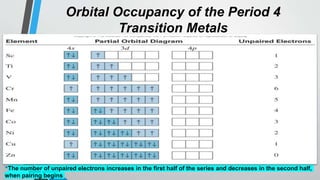
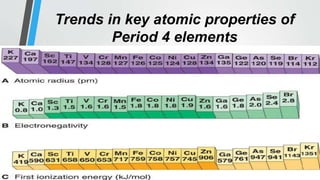
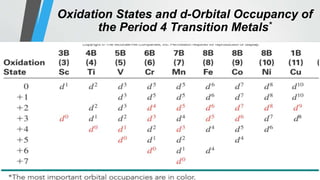
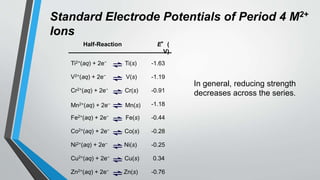
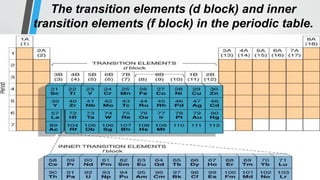
The document discusses the properties and trends of transition metals in the periodic table, including their electron configurations, oxidation states, and differences from main group elements. It highlights that transition metals often exhibit multiple oxidation states, colored compounds, and paramagnetism due to unpaired electrons. Additionally, it outlines trends in atomic size, electronegativity, and ionization energy across periods and groups of transition metals.


![Electron Configurations of Transition
Metals and their Ions
The d-block elements have the general condensed ground-
state configuration [noble gas]ns2(n – 1)dx where n = 4 to 7
and x = 1 to 10.
Periods 6 and 7 elements include the f sublevel:
[noble gas]ns2(n – 2)f14(n – 1)dx where n = 6 or 7.
Transition metals form ions through the loss of the ns
electrons before the (n – 1)d electrons](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/transitionelements-201117053910/85/Transition-elements-4-320.jpg)