The document discusses tips for managing ascites, including performing large volume paracentesis with albumin and continuing diuretics if renal sodium excretion is over 30 mmol/day. It also discusses using non-selective beta-blockers and transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts (TIPS) to treat refractory ascites, noting that TIPS significantly reduces hepatic encephalopathy compared to large volume paracentesis alone. TIPS is an effective option for controlling ascites but carries a higher risk of hepatic encephalopathy compared to large volume paracentesis.


![Refractory ascites (ra)
• In about 5-10% of cirrhotic pts per year and as liver disease progresses, response to sodium restriction
and diuretics diminishes, leading to RA.[1]
• RA is defined by the failure to mobilize ascites despite high-dose diuretics, typically about 400 mg/day
spironolactone and 160 mg furosemide or equivalent dose of loop-acting diuretic.[1]
• Ascites is also considered to be refractory when effective doses of diuretics cannot be used because of
development of diuretic-associated complications. RA is often a/with dilutional hyponatremia, type 2
HRS, SBP, and muscle wasting.[2]
Definition table in next slide
1. Arroyo V, Gines P, Gerbes AL, Dudley FJ, Gentilini P, Laffi G, et al. Definition and diagnostic criteria of refractory ascites and hepatorenal syndrome in cirrhosis. International ascites club. Hepatology 1996;23:164-176.
2. Gines P, Cardenas A, Arroyo V, Rodes J. Management of cirrhosis and ascites. N Engl J Med 2004;350:1646-1654.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tipsinascitesfinal-200809165039/85/TIPS-in-Ascites-4-320.jpg)



![1960s
Inadvertent portal access during
transjugular cholangiography
1969
Rosch [1] discussed the potential of a
“radiologic portocaval shunt”
1982
Colapinto [2] creates the first
human balloon dilated TIPS
1988
Richeter [3] creates the first
human Palmaz stent TIPS
Early to mid-
1990s
Widespread clinical use with self-
expanding bare stents
HISTORY OF TIPS
1. Rösch J, HanafeeWN, SnowH. Transjugular portal venography and radiologic portacaval shunt: an experimental study. Radiology 1969;92(5):1112–1114
2. Colapinto RF, Stronell RD, Gildiner M, et al. Formation of intrahepatic portosystemic shunts using a balloon dilatation catheter: preliminary clinical experience. AJR AmJ Roentgenol 1983;140(4): 709–714
3. Richter GM, Palmaz JC, Noldge G, et al. The transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent-shunt (TIPSS): a new nonoperative percutaneous procedure. Radiologie 1989;29:406–411
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tipsinascitesfinal-200809165039/85/TIPS-in-Ascites-8-320.jpg)
![Mid- to late-
1990s
Animal experimentation using
silicone and e-PTFE coated stents to
improve TIPS patency [1-3]
2001
Procedure endpoint defined as a
reduction in PSG to <12 mm Hg
Early 2000s
• Early human e-PTFE covered stent-graft experience[4-7]
• Defining TIPS candidacy by prognostic parameters (e.g.,
MELD)
2005
AASLD places practice guidelines on the
“role of TIPS in the MX of PHTN”
2009
AASLD adds BCS as an additional
indication & considers e-PTFE
covered stent grafts as standard of
practice
HISTORY OF TIPS
9References are at the end of the slides](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tipsinascitesfinal-200809165039/85/TIPS-in-Ascites-9-320.jpg)
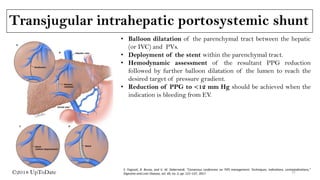
![Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt
(TIPSS): Introduction
• TIPS involve creation of a low-resistance channel between
the hepatic vein and the intrahepatic portion of the
portal vein (usually the right branch) using angiographic
techniques.
• The tract is kept patent by deployment of an expandable
metal stent across it, thereby allowing blood to return to
the systemic circulation.
• A TIPS is placed to reduce portal pressure in pts with
complications related to PHTN.[1,2]
1. Colombato L. The role of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) in the management of portal hypertension.
J Clin Gastroenterol. 2007 Nov-Dec. 41 Suppl 3:S344-51.
2. Gaba RC, Omene BO, Podczerwinski ES, Knuttinen MG, Cotler SJ, Kallwitz ER, et al. TIPS for Treatment of Variceal
Hemorrhage: Clinical Outcomes in 128 Patients at a Single Institution over a 12-Year Period. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2011
Dec 16. Pic src: Sankar K, edt al. Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts. JAMA. 2017;317(8):880.
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tipsinascitesfinal-200809165039/85/TIPS-in-Ascites-10-320.jpg)





![LATE EVENTS: Endotipsitis
• Defined by the presence of sustained bacteriemia a/with the evidence of thrombus or vegetations
inside the TIPS. This clinical condition is rare (1%).
• Early endotipsitis (< 120 days of the procedure) is usually related to Gram-positive organisms and the
antibiotic therapy must be long-lasting (at least 3 months) to avoid recurrence (1).
• In pts with uncontrolled or recurrent infection LT should be considered(2).
• There is no evidence for adopting long-term prophylaxis for the prevention of endotipsitis.
1. Navaratnam AM, Grant M, Banach DB. Endotipsitis: A case report with a literature review on an emerging prosthetic related infection. World J Hepatol. 2015 Apr 8;7(4):710–6.
2. Kochar N, Tripathi D, Arestis NJ, Ireland H, Redhead DN, Hayes PC. Tipsitis: incidence and outcome-a single centre experience. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010 Jun;22(6):729–35.
3. Sanyal AJ, Reddy KR. Vegetative infection of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts. Gastroenterology. 1998;115:110-115.
The term “endotipsitis” was proposed by Sanyal and Reddy[3], who defined it as: (1) the presence of continuous
bacteremia indicating an infectious focus in continuity with the venous circulation and (2) failure to find an alternate
source of infection despite an extensive search.
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tipsinascitesfinal-200809165039/85/TIPS-in-Ascites-18-320.jpg)



![TIPS: Bare stent Vs PTFE-covered stent
• A major complication after TIPS insertion using bare stent grafts is the development of HE, which
can occur in up to 50% of pts.[1,2]
• The incidence of this complication can be significantly reduced to about 18% with the use of PTFE-
covered stent grafts of 8 mm,[3] a result confirmed by a recent RCT comparing 8 mm and 10mm
stent grafts.[4]
• Dysfunction of TIPS with bare stent grafts because of stent thrombosis and stenosis can develop in
up to 80% of cases.[1] This complication has been significantly reduced with the use of PTFE-covered
stents.[5]
References are present at the end of the slides. 22
Note: Use of polytetrafluoroethylene coated stents was first reported in 1995 [6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tipsinascitesfinal-200809165039/85/TIPS-in-Ascites-22-320.jpg)
![TIPS: Covered Vs Bare
Bureau et al. 2015[2] Perarnau et al. 2015[3]
39 Vs 41 66 Vs 71
After median follow-up of 300 days;
Shunt dysfunction: 13% Vs 44%,P < 0.001.
HE @1 yr: 21% Vs 41% (NS).
The 1-year and 2-year survival rates: 70.9 % and 64.5 %
Vs 59.5 % and 40.5 % (NS)
The use of CS improves shunt patency without increasing
the risk of HE.
Median follow-up :23.6 and 21.8 months, respectively.
Shunt dysfunction :RR= 0.60; 95% CI:0.38-0.96, p=0.032.
The 2-year rate of shunt dysfunction: 44.0% vs. 63.6% .
Risk of HE: 0.89; 95% CI: 0.53-1.49,NS
2-year survival: 70% vs. 67.5%, NS
CS provided a significant 40% reduction in dysfunction
compared to BS. No significant difference with regard to
HE or death.
Multi center single blind RCT
Stent diameter data: NA
Multi center single blind RCT
CS: 10.5 ± 0.9 versus BS: 11.7 ± 0.8 mm
In the recent meta-analysis by Qi et al[1], covered stents not only significantly
improved the shunt patency, but also significantly ↓the risk of death. Additionally,
the risk of HE was not ↑ by the use of covered stents.
23References are present at the end of the slides.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tipsinascitesfinal-200809165039/85/TIPS-in-Ascites-23-320.jpg)
![TIPS in mx of refractory ascites (ra)
• The goal of TIPS creation in the case for RA is to reduce the portosystemic pressure gradient to <12
mm Hg.[1]
• TIPS improves ascites via increased natriuresis through reduction in both proximal tubular sodium
reabsorption and activity in the RAAS.[2]
• Notably, even after TIPS creation, pts must continue to restrict their sodium intake, and a majority of pts
will require low dose diuretics to maintain an ascites-free state.
1. Sanyal AJ, Genning C, Reddy KR, Wong F, Kowdley KV, Benner K, et al. The North American study for the treatment of refractory ascites. Gastroenterology 2003;124:634-641.
2. Rossle M, Gerbes AL. TIPS for the treatment of refractory ascites, hepatorenal syndrome and hepatic hydrothorax: a critical update. Gut 2010;59:988-1000.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tipsinascitesfinal-200809165039/85/TIPS-in-Ascites-24-320.jpg)
![Controlled studies and meta-analysis
• Numerous RCTs have compared LVP and TIPS.
• The clinical effects of TIPS with bare stents in pts with refractory or recurrent ascites have been
assessed in 6 prospective RCTs (next slide),[1-6] whose main features are reported.
• Based on these RCTs, 7 meta-analyses were performed.[7-13]
References are at the end of the slides
The final messages can be summarised as follow:
i) TIPS controlled ascites better than LVP,
ii) TIPS is followed by a greater incidence of HE.
However, discrepant results were obtained with respect to survival.
Note: Recurrent or recidivant ascites is a severe stage prior to further progression to refractory ascites and is defined
as ascites that recurs on at least 3 occasions within a 12-month period despite prescription of dietary sodium
restriction and adequate diuretic dosage.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tipsinascitesfinal-200809165039/85/TIPS-in-Ascites-25-320.jpg)

![Summary
• Thus, currently available data suggest that TIPS improves survival compared to LVP in pts with
Recurrent Ascites, but it does not in those with RA.
• A careful selection of pts is also crucial to maximise the beneficial effects of TIPS, as TIPS can even
be detrimental in pts with the most advanced stages of cirrhosis, such as those belonging to CP C.[1]
1. Lebrec D, Giuily N, Hadengue A, Vilgrain V, Moreau R, Poynard T, et al. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts: comparison with paracentesis in patients with cirrhosis and refractory ascites: a
randomized trial. French Group of Clinicians and a Group of Biologists. J Hepatol 1996;25:135–144.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tipsinascitesfinal-200809165039/85/TIPS-in-Ascites-27-320.jpg)
![Predictor of survival
• A risk score (R) system based on SCr, INR, serum bilirubin and aetiology of cirrhosis has been
proposed to predict survival after TIPS insertion for RA.[3] Pts with R > 1.8 had a median survival of
3 months or less. This model was superior to both the CP classification, as well as the CP score, in
predicting survival.
• Another simple predictor of survival suggested for pts receiving TIPS for RA consists of the
combination of serum bilirubin and platelet count.[1]
• Another factor that seems to influence mortality is the number of TIPS procedures performed in a
centre, as the risk of inpatient mortality is lower in hospitals performing ≥20 TIPS per year.[2]
1. Bureau C, Metivier S, D’Amico M, Peron JM, Otal P, Pagan JC, et al. Serum bilirubin and platelet count: a simple predictive model for survival in patients with refractory ascites treated by TIPS. J Hepatol
2011;54:901–907.
2. Sarwar A, Zhou L, Novack V, Tapper EB, Curry M, Malik R, et al. Hospital volume and mortality after trans-jugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt creation in the United States. Hepatology 2017.
3. Malinchoc M, Kamath PS, Gordon FD, Peine CJ, Rank J, ter Borg PC. A model to predict poor survival in patients undergoing transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts. Hepatology 2000;31:864–871.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tipsinascitesfinal-200809165039/85/TIPS-in-Ascites-28-320.jpg)
![Models used for prediction of post–tips survival
• Numerous models have been used to predict post-TIPS survival (for any indication), of which the CP
score and MELD score have been the most used.[1]
• Of the two, the MELD score has shown to be superior to CP score as a predictor for short-term
outcomes.[2]
• In a meta-analysis by Salerno et al, a MELD score between 11 and 19 was found to have a significant
survival benefit in pts who underwent TIPS versus pts who underwent LVP.[3]
1. Malinchoc M, Kamath PS, Gordon FD, Peine CJ, Rank J, ter Borg PC. A model to predict poor survival in patients undergoing transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts. Hepatology 2000;31:864-871.
2. Salerno F, Merli M, Cazzaniga M, Valeriano V, Rossi P, Lovaria A, et al. MELD score is better than Child-Pugh score in predicting 3-month survival of patients undergoing transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic
shunt. J Hepatol 2002;36:494-500.
3. Salerno F, Camma C, Enea M, Rossle M, Wong F. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for refractory ascites: a meta-analysis of individual patient data. Gastroenterology 2007;133:825-834.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tipsinascitesfinal-200809165039/85/TIPS-in-Ascites-29-320.jpg)
![• In addition, a survival benefit for TIPS was seen across all MELD categories.
• Furthermore, in a recent single-center study of 100 pts who underwent TIPS placement, with an
expanding covered stent, the 1-year survival rate for a MELD score less than 15, 15 to 18, and greater
than 18 was 84%, 67%, and 54%, respectively.[1]
1. Bercu ZL, Fischman AM, Kim E, Nowakowski FS, Patel RS, Schiano TD, et al. TIPS for refractory ascites: a 6-year single-center experience with expanded polytetrafluoroethylene-covered stent-grafts. AJR Am J
Roentgenol 2015;204:654-661.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tipsinascitesfinal-200809165039/85/TIPS-in-Ascites-30-320.jpg)
![• Currently, no RCTs have evaluated TIPS for RA in pts with a MELD score greater than 20.
• As such, each pt with RA should be evaluated carefully by looking at other clinical factors that can
adversely affect outcomes. These factors include older age, high bilirubin, history of HE, and low sodium
concentration.[1]
• In those without severe hyperbilirubinemia or HE, TIPS may be considered in highly selected
individuals on a case-by-case basis and by individual assessment of risks and benefits.
1. Salerno F, Camma C, Enea M, Rossle M, Wong F. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for refractory ascites: a meta-analysis of individual patient data. Gastroenterology 2007;133:825-834.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tipsinascitesfinal-200809165039/85/TIPS-in-Ascites-31-320.jpg)
![Estimated 1-year mortality rate for various meld
scores of tips versus lvp
1. Rossle M, Gerbes AL. TIPS for the treatment of refractory ascites, hepatorenal syndrome and hepatic hydrothorax: a critical update. Gut 2010;59:988-1000.
From Gut.[1] Copyright 2010, British Society of Gastroenterology.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tipsinascitesfinal-200809165039/85/TIPS-in-Ascites-32-320.jpg)





![TIPS in BCS ?
• In BCS pts, in a stepwise approach, TIPS with covered stent is indicated in case of failure of
anticoagulation (and angioplasty when feasible), represented by persistent ascites, AKI or elevated
transaminases .
• Listing for LT should be considered in case of a prognostic index score greater than 7 in pts candidate to
TIPS for BCS.
• When TIPS is attempted to treat hyper acute BCS with ALF presentation, the listing process for LT
should not be delayed.
BCS-TIPS PI (only for patients who underwent TIPS procedure): age × 0.08 + bilirubin × 0.16 + INR × 0.63[1].
1. Garcia-Pagán JC, Heydtmann M, Raffa S, Plessier A, Murad S, Fabris F, Vizzini G, Gonzales Abraldes J, Olliff S, Nicolini A, et al. TIPS for Budd-Chiari syndrome: long-term results and prognostics factors in
124 patients. Gastroenterology. 2008;135:808–815.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tipsinascitesfinal-200809165039/85/TIPS-in-Ascites-38-320.jpg)







