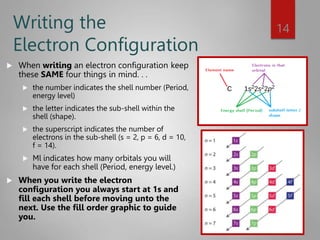
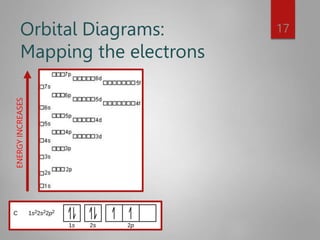
This document discusses electron configurations and orbital diagrams. It begins by defining atomic orbitals as regions where electrons are likely to be found, and notes that electron configurations show how electrons are arranged around the nucleus for each element. It then explains the four quantum numbers - principal, angular momentum, magnetic, and spin - that describe electrons and their locations. The document provides examples of writing electron configurations and constructing orbital diagrams according to Aufbau principle, Pauli exclusion principle, and Hund's rule.











![Noble Gas configuration
To write a noble gas (shorthand) configuration for any element,
count backwards from that element until you reach a noble gas.
Write that element in brackets.
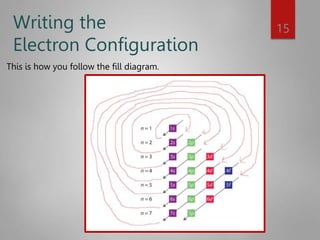
Then, continue forward with next sub-shell(s) - see the
following version of the periodic chart that shows the sub-shell
order with respect to the elements.
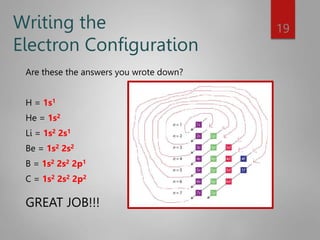
For example C = 1s2 2s2 2p2
Carbon’s Noble Gas Configuration is = [He] 2s2 2p3
It may not seem like a big difference but when you work with
elements of higher atomic numbers it is a great time saver when
writing out their configuration.
For example Br = 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p5
The Noble Gas configuration of bromine is = [Ar]4s2 3d10 4p5
22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/electronconfiguration2021-230515160258-dbe29e5d/85/Electron-configuration-2021-pptx-22-320.jpg)
![Noble Gas configuration
For example, if we wanted to do the shorthand
configuration for sodium (Na), you would count back
one element to neon (Ne) and put Ne in brackets.
[Ne]
Put this element symbol in brackets and then, noting
that the next correct sub-shell is 3s, include the rest of
the electrons as we did with the smaller elements.
[Ne]3s1
23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/electronconfiguration2021-230515160258-dbe29e5d/85/Electron-configuration-2021-pptx-23-320.jpg)

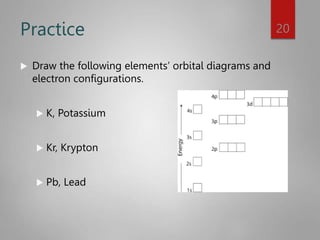
![Practice
Write the following noble gas configuration for the
following elements.
Be, Beryllium
[He]2s2
F, Fluorine
[He]2s22p5
Pt, Platinum
[Xe]6s2
25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/electronconfiguration2021-230515160258-dbe29e5d/85/Electron-configuration-2021-pptx-25-320.jpg)