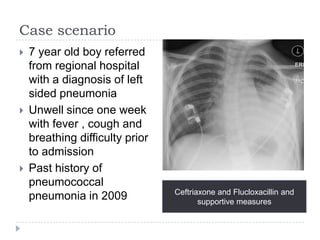
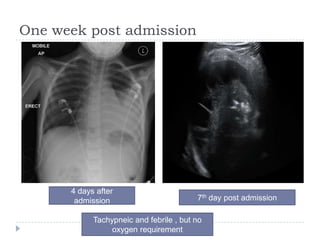
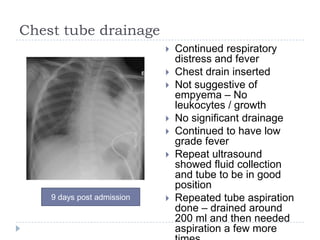
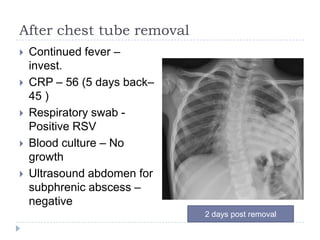
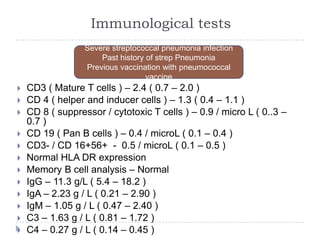
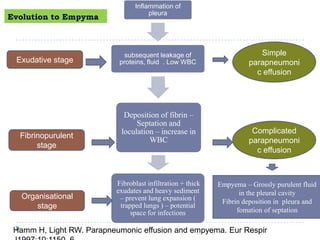
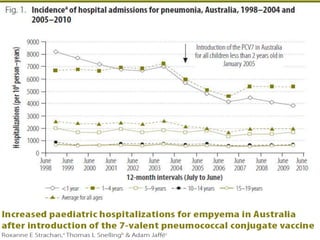
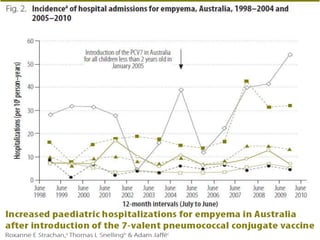
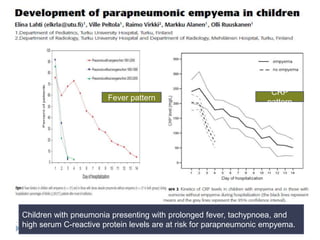
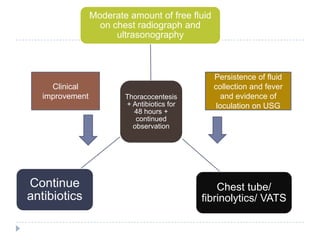
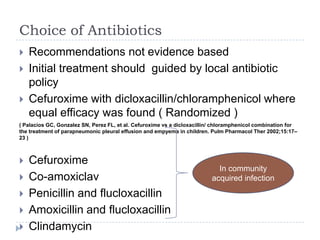
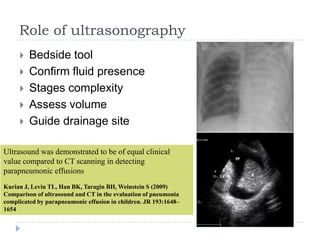
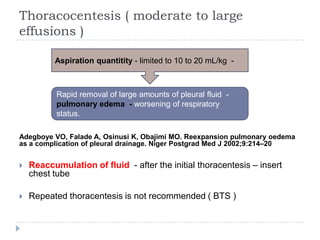
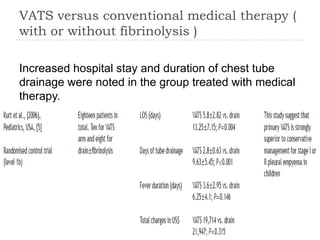
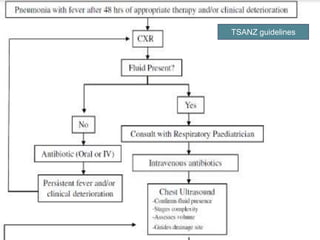
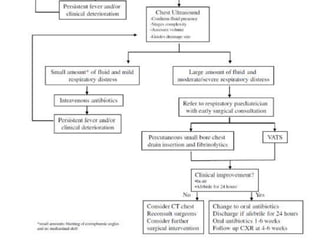
The document discusses parapneumonic effusion and empyema in children, detailing a case study of a seven-year-old boy with pneumonia and subsequent effusion complications requiring management strategies such as chest tube drainage and antibiotics. It emphasizes the importance of proper imaging, antibiotic selection, and interventions like video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) to improve outcomes. The guidelines advocate for high-dose antibiotics and drainage methods while highlighting the need for follow-up to ensure resolution of symptoms and chest radiograph normalization.