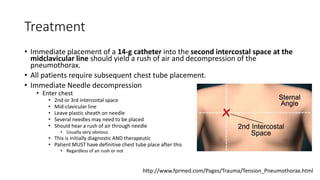
This document discusses parapneumonic effusion and pneumothorax. It defines parapneumonic effusion as a pleural effusion caused by pneumonia or lung abscess. It describes the three stages of parapneumonic effusion: exudative, fibropurulent, and fibrotic. Pneumothorax is defined as air in the pleural space. Primary spontaneous pneumothorax occurs without lung disease, while secondary pneumothorax is associated with lung conditions like COPD. Risk factors, signs and symptoms, and management strategies are outlined for both conditions.