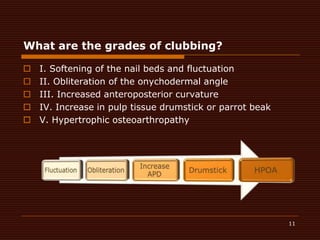
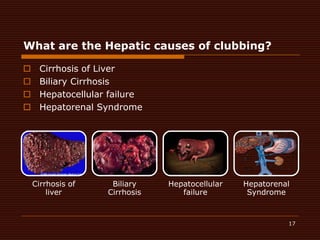
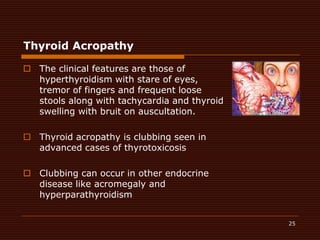
Clubbing, also known as Hippocrates fingers, is the bulbous enlargement of the fingertips and nails. It is caused by proliferation of subcutaneous tissues due to chronic hypoxemia from conditions like lung diseases, heart diseases, and liver or gastrointestinal diseases. Examination involves comparing the fingernails to look for reduced or absent diamond-shaped spaces, indicating clubbing. While clubbing itself has no treatment, addressing the underlying condition can potentially reverse it over time.